obstetric emergency flow chart
advertisement

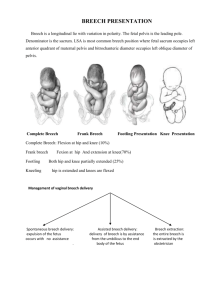
Unexpected Situations & Emergencies during Childbirth in the Maternity Unit Vaginal Breech Delivery Postpartum Haemorrhage Shoulder Dystocia Vaginal Breech Delivery Identify breech presentation 1. 2. Remember Epidural analgesia need not be routinely advised Episiotomy need not be routinely used 1. 2. 3. 4. Reassure parents Call for team support from Obs SpR, LW co-ordinator & neonatologist Prepare room (lithotomy poles available) Prepare for neonatal resuscitation Await descent onto perineum before pushing If breech not through or distending perineum or deliverable by episiotomy consider caesarean section If slow/no progress of legs during contraction then consider popliteal pressure 1. splint thigh, flex leg at knee and abduct leg in direction of hip 2. repeat with second leg if required 3. NO DOWNWARD TRACTION Hands off to allow breech to descend If slow/no progress of delivery of shoulders / arms during contractions then: 1. holding shoulder girdle rotate baby towards maternal symphysis pubis & bring down arm lying under SP, rotate baby back round to face other direction & bring down arm lying under SP 2. NO DOWNWARD TRACTION Hands off to allow breech to descend If slow/no progress of delivery of head and / or concerns about fetal wellbeing then: 1. Franks nudge – press baby’s clavicle bone and rotate occiput around maternal symphysis pubis 2. Mauriceau Smellie Veit - 2 fingers to apply pressure on occiput, 2/3 fingers on cheek bones and chin - Flexion before gentle traction 2 Post partum haemorrhage Identify PPH Call for help: Pull Emergency bell Call 2222 state ‘obstetric emergency’ and your location Identify cause Check uterus (tone) check for trauma check placenta is complete (tissue) check blood is clotting (thrombin) check bladder Action Give drugs and replace fluids Action 1. Rub up contraction Action – Observations and communication 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. Give IV ergometrine 500g Site 2 large bore cannula Take blood (FBC, Clotting and Xmatch 6 Units) Commence: a. b. c. Repair trauma Remove placenta from uterus Empty bladder Bimanual compression Observe colour & consciousness Airway management [Commence O2] B/P & pulse every 5 mins Reassure and explain to parents IVI of NaCl or Hartmanns Commence IVI syntocinon Commence Blood/Blood replacement products 1. 2. Hemabate IM 250microgms every 15 mins Misoprostol PR 3. Prepare for theatres: a. Antiemetics b. Labels c. Consent form Documentation/Paperwork – complete proforma 4. Transfer to theatre Blood loss of over 1500mls that is not controlled escalate to a MASSIVE Obstetric haemorrhage and request consultant obstetrician and anaesthetist to attend in person 3 Shoulder dystocia The order in which these manoeuvres are done depends on the individual case & clinical judgement, however McRoberts and suprapubic pressure are recommended as first line management Identify shoulder dystocia Call for help & phone 2222 1. 2. 3. 4. Assistance: Obs SpR, senior MW, neonatologist Prepare for neonatal resuscitation Communicate and reassure parents Commence timing + documentation McRoberts 1. 2. lie flat & elevate legs, knees towards armpits Attempt to deliver baby Suprapubic pressure 1. 2. 30 seconds continuous or rocking pressure Attempt to deliver baby Evaluate for episiotomy if required to do internal manoeuvres Internal manoeuvres 1. pressure on posterior aspect of anterior shoulder – 2. 3. adduct shoulders & push baby into oblique (attempt to deliver baby) pressure on posterior aspect of anterior shoulder & anterior aspect of posterior shoulder rotate 180o pressure on posterior aspect of posterior shoulder – rotate 180o in other direction Remove posterior arm Attempt to deliver baby Roll onto all 4’s & Attempt to deliver baby If unsuccessful consider: NEVER apply excessive traction or flexion to foetal head Repeat all manoeuvres (Zavanelli manoeuvre) 4