Classification of Animals.
advertisement

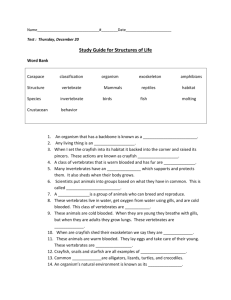
Name __________________________________ Period _______ Date ______________ Chapter 4.3 Environmental Science CLASSIFICATION OF ANIMALS FOLDABLES PROJECT Directions: Make the foldable and record the 12 different kinds of animals. 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) Turned in completed project on time and placed behind C.4 Word Study. (Thurs., Sept. 19-B) or (Fri., Sept. 20-A) _____ yes 5 Vertebrates were labeled, colored, and accurately described. _____ yes 7 Invertebrates were labeled, colored, and accurately described. _____ yes Writing was dark and large enough to be clearly seen. _____ yes Information was spelled correctly, and all directions were followed. ______ yes _____ Completed _____Not Completed (Environmental Science - Part of Notebook Grade) ______no ______no ______no ______no ______no DIRECTIONS: 1.) Use 7 pieces of paper (white & green), space them about 2 centimeters apart, fold in half, and have Ms. M. staple them. 2.) On the top line write your first and last name, your class period, and your date. 3.) On the second line write Classification of Animals. 4.) Use the following classifications to fill up the rest of your title pages. ON EACH PAGE WRITE THE SHORT INFORMATION ABOUT EACH. DRAW AT LEAST TWO EXAMPLES IN THEIR NATURAL HABITAT. LABEL THE EXAMPLES. Vertebrates - Reptiles - Reptiles have dry, scaly skin. They lay eggs on dry land. They are cold blooded. Examples include snakes, alligators, and turtles. Vertebrates - Fish - Fish have scales on their bodies. They have gills for breathing. They are cold-blooded. Examples include trout and sharks. Vertebrates - Amphibians - Most amphibians have moist skin. Most lay their eggs in water. All amphibians are cold-blooded. Vertebrates - Birds - Birds have feathers and wings. They have beaks and lay eggs. Birds are warm-blooded. Vertebrates - Mammals - Mammals have fur or hair. They feed milk to their young. They are warm blooded. Invertebrates - Protozoa - Protozoa are simple-celled organisms. They cannot be seen without a microscope. They have a nucleus which makes them eukaryotic. Invertebrates - Flat Worms - Flat Worms are simple and soft-bodied. Examples include tape worms and flukes. Invertebrates - Annelid Worms - Annelid worms have segregated bodies. Examples include earthworms and leeches. Invertebrates - Echinoderms - Echinoderms are spiny sea creatures such as starfish, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, and sand dollars. Invertebrates - Coelenterates - Coelenterates have soft bodies and stinging cells. Examples include jellyfish, sea anemones, and corals. PUT MULLUSCA AND PORIFERA ON THE SAME PAGE Invertebrates - Mullusca - Mullusca are soft bodied, many have shells and include snails, slugs, clams, mussels, and octopi. Invertebrates - Porifera - Porifera have bodies full of pores that allow water to circulate through them and include sea sponges. Invertebrates - Arthropods - Arthropods have hard, external skeletons and include arachnids, crustaceans, insects, and myriapods.