Chemical Reactions incl. Reactions in Solution
advertisement

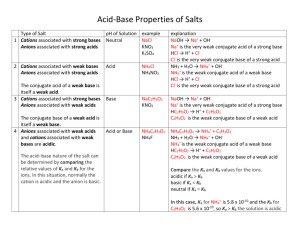
AP Chemistry Unit Two - Chemical Reactions incl. Reactions in Solution List the five common types of chemical reactions and the defining characteristics of each. For each equation shown, label the type of reaction. 1. Ca + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2 2. Na2CO3 → Na2O + CO2 3. C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O 4. Pb(NO3)2 + 2KCl → 2KNO3 + PbCl2 Complete the following sentences regarding synthesis reactions. A metal combines with a nonmetal to form ____________. Metallic oxides and water react to form ____________. Nonmetallic oxides and water react to form ____________. Predict the products of the following synthesis reactions. Balance the equations. 5. K2O + H2O 6. Al + O2 Complete the following sentences regarding decomposition reactions. A binary compound will break down to _____________________. Metallic chlorates decompose into _______________ and ________________. Metallic carbonates decompose into _______________ and _______________. Metallic hydroxides decompose int0 _______________ and _______________. Predict the products of the following decomposition reactions. Balance the reactions. 7. K2CO3 8. Al(OH)3 Explain why and how to use the activity series for metals. List the general order of the activity series for metals. NOTE: You do NOT have an activity series provided to you on the AP Exam, so this general order must be memorized. List the order of the activity series for halogens. Use the activity series to predict whether the following reactions will or will not occur as written. 9. AgNO3 + Ca 10. Br2 + NaCl 11. Cu + Mg(ClO3)2 12. Fe + CuSO4 What are the possible products that drive a double replacement reaction to completion? Memorize the solubility rules. Label the following compounds as soluble or insoluble. 13. KBr 14. Ag2CO3 15. PbCl2 16. KOH 17. Fe(NO3)3 18. BaSO4 What is the Bronsted-Lowry definitions of an acid and a base? List the six strong acids. List the eight strong bases. What is the general form of an acid-base neutralization reaction? Define “salt” Predict the products of the following acid-base reactions. 19. Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 20. HNO2 + Ba(OH)2 Define conjugate acid and conjugate base. Label the acid, base, conjugate acid and conjugate base in the following reactions. 21. H2O + CH3COOH → CH3COO- + H3O+ 22. HF + OH- → H2O + F- Define solute, solvent, and solution. Define electrolyte, weak electrolyte and nonelectrolyte. Explain what types of substances fall into each category. In what form do strong-, weak-, and non-electrolytes exist in aqueous solution? Because of this, how are strong-, weak-, and nonelectrolytes written in complete ionic and net ionic equations. Complete, then memorize the following chemical facts for use when predicting products and writing net ionic equations. H2CO3 decomposes to: H2SO3 decomposes to: NH4OH decomposes to: H2SO4 is a strong acid that completely dissociates to: For each of the following reactions, predict the products and write a balanced net ionic equation. 23. Solutions of silver nitrate and sodium sulfate are mixed. 24. A piece of aluminum foil is dropped into an iron (II) nitrate solution. 25. Solid calcium phosphate is added to hydrochloric acid. 26. The hydrocarbon benzene (C6H6) is burned in excess oxygen. 27. Calcium metal is heated strongly in nitrogen gas. 28. Chlorine gas is bubbled into a solution of potassium iodide. Write down a set of rules for assigning oxidation numbers. Assign oxidation numbers to each element in the substances shown. Define oxidation and reduction. Define oxidizing agent and reducing agent. 