L54-chapter 7 notes blankouts
advertisement

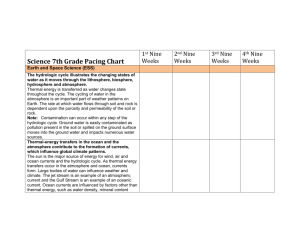
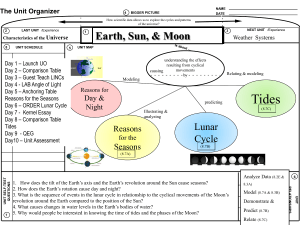
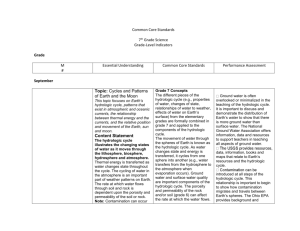
Chapter 7 p. 222-245 1. The Atmosphere Atmosphere: ___________________________________________________________. The Earth’s gravitational force is greater at the surface and therefore __________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________. 1.1 The Composition of the Atmosphere Air: __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________. Atmospheric Pressure: __________________________________________________________________________ As the altitude ___________________, the pressure _______________ (fewer particles = _______ collisions) and the temperature fluctuates. As the altitude __________________, the pressure ________________ (more particles = more collisions) and the temperature fluctuates. Atmospheric Layers Layer Name 1 2 Characteristics Height Chapter 7 Atmospheric Gas p. 222-245 % of atmosphere 1.2 Atmospheric Circulation Atmospheric circulation: ____________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Hot air rises (low density) Cold air falls (high density) Air rises at the ___________________________ because _____________________________ and moves toward the poles. At the _____________, air becomes _____________________ and more dense and moves back toward the _______________________ = CONVECTION Wind in the Northern Hemisphere appears to move to the _____________________. Wind in the Southern Hemisphere appears to move to the _____________________. This is a consequence of the ______________________________________. Air mass: _________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________. - Québec is affected by _________ air masses from _______________________ and _________ air masses from the __________________. 2 Chapter 7 p. 222-245 When two air masses meet: - They move ____________________________________ - They don’t combine - Cold air is ___________________ and __________________ under the warm air - The _______________________________________________ is called a front. In a _____________________________________ called a __________________the direction of the wind, the temperature and relative humidity can change rapidly. A) cold front: formed when a cold air mass meets a warm air mass. - Warm air rises rapidly and then cools forms puffy clouds = cumulus. - ______________________________________________. B) warm front: formed when a warm air mass rises as it moves toward a cold air mass. - Creates _____________________ clouds (stratified). - Slower than a cold front because it is less dense. Cyclones and Anticyclones Air masses can also move __________________________. a) Anticyclone: Symbol is _________ (high pressure) - cool air particles collide infrequently 3 Chapter 7 p. 222-245 - the particles are closer together - the density is high = ____________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________________ b) Depression: Symbol is ____________ (low pressure) - Warm air particles collide ____________________________ - low density - The air mass rises creating a space of _____________ pressure beneath it. As the air rises or falls it starts to rotate according to the Coriolis Effect. - In the northern hemisphere: anticyclones rotate ______________________ and depressions rotate _______________________________. - In the southern hemisphere: anticyclones rotate _____________________________ and depressions rotate __________________________. o In a depression rising air encourages the formation of ___________________. o In an anticyclone the sky is ____________ because falling air does not promote the formation of clouds. A cyclone forms _________________________________________________________________________________. - Cyclone: tropical storm characterized by violent winds revolving around an area of low pressure. - The spiral storm can stretch over 1000 kilometers with winds. - Cyclone = ________________ = typhoon 1.3 The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse effect: natural process that the Earth to retain some of the receives from the Sun. 4 allows heat it Chapter 7 p. 222-245 - Atmospheric gases behave like the greenhouse glass - Most of the sun’s rays that reach the Earth’s surface are absorbed by the ground. The heated ground emits infrared rays (heat): - _________________________________________________________________________________________. - the rays can be trapped by the greenhouse gases which heats the surface furthermore. Greenhouse gases: Then & Now Then: CO2 was mainly emitted from forest fires, volcanic activity and cellular respiration. CO2 was absorbed through photosynthesis and oceans. - ______________________________________________________ - Temperature is relatively stable. Now: CO2 emissions are increased because of _________________________________ from fossil fuels. - Billions of tonnes are released into the atmosphere because of human activity. Increased levels of CO2: - Burning forests to clear land (combustion) Decreased levels of O2: - Deforestation (reduced photosynthesis) Global Warming - More CO2 emitted in the atmosphere = more heat trapped within the atmosphere. 