chapter 3
advertisement

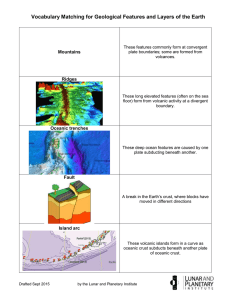
Chapter 3 Section 1 Seismic waves- vibrations that travel through earth carrying the energy released during an earthquake Mantle- The layer of hot, solid material between earth’s crust and core Pressure-the force exerted on a surface divided by the total area over which the force is exerted Lithosphere- a rigid layer made up of the upper post part of the mantle and the crust Crust- the layer of rock that forms earth’s outer surface Asthenosphere- the soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats Basalt- a dark, dense, igneous rock with a fine texture, found in oceanic crust Outer core- a layer of molten iron and nickel that surround the inner core of earth Granite- A usually light- colored igneous rock that is found in continental crust Inner core- a dense sphere of solid iron and nickel at the center of Earth Section 2 Radiation- The direct transfer of energy through space by electromagnetic waves Conduction-The direct transfer of thermal energy from one substance to another substance that it is touching Convection- the transfer of thermal energy by the movement of a fluid Density- The amount of mass of a substance in a given volume; mass per unit volume Convection current- The movement of a fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid to another Section3 Continental drift- the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across earth’s surface Pangaea- The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to day’s continents Fossil- a trace of an ancient organism that has been preserved in rock Section 4 Mid-ocean ridge- An undersea mountain chain where new ocean floor is produced Sonar- A device that determines the distance of an object under water by recording echoes of sound waves Sea-floor spreading- the process by which molten material adds new oceanic crust to the ocean floor Deep-ocean trench-A deep valley along the ocean floor beneath which oceanic crust slowly sink toward the mantle Subduction- the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean trench and back into the mantle at a convergent plate boundary Section 5 Plate- A section of the lithosphere that slowly moves over the asthenosphere, carrying pieces of continental and oceanic crust Scientific theory- a well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations Plate tectonics- the theory that pieces of earth’s lithosphere are in constant motion, driven by convection currents in the mantle Fault- A break or crack in earth’s lithosphere along which the rocks move Divergent boundary- a plate boundary where two plates move away from each other Rift valley- a deep valley that forms where two plates move apart Convergent boundary- a plate boundary where two plates move toward each other Transform boundary- a plate boundary where two plates move past each other in opposite directions