Air pressure varies in different regions.
advertisement

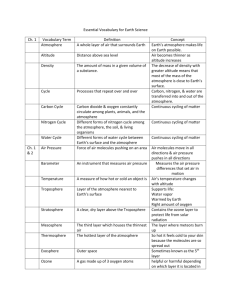
Study notes for quiz on air pressure & wind10/3/2012 10:55:00 PM Properties (characteristics) of the atmosphere: atmosphere – a whole layer of air that surrounds Earth altitude-the distance above sea level density – the amount of mass in a given volume of a substance air pressure – the force of molecules pushing on an area. Temperature- how hot or cold an object is Altitude Air becomes thinner as altitude increases; contains less mass; no definite top to the atmosphere (300 mi becomes outer space); fewer oxygen molecules to breathe; measured with an altimeter Density Density decreases as you travel upward; air on the top of mountain is less dense than air at sea level; most of the mass of the atmosphere is close to Earth’s surface Air pressure Air molecules move in all directions, air pressure pushes in all directions. Air pressure decreases with altitude. The air molecules in air at sea level are denser than air molecules in air over a mountain. Air pressure is higher in dense air than in thin air. Areas of high pressure move to areas of low pressure. Measured with a barometer. Temperature Air temperature changes with altitude. Temperature is warmer at sea level but decreases with altitude in the mountains. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Questions: What happens to the atmosphere’s density as you travel upward? The air becomes thinner and less dense. Why would a climber going to the top of Mt. Everest need an oxygen mask? There are less oxygen molecules and not enough oxygen to breathe. Air pressure is related to altitude and what else? density How do differences in air pressure affect the movement of air? higher air pressure will move to areas of lower pressure Notes: Air becomes less dense as altitude increases. Differences in density cause air to rise and sink. The movement of air molecules causes air pressure. The greater the number of air molecules, the greater the air pressure. Air pressure varies in different regions. When an air molecule bounces off an object, it ___pushes or exerts force________ on that object. Why does air pressure push in all directions? air molecules move in all directions 3. Is the air pressure in a can of tennis balls higher or lower than the air outside of the can? lower What would you likely hear when you open this can? A hissing sound What causes this sound? Air pressure from the outside rushing into the can 4. Air moves along Earth’s surface. What causes this to happen? Uneven heating and the differences in air pressure 1. Air molecules move constantly and bounce off surfaces, exerting force or pressure on surfaces. 2. Air pressure decreases as altitude increases. 3. Higher air pressure indicates that air is denser. 4. Air pressure would be higher in the valley because air pressure decreases as altitude increases. 5. Air will start to move from the area of higher pressure toward the area of lower pressure. 6. The higher pressure inside the ear pushes the eardrum outward as the air pressure in the elevator decreases. Wind Patterns Term Definition Details Weather the condition of Earth’s atmosphere at a particular time and place only found in the troposphere; wind is an important part Wind air that moves horizontally, or parallel to the ground difference in density, difference in air pressure & uneven heating Global wind winds that travel caused by uneven thousands of miles in steady patterns; can last for weeks heating between the equator and the north & south poles (leads to pressure differences!) the influence of Earth’s rotation on the direction of the wind Northern hemisphere = winds curve to the right; Southern Coriolis effect hemisphere = winds curve to the left Calm regions regions where the wind stays calm in high & low pressure Doldrums (lowpressure zone near the equator) Horse latitudes (high-pressure zone located about 30 degrees north and south of the equator) Wind belts winds that curve towards the east or the west due to the Coriolis effect Trade winds (blow from the east towards the equator) Westerlies (blow from the west toward the poles) Easterlies (blow from the east moving from the poles toward the mid-latitudes) Jet stream Local winds winds that flow in the upper polar jet stream influences the troposphere/lower weather in North stratosphere from west to east for thousands of kilometers America winds that change daily in a regular pattern Sea breeze during the day (warmer air rises over land during the day & cooler air blows in from the water.) Land breeze during the evening ( cooler air blows out from land & warmer air rises over water at night.) Valley breeze during the day (flow up the mountain.) Mountain breeze during the evening ( flow down the mountain.) Monsoons winds that change direction with the seasons Winter monsoons begin over land & are cool and dry. Summer monsoons begin over water & are moist; they bring heavy rains. 10/3/2012 10:55:00 PM 10/3/2012 10:55:00 PM