5 Chapter 7 p. 222-245 This phenomenon is called global warming and leads to changes in climate. Climate change: the __________________ modification of climatic conditions on Earth, caused by _______________________________________. Methane and nitrous oxide are also emitted in higher concentrations but their effect is not as great as that of carbon dioxide. - If methane was emitted in ____________________________________ as carbon dioxide it would have an effect ______ times greater on global warming. From 1850-2005 = average temperature rose by 1oC. If it rises by another degree = more droughts, heat waves and floods + rise in sea levels. 1.5 Energy Resources Wind energy: ________________________________________________________ (Mechanical to electrical) How does it work? _________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Advantages: - __________________________________________________________ - ________________________________________________________ Disadvantages: - ________________________________________________________ - ________________________________________________________ - ___________________________ (must combine with other source of energy – usually a dam) 6 Chapter 7 p. 222-245 2. The Effect of the Sun and the Moon on the Earth 2.1 Solar Radiation - Nuclear reactions of the Sun transform ________________________________________ which in turn produces energy. - The energy which is ____________________________ across the solar system, from the _____________, reaches Earth in 8 minutes. - The radiation _____________________ by the Sun contains all the waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. Only __________________________, radio waves, some _______________________ rays and some ___________________________ rays reach Earth’s surface. These rays heat the atmosphere, the oceans and the land. The Earth’s _______________ and _______________________ cause ___________________________ regions to be _______________________ because _________________________________________________________. Solar energy = _____________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________________. Technologies that take advantage of solar energy: - Passive heating systems: houses are _________________________________________ so that it can ___________________________________________________________________________________________. - Photovoltaic cells: silicon in these “cells” is activated by light and set electrons in motion creating an electric current. (solar panels = large concentration of photovoltaic cells) - Solar collectors = copper pipes found ______________________________large glass panels are filled with water which is ______________________ by _______________________________. 7 Chapter 7 p. 222-245 2.2 The Earth-Moon System The moon ______________________ around the Earth and _____________________ on its own axis. Rotation and revolution of the moon: ___________________. Tides - A gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun is responsible for daily tides on Earth. Tide: ____________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ Why does the opposite side of the Earth also experience simultaneous tides? - The water is less attracted to the Moon than the Earth itself is, so the Earth is drawn away from the water, toward the Moon. Spring and Neap Tides - Twice each month, at the time of the new moon and the full moon, the gravitational influences of the moon and sun reinforce one another and cause the tides to rise to greater heights and fall lower than average tides. These are called ____________________________. 8 Chapter 7 - p. 222-245 At the time of the quarter moon, when the sun, earth, and moon form a right angle, the difference between high and low tide is less than average. These are called ____________________________. The _____________________ in water levels at low and high tide is called the tidal range. The Bay of Fundy (near Nova Scotia) has tides with a range of up to 17 meters. Tidal energy: _______________________________________________________________________________________. When the tide comes in it fills a water basin. When the tide goes out and creates a difference in water level between the basin and the sea. When a gate is opened, the water in the basin is released to flow through a turbine which generates an electric current. Advantages - ___________________________________ - ___________________________________ - Reliable because tides are predictable according to the positions of the Sun and the Moon. Disadvantages - ____________________________________________________ - Few places with high tidal range 9 Chapter 7 10 p. 222-245