Climate Controls
advertisement

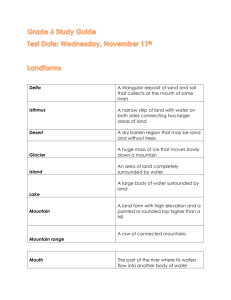
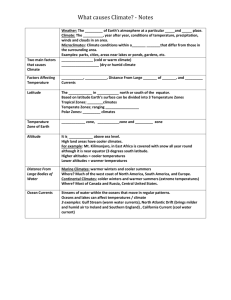
GC #___ Climate Controls PowerPoint Notes Integrated Science 2 Name: Per. I. The Significance of Climate and Biomes A. What is the difference between climate and weather? 1. Climate: The __________________, year after year conditions in a particular region 2. Weather: The condition of the ___________________ at a certain time and place. 3. Both climate and weather are measured in terms of _______________________, wind speed, humidity, ______________________, precipitation and other variables. B. What is a biome? 1. Biomes are areas that are similar in _________________ and other physical factors. 2. These areas tend to develop similar communities of ____________________ and animals Powered by the ___________, the climate system is a complex exchange of energy and _____________ among Earth’s atmosphere. II. Global Climate Controls – LETWAV L = ___________________________ E = _____________________________ T = ___________________________ W = ____________________________ A = ___________________________ V = _____________________________ A. Latitude 1. Because the Earth tilts on its _____________, and because the earth is _____________________ the Sun’s rays strike the Earth at different angles a. As a result, different parts of Earth receive different amounts of solar ______________ 3. The ___________________ receive the most solar radiation because the sun’s rays strike almost _____________________. Temperatures in the tropics are _______________ year-round. 4. The _____________________ zones have ____________________ conditions. 5. The _____________________ zones receive the least radiation because the sun’s rays strike at a very _______________ angle. Temperatures in polar regions are usually _________________. B. Elevation 1. Elevation is the height above ______________________. 2. On average, air temperature drops about _______________ for every 1000 m of altitude. 3. The higher the elevation, the ________________ the climate C. Topography 1. Climates often differ on either side of a ______________________. a. As air rises over a mountain, it __________________. As it cools, it _________________, and releases moisture (rain). This is called the ___________________ side. b. As the dry air flows over the mountain, it ___________________ and warms, usually producing deserts. This is called the ____________________ side. 2. Deserts such as the Atacama in Chile are common on ________________________ sides of mountains 3. The dry area is called a ______________________ and can extend for hundreds of km downwind of a mountain range. D. Water Bodies 1. Land gains and loses heat much _________________ than water 2. The temperature of a large body of water can influence the _______________ of the air above it. 3. Based on other factors certain areas close to _________________ bodies of water may have a relatively ______________ yearly temperature range. a. example: The California coast vs the interior of California 4. Continental __________________ have large yearly temperature ranges 5. Dry air gains and loses _________________ much faster than humid air, so ________________ have large daily temperature ranges. Water Bodies (Continued) 1. Ocean __________________ can warm or cool the air above 2. Ocean currently may be considerably warmer or cooler than the normal air _________________ for that latitude. E. Atmospheric Circulation 1. Solar energy and earth’s ________________________ create motion in the atmosphere called planetary winds. 2. There are _______________ basic wind systems in each hemisphere, Polar Easterlies, Northeast or Southeast ________________________, and Prevailing ___________________. 3. These winds blow air masses with distinct regions of ______________ (ie: formed over land or water, formed at certain _________________) 4. Winds move warm air ________________ the poles and cool air toward the ________________ These belts shift seasonally as the earth spins on it’s ____________ and different latitudes receive direct ________________. In the Northern Hemisphere, belts shift northwards in the ______________, and southwards in the winter. F. Vegetation 1. Vegetation influences how much of the sun’s energy is ______________________ and how quickly this energy is released, which affects the climate. 2. During _______________________ , plants release water vapor from their leaves into the air. 3. Some plants release particles that promote the formation of ________________. 4. Large areas of ______________________ mimic large bodies of water. Application Patagonia, Chile ____________________________ San Francisco _____________________________ Denver, Colorado ___________________________ Carson City, Nevada ______________________