NAME: PERIOD: ______ Meiosis and Genetics Study Guide 1. Who
advertisement

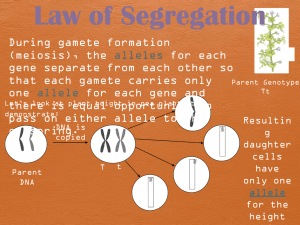
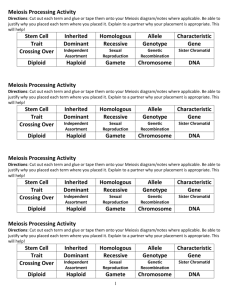
NAME: ________________________________________ PERIOD: __________ Meiosis and Genetics Study Guide 1. Who was the Father of Genetics? What type of plants did he use in his experiments? What plant traits did he test? Define fertilization. What is the difference between self pollination and cross-pollination? 2. Define true-breeding. Define genotype. Write a genotype for a plant that is true-breeding for tall. Define phenotype. 3. Define hybrid. Write a genotype for a plant that is a hybrid offspring between parents that were true-breeding for tall and short. 4. What is a gene? 5. What is an allele? Write the genotypes for alleles that are homozygous for tall and homozygous for short. Identify which alleles are dominant and which are recessive. 6. What does the Principle of Dominance state? 7. Define segregation. When does it occur during meiosis? What is the P generation? What is the F1 generation? What is the F2 generation? 8. Define gametes. 9. Define probability. How are the principles of probability used in genetics? 10. What is the purpose of a punnett square? Define homozygous. Write a homozygous genotype. Define heterozygous. Write heterozygous genotype. Solve this monohybrid punnett square problem. In garden peas, round seed coats (R) is dominant over wrinkled seed coats (r). What will the results be of a cross between a homozygous dominant male and a recessive female. 11. What does the Principle of Independent Assortment state? (page 271) When does it occur? What effect can it have on a species? Solve this dihybrid punnett square problem. In Pea Plants T is the allele for the dominant, tall characteristic; t is the allele for the recessive, short characteristic. Y is the allele for the dominant, yellow color characteristic; y is the allele for the recessive, green color characteristic. Cross two pea plants that are heterozygous for both height and seed color. Determine the genotypes of the offspring. Calculate the phenotypic ratio of the offspring. How many will be tall and yellow? _______ How many will be tall and green? _______ How many will be short and yellow? ______ How many will be short and green? _______ 12. Summarize Mendel's Principles. a.) b.) c.) d.) 13. Define Incomplete Dominance. Give an example. Illustrate it in a punnett square. 15. Define Multiple Alleles. Give an example. 14. Define Codominance. Give an example. 16. Define Polygenic Traits. Give an example. 17. Define Meiosis. What are homologous chromosomes? Draw an example of a pair of homologous chromosomes. How many sets of chromosomes does a diploid cell (2N) have? How many sets of chromosomes does a haploid cell (N) have? Give an example of a diploid cell. Give an example of a haploid cell. 18. Define crossing-over. (page 277) During which phase of meiosis does it occur? What effect does this process have on a species? 19. How many cells are produced at the end of Meiosis I? (page 276) Are these cells diploid or haploid? 20. How many cells are produced at the end of meiosis II? (Page 2770 Are these cells diploid or haploid? What are these cells called? What is their function?