Genetics Study Guide
advertisement

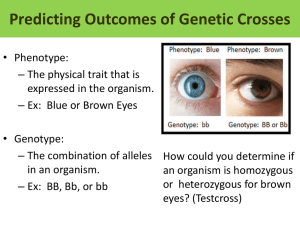
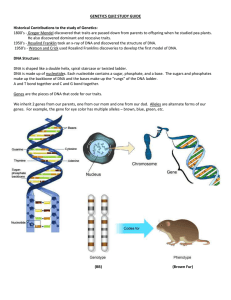
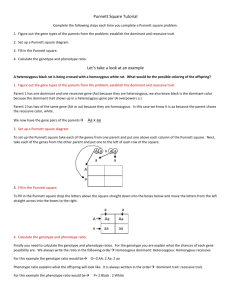
Genetics Study Guide: Things to study: 1. 2. Science journal pages 7, 8, 9, and 10. Vocabulary: know what each of these words/people are or do: Sir Edward Henry heterozygous heredity Martha Chase homozygous genetics Gregor Mendel phenotype dominant Thomas Hunt Morgan genotype recessive Francis Crick Dermatoglyphics Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)- Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine purebred hybrid IAFIS arch loop whorl 3. Punnett Squares Review Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. What is another name for heterozygous? What is another name for homozygous? What is the difference between phenotype & genotype? What are the 4 nucleotides that make up DNA? What does DNA stand for? Who discovered that DNA is in the form of a double helix? Who is the father of modern genetics, he discovered that you inherit one gene from each parent? Who developed a fingerprint classification system? Who discovered that DNA carries genetic material? What is another name for fingerprinting? What does IAFIS stand for? Name the 3 basic fingerprint patterns? Be able to identify if a sample fingerprint is a loop, whorl or arch. If brown hair (B) is dominant to blonde hair (b) and both parents are heterozygous,what is the chance of them having a blonde haired offspring? (draw a punnett square) Brown (B) eyes are dominant to blue (b) eyes. If a heterozygous male breeds with a homozygous recessive female, what are the possible genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring? What is the chance for a having a blue eyed offspring? (draw a punnett square to help) Red flowers (R) are dominant to pink (r) flowers. What phenotype would you have for each genotype below. Rr _______________ RR ______________ Rr _______________