29. H2SO4 H _____ S _____ 30. NI3 N _____ I _____ 31. MoO42- Mo _____ O _____ 32. MgCr2O7 Mg _____ Cr _____ O _____ O _____ In each of the following reactions, determine the element oxidized, the element reduced, the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent. 33. Mg + 2AgNO3 → Mg(NO3)2 + 2Ag 34. Mg(ClO3)2 → MgCl2 + 3O2 Write down the steps used to balance redox reactions in acidic solution. Balance the following redox reactions that occur in acidic solution. 35. S2O32- + OCl- → Cl- + S4O62- 36. NO3- + Cu(s) → NO2(g) + Cu2+ Write down the steps used to balance redox reactions in basic solution. Balance the following redox reaction that occur in basic solution. 37. SO32- + MnO4- → SO42- + MnO2(s) Write down the molarity equation. Define each variable and list the common unit for each. Write down the dilution equation. Complete the following calculations. 38. Calculate the molarity of a solution containing 10.4 g of calcium chloride in 225 mL of solution. 39. In a 0.270M sodium chloride solution, what volume (in mL) contains 2.14 grams of dissolved solute? 40. Calculate the mass of KI in grams required to prepare 500. mL of a 2.80 M solution. 41. You have a 4.00M stock solution of HNO3. What volume of stock solution must be used to prepare 500.0 mL of 0.125M HNO3 solution? Explain the process of preparing a solution from a solid. Explain the process of preparing a solution from a stock solution. Answer the questions. 42. How would you prepare 100. mL of a 0.50M solution of NaOH from a 6.0M stock solution? 43. Explain how to prepare 500. mL of a 0.10M solution of K2SO4 from the solid salt. Complete the following solution stoichiometry problems. 44. What are the concentrations of all ions in a 0.50M solution of (NH4)2S? 45. What mass of precipitate forms when excess K3PO4 reacts with 25mL of 1.50M CaCl2? 46. When 50.0mL of 6.0M AgNO3 and 40.0mL of 5.0M Na2SO4: (a) What mass of precipitate can be formed? (b) What is the molar concentration of all ions remaining in solution? Sketch and label a typical titration apparatus. Define equivalence point and end point. Compare and contrast the two. Complete the following calculation. 47. What volume of 0.50M HCl solution is needed to neutralize completely each of the following: (a) 25.0 mL of 0.40M NaOH solution (b) 10.0 mL of 1.50M Ba(OH)2 solution Answers: 1. single replacement 2. decomposition 3. combustion 4. double replacement 5. K2O + H2O 2KOH 6. 4Al + 3O2 2Al2O3 7. K2CO3 K2O + CO2 8. 2Al(OH)3 Al2O3 + 3H2O 9. yes 10. no reaction 11. no reaction 12. yes 13. soluble 14. insoluble 15. insoluble 16. soluble 17. soluble 18. insoluble 19. CaSO4 + H2O 20. Ba(NO2)2 + H2O 21. H2O - base, CH3COOH - acid, CH3COO- - conjugate base, H3O+ - conjugate acid 22. HF - acid, OH- - base, H2O - conjugate acid, F- - conjugate base 23. 2Ag+ + SO42- → Ag2SO4 26. 2C6H6 + 15 O2 → 12 CO2 + 6H2O 24. 2Al + 3Fe2+ → 2Al3+ + 3Fe 27. 3Ca + N2 → Ca3N2 25. Ca3(PO4)2 + 6H+ → 2H3PO4 + 3Ca2+ 28. Cl2 + 2I- → 2Cl- + I2 29. H: +1 30. N: +3 31. Mo: +6 32. Mg: +2 33. ox: Mg S: +6 I: -1 O: -2 red: Ag OA: AgNO3 RA: Mg 34. ox: O O: -2 Cr: +6 red: Cl O: -2 OA and RA: Mg(ClO3)2 35. 2S2O32- + OCl- + 2H+ → S4O62- + Cl- + H2O 36. 4H+ + 2NO3- + Cu → 2NO2 + Cu2+ + 2H2O 37. 3SO32- + 2MnO4- + H2O → 3SO42- + 2MnO2 + 2OH38. 0.427M 39. 136 mL of solution 40. 232 g KI 41. 15.6 mL of stock solution 42. Use a volumetric pipette to measure out 8.3 mL of the stock solution. Place in a 100mL volumetric flask. Add water to the mark, cap and fully mix. 43. Measure out 8.7g of solid K2SO4. Place in a 500mL volumetric flask. Add sufficient water to fully dissolve solid. Add water to the mark, cap and fully mix. 44. 1.0M NH4+, 0.50M S246. (a) 47g 47. 20. mL HCl (b) [Ag+] = 0M, 45. 3.9 g of precipitate [Na+] = 4.4 M, [NO3-] = 3.3 M, [SO42-] = 0.56M 48. 60. mL HCl