Study Guide __i_1. Geyser The huge hole left by the collapse of a
advertisement

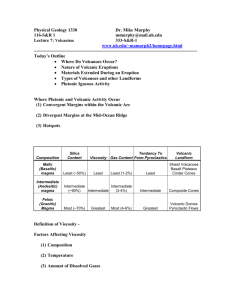
Study Guide __i_1. Geyser a. The huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain b. A weak spot in the crust where magma comes to the surface. c. A substance that cannot be broken down into other substances. d. Lava that flows easily and hardens into a rippled surface. e. What magma is called when it reaches the surface. f. Volcanic belt surrounding the Pacific Ocean that contains 75% of the world’s volcanoes. g. Lava that is cooler and slowermoving. h. A substance made of two or more elements that have been chemically combined. i. A fountain of water and steam that erupts from the ground. j. A molten mixture of rock-forming substances, gases, and water from the mantle. __f _2. Ring of Fire ___j__3. Magma __c__4. Element __g__5. Aa __a__6. Caldera __b__7. Volcano __e__8. Lava __d_9. Pahoehoe __h_10. Compound 11. Volcanoes can form along diverging plate boundaries on land. T F 12. Hot spots form only under oceanic crust. T F 13. Liquid magma rises until it reaches the surface, or until it becomes trapped beneath layers of rock. T F 14. The pipe of a volcano is a horizontal crack in the crust. T F 15. The Hawaiian Islands are cinder cone volcanoes. T F 16. A composite volcano has both quiet and explosive eruptions. T F 17. Some types of volcanic activity do not involve the eruption of lava. T F 18. The greater the viscosity, the __________ a liquid flows. The _______________ the viscosity, the more easily a liquid flows. a. faster, lower b. slower, lower 19. What factors determine the viscosity of magma? c. faster, greater d. slower, greater a. silica content, temperature b. silica content, pressure c. temperature, pressure d. viscosity, comound 20. What factors determine the force of a volcanic eruption? a. silica content, temperature b. viscosity, pressure c. silica content, viscosity d. viscosity, temperature a. Pipe b. crater c. vent d. magma