Name Date ______ Measuring and DRAWING WAVES
advertisement
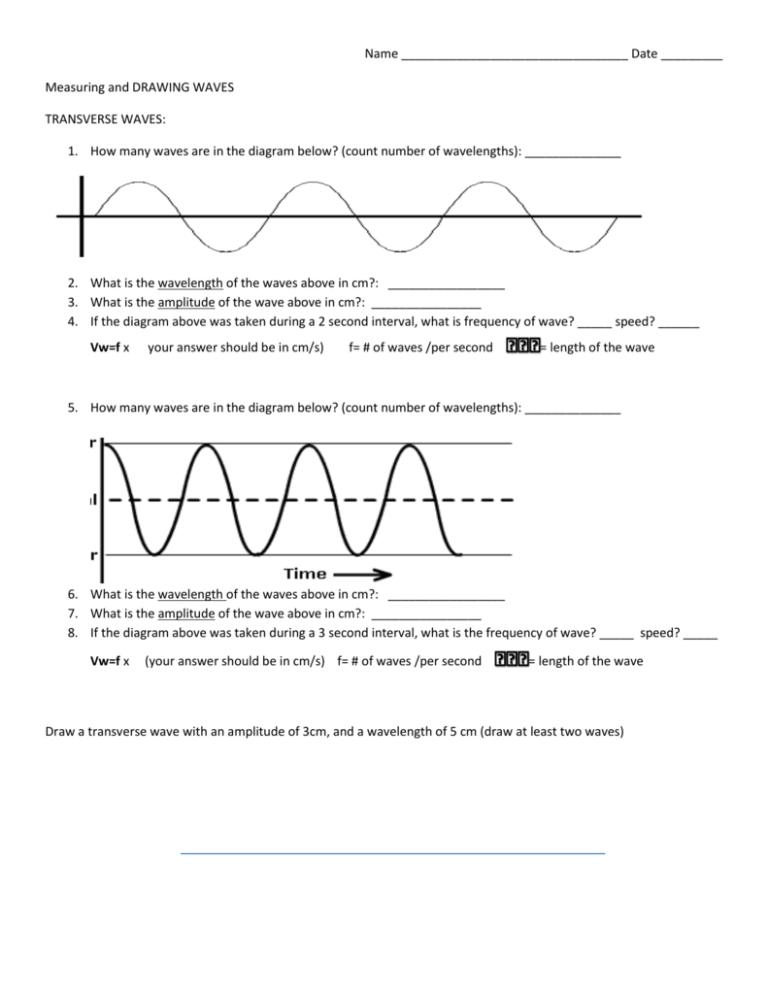
Name _________________________________ Date _________ Measuring and DRAWING WAVES TRANSVERSE WAVES: 1. How many waves are in the diagram below? (count number of wavelengths): ______________ 2. What is the wavelength of the waves above in cm?: _________________ 3. What is the amplitude of the wave above in cm?: ________________ 4. If the diagram above was taken during a 2 second interval, what is frequency of wave? _____ speed? ______ Vw=f x your answer should be in cm/s) f= # of waves /per second = length of the wave 5. How many waves are in the diagram below? (count number of wavelengths): ______________ 6. What is the wavelength of the waves above in cm?: _________________ 7. What is the amplitude of the wave above in cm?: ________________ 8. If the diagram above was taken during a 3 second interval, what is the frequency of wave? _____ speed? _____ Vw=f x (your answer should be in cm/s) f= # of waves /per second = length of the wave Draw a transverse wave with an amplitude of 3cm, and a wavelength of 5 cm (draw at least two waves) Name _________________________________ Date _________ Longitudinal Wave aka (compression wave) 1. How many waves are in the diagram below? (count number of wavelengths): ______________ 1. What is the wavelength of the waves above in cm?: _________________ 2. What is the compression of the wave above in cm?: ________________ 3. If the diagram above was taken during a 1 second interval, what is frequency? _________ speed? ________ Vw=f x (your answer should be in cm/s) f= # of waves/ per second = length of the wave Draw a compressional wave with compression of 3cm, and a wavelength of 6 cm (at least 2 waves) Follow along with the online simulation: 1. Set the both the frequency and the amplitude to 35. What happens to the string? 2. Set the frequency to 50 and adjust the amplitude to several different settings. What happens to the string as you adjust the amplitude? Record your observations. 3. Adjust the frequency button to several different settings. What happens to the string as you change the frequency? Record your observations. 4. You will now explore the relationship between frequency and wavelength. Set the amplitude to 50 and calculate the frequency of the wave for 4 different settings of frequency. To calculate frequency use the timer and count the number of peaks that pass through a given point per second. Measure the wavelength at each frequency Frequency # #peaks per/s (frequency) wavelength ________ __________ __________ ________ __________ __________ ________ __________ __________ ________ __________ __________ 5. Write down your observations about the relationship between wavelength and frequency. What happens when frequency goes up? What happens when frequency goes down?







