Grade 4 Chapter 2 Keeping Healthy
advertisement

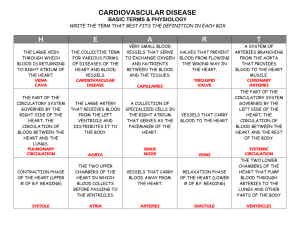
Royal Buckingham International School www.royalbuckinghaminstitution.com Grade 4 Chapter 2 Keeping Healthy Q 1 What is energy? Where do we get energy from? A: Energy is ability to do work. We get energy from the food. Q 2 Why do we need energy? A: We need energy to our daily work and for life processes like respiration and digestion. Q 3 What are the main groups of food? A: 1) Carbohydrates 2) Proteins 3) Vitamins and minerals 4) Fats Q 4 What is a balanced diet? A: A Balanced diet includes foods which contain carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, salts, fiber and water, in the right amount. Q 5 Why do we need a balanced diet? A: Because some food give us energy, some keep us healthy and some help us to grow. Q 6 How do we measure energy? A: Amount of energy provided is measured in kilocalories and kilojoules (kJ). Q 7 How much energy does a person need each day? A: A young person needs 7 000 kJ, a teenager needs 13 000 kJ, an adult needs 12 000 kJ and a senior citizen needs 8 000 kJ each day. Q 8 How can we stay fit and healthy? A: 1) Eat sensibly. 2) Do regular exercise 3) Avoid smoking, taking illegal drugs and drinking alcohol. Q 9 What are drugs? A: Drugs are chemical substances which affect the nervous system and change some functions of the body and mind such as the way we feel or behave. Q 10 What are side effects of drugs? A : Drugs can cause serious illness like bronchitis, dull wrinkled skin, stained teeth, yellow nails and fingers and difficulty in paying attention, remembering and learning things. Q 11 Draw a table to show the vitamins, their sources, benefits and lacking affects. Vitamin Sources Benefits Lacking affects Vitamin A Sweet potatoes, carrots Helps maintain eye sight Poor eye sight Vitamin B Green leafy vegetables Helps body make protein Poor eye sight, bad skin Vitamin C Green vegetables, guavas, tomatoes, oranges, chillies Healing skin and gums healthy, preventing cold, increase immunity Scurvy = swollen and bleeding gums, loosening of teeth and poor healing of wounds. Vitamin D Meat and milk products, sunlight Helps to absorb calcium needed for strong bones and teeth Rickets = poor teeth and weak bones. Vitamin E Vegetable oil, nuts Healthy skin and bones Weak bones, dull skin Iron leafy green vegetables, liver, kidney, red meats, egg yolk Make hemoglobin in red blood cells Anemia which leaves a person pale, tired and weak. Calcium Milk, cheese, Strong bones and teeth, helps in clotting of blood. Rickets = weak bones and poor teeth. Q 12 Make a chart to show food groups, their sources and benefits. Food Group Sources Functions in body Effect of too much on the body Effect of too little on the body Carbohydrate Bread, rice, corn, potatoes, noodles, cereals, jam, honey, sweets, cake Gives energy, helps to digest food, make Become fat Become very weak Proteins Egg, meat, fish, peas, bean curd, nuts, yoghurt and Milk Make, repair and replace damaged cells, helps our bones, teeth and nails to grow Become fat Muscles are poorly developed, become very weak. Fats Oils, butter, full fat milk, cake, sweets, chocolates and biscuits Gives us little energyHelps to absorb certain vitamins Become fat as excess fats are stored. Fiber Vegetables, fruits, cereals, nuts Prevents constipation Gas, stomach pain Dirrhea, nausea Constipation Water Vegetables, fruits, soups, drinks Transport digested food, oxygen and waste materials, controls body temperature, helps in digestion Nausea, vomiting, headache Constipation, weakness, tiredness Blood circulatory system Q 13 What is a heart? A: Our heart is a muscular organ which pumps blood around the body through the blood vessels. It has four valves and four chambers. Q 14 Where is the heart located in our body? A: Heart is located in our chest, between two lungs. Q 15 What protects the heart? A: The heart and lungs are protected by our ribs. Q 16 How much does the heart weighs? A: The average human weighs about 280 gms. Q 17 What is the size of the heart? A: The size of the heart is same as our fist. Q 18 How many times does the heart beat each day? A: The heart beats about 100,000 times each day. Q 19 How many times does the heart beat each minute? A: The heart beats about 70 times each minute Q 20 How much blood does the heart pump in a day? A: The heart pumps about 36,000 liters blood each day. Q 21 What do doctors use to listen to the heart beat? A: Doctors use stethoscope or heart monitor to listen to the heart beat. Q 22 What is the function of the heart? A: The heart purifies our blood. Q 23 Name the system in which the heart purifies the blood. A: Blood circulatory system transport materials throughout the body. Q 24 Name the organs that are involved in the blood circulatory system. A: Heart, blood and blood vessels. Q 25 What are blood