Week 8 Homework Answer Key_LKJ
advertisement

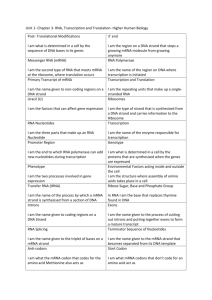
Name: _____________________________ Discussion Section (circle one): D10, D11, D12 Bio 93 Discussion Week 8 Homework: DUE DECEMBER 4 ANSWER KEY 1. You are provided with an actively dividing culture of E. coli bacteria to which radioactive thymine has been added – what would happen if a cell replicates once in the presence of this radioactive base? A. B. C. D. E. One of the daughter cells, but not the other, would have radioactive DNA Neither of the daughter cells would be radioactive All four bases of the DNA would be radioactive Radioactive thymine would pair with nonradioactive guanine DNA in both daughter cells would be radioactive Radioactive thymine would be incorporated into all newly synthesized DNA. This would lead both daughter cells to be radioactive but would not alter Watson and Crick base pairing rules or make the other bases radioactive. 2. In the diagram below draw the leading and lagging strands for each strand of DNA. Origin of replication Lagging 3’ Leading 3’ 5’ 5’ 5’ 3’ 5’ 3’ The leading strand is 5’ to 3’ from OR The lagging strand is 3’ to 5’ from OR Origin of replication A. Name the molecule involved in untwisting the double helix at the replication fork Helicase B. Name the molecule involved in correcting overwinding ahead of the replication fork. Topoisomerase C. Which strand has the Okazawi fragments? Draw it in. Lagging strand 3. What is the difference between DNA polymerase I and DNA polymerase III? Pol I- Replaces RNA nucleotides of primer with DNA Pol III- Synthesizes new DNA strand by adding DNA molecules 4. What are some differences between transcription and translation in eukaryotes versus transcription and translation in prokaryotes? Prokaryotes- one OR, no post-translational modifications, transcription end is signal terminator, because bacteria lack nuclei, transcription and translation are coupled, ribosomes attach to mRNA molecule while transcription is still in progress. Eukaryotes- multiple ORs, post-translation modification, transcription end is poly A tail, Almost all transcription occurs in the nucleus, translation occurs mainly at ribosomes in the cytoplasm. 5. Based on the following sequence of DNA 5’ GCG TTA ATT ACG CAT CCC 3’ answer the following questions: I. Provide the primary transcript (label the 3’ and 5’ ends). mRNA 3’ CGC AAU UAA UGC GUA GGG 5’ II. Would the transcript be synthesized from left to right or right to left? Why? Right to left because RNA Polymerase always adds to the 3’ end III. Translate the transcript 5’ GGG AUG CGU AAU UAA CGC 3’ Met-Arg-Asn 6. You are given the anti-codon sequence 5’ UUCGUCAUCUACC 3’. Provide the DNA sequence which gave rise to this anti-codon sequence (include the 5’ and 3’). 3’ tRNA anticodon 5’ 5’ mRNA codon 3’ 3’-CCAUCUACUGCUU-5’ 5’-GGUAGAUGACGAA-3’ 7. In 1961 the biochemists Nirenberg and Khorana made synthetic mRNA to try to understand the genetic code. When they produced mRNA containing only uracil nucleotides, it coded for one type of amino acid, phenylalanine. When mRNA was produced with alternating uracil and guanine nucleotides, two types of amino acid were coded for, valine and cysteine. Alternating U’s and C’s produced Serine and Leucine. Nucleotide sequence in mRNA UUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUUU UGUGUGUGUGUGUGUGUG UCUCUCUCUCUCUCUCUCU Amino acids coded for Phenylalanine Valine and Cysteine Serine and Leucine A. For the amino acid phenylalanine what is the tRNA anti-codon sequence? Make sure to indicate the 5’ and 3’ 3’-AAA-5’ A tRNA anticodon contains 3 bases. Since the mRNA codon is 5’-UUU-3’, the tRNA Codon must be complementary and run in the opposite direction: 3’-AAA-5’. B. What are the potential mRNA codons for Valine predicted by this experiment? Make sure to indicate the 5’ and 3’? 5’-UGU-3’ and 5’-GUG-3’ The two possible codons with correct prime end labels are listed above . These are the only possible codons in the given mRNA strand. C. What are the potential mRNA codons for Leucine? Make sure to indicate the 5’ and 3’? 5’-UCU-3’ and 5’-CUC-3’. 8. What is transcription? Identify and describe the 3 steps of transcription. Make sure to name key players and their roles in transcription (example: RNA polymerase). Transcription: Synthesis of mRNA from DNA template 1. Initiation: Promoters (TATA box), transcription factors, RNA polymerase (the transcription initiation complex 2. Elongation: RNA nucleotides 3. Termination: Prokaryotes- terminator, eukaryotes- poly A tail 9. Which of the following STATEMENTS is false? A. A single DNA template strand can give rise to different proteins due to alternative splicing B. The TATA box is a region on the mRNA that allows RNA polymerase to attach (on DNA) C. A gene codes for a polypeptide D. An organism’s genotype is carried in its sequence of bases E. The phenotype is a consequence of the proteins that are expressed