Oxidation rules
advertisement

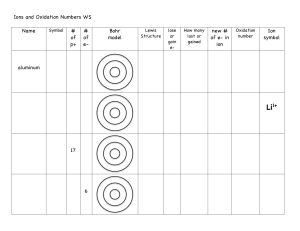
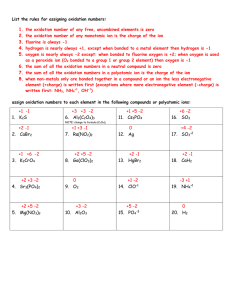
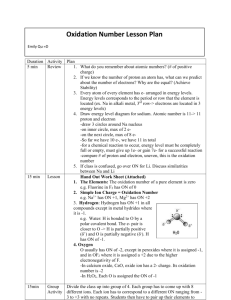
Oxidation Rules!!! 1. Atoms in pure elements have an oxidation number of zero. Examples: Na, O2, S8 2. The more-electronegative element in a binary molecular compound is assigned the number equal to the negative charge it would have as an anion. The less electronegative element is assigned the number equal to the positive charge it would have as a cation. The LESS-ELECTRONEGATIVE element is ALWAYS FIRST! 3. Exceptions to oxygen being -2: When it is in a peroxide it is a -1. (Dihydrogen dioxide) When it is with fluorine it’s a +2. (Oxygen difluoride) 4. Sum of oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound is zero. 5. Sum of oxidation numbers of all atoms in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion. 6. Monotomic ions have an oxidation state equal to the charge of the ion. Ca2+