vessels? A: Blood vessels form a network of tubes to transport blood around the body. Q 26 Make a table to show types of blood vessels and their functions in our body. Types of blood What are they? vessels Functions Arteries Arteries are thick walled. Carry blood rich in oxygen, digested food and water to all parts of body. Capillaries Capillaries are thin tubes that join arteries and veins. Allow exchange of gases. Veins Veins have thinner walls than Veins contain blood rich in carbon dioxide and waste arteries. materials to excretory organs to get rid of it. Q 27 What is the function of blood vessels? A: Blood vessels carry pure blood & digested food to the body parts and waste products and impure blood to the excretory organs. Q 28 How does our blood circulatory system work? A: 1 Right atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood from inferior vena cava and superior vena cava. 2 Right ventricle: Pulmonary artery sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs for exchange of gases. 2 left atrium: Pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium. 4 Left Ventricle: Aorta carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body. Q 29 How do the chambers of the heart work? When the heart contracts it pumps blood out into the body When the heart relaxes it fills up with blood The right ventricle pumps deoxygenate blood to the Deoxygenate blood (from the body) enters the right lungs. atrium. The left ventricle pumps oxygenate blood to the rest Oxygenate blood (from the lungs) enters the left of the body. atrium. Q 30 What is heart beat? A: One contraction and one relaxation of the heart make one heart beat. During a contraction, the heart valve closes and makes a ‘lub’ sound. During a relaxation, the semilunar valve closes and makes a ‘dub’ sound. Q 31 What is septum? A: Septum is a muscular wall. It separates the left side of the heart from the right. Q 32 What is the function of the septum? A: Septum prevents the mixing of oxygenated blood in the left chambers with deoxygenated blood in the right chambers. Q 33 What are valves and what is their function? A: There are two heart valve and two semilunar valves in the heart. These valves act as doors. They ensure that blood flows in one direction and prevent blood from flowing back. Q 34 What is pulse? A: Pulse is a pressure wave from the heart beat. Q 35 Show flow of the blood in the heart. Grade 4 Chapter 2 Keeping Healthy Fill in the blanks 1. We need to eat a varied diet and exercise to stay __________. 2. Carbohydrates provide us __________ in the form of sugar and starch. 3. Amount of energy is measured in __________ and kilojoules. 4. A 10 year old child needs__________ kilocalories each day. 5. Heart is located in our __________ , between two lungs. 6. Heart ____________ our blood. 7. The average human heart weighs about _____________. 8. Our heart beats about ____________ times each day. 9. Our heart pumps about ___________ litres blood each day. 10. Our heart beats about ____________each minute. 11. Doctors use ____________ or heart monitor to listen your heart beat. 12. __________ is a pressure wave from the heart beat. 13. __________________carry blood around the body. 14. _______________ are blood vessels that carry blood rich in oxygen, digested food and water to all parts of body. 15. Arteries branch into very fine blood vessels called ___________. 16. Capillaries merge to form bigger blood vessels called _________. 17. Our ___________ side of heart pumps blood to our body. 18. When the heart ____________, it pumps pure blood into arteries. 19. When the heart ____________, it fills up with blood from the veins. 20. A __________ is a substance that can causes body changes. True / False 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. We need to eat a varied diet and excercise to stay healthy. A healthy balanced diet does not contain food from all the groups. Carbohydrates provies us energy in the form of sugar and starch. Amount of energy provided is measured in kilograms. A 10 year old child needs 24000 kilocalories each day. Our heart is a muscular organ. Heart is located in our skull, between two lungs. 8. Our heart and lungs are protected by our ribs. 9. Heart impurifies our blood. 10. Blood circulatory system help to digest food. 11. Heart, blood and blood vessels are involved in blood circulatory system. The average human heart weighs about 28 kilograms. 12. The size of our heart is same as our fist. 13. Our heart beats about 100 times each day. 14. Our heart pumps about 36,000 litres blood each day. 15. Our heart beats about 70 times each hour. 16. Doctors use stethoscope or heart monitor to listen your heart beat. 17. Pulse is a pressure wave from the brain beat. 18. Blood vessels carry blood around the body. 19. Our heart has two chambers. 20. Our left side of heart pumps blood to our body. 21.