Becoming Human
advertisement

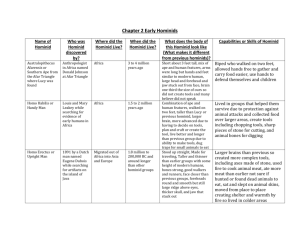
Becoming Human www.becominghuman.org Answers Objective: Students will understand the process that is used to collect fossils and determine relationships among extinct species with a focus on the evolution of the hominid species. Instructions: Access the website at www.becominghuman.org. Each section of this activity requires you to visit one of the areas at the site, watch video clips and explore multimedia. Notice the top menu bar which has the listing of the areas: | Prologue | Evidence | Anatomy | Lineages | Culture | You can use these links to easily navigate to the different sections. Prologue 1. After watching the video in the prologue, list three questions you have about human evolution. Answers will vary Evidence 2. Where is Hadar and why is it significant? – North Eastern Africa 3. Why was the 3.2 milion year old hominid fossil found in Hadar called "Lucy"? - Song Lucy in the Sky with Diamonds by the Beatles was playing when it was discovered. 4. What is a paleoecologist? Person who attempts to recreate the ecological environment of our ancestors in a place during the prehistoric period. ( Use the menu at the bottom titled "Related Exhibits" to access the exhibits related to evidence. The answers to the following questions can be found within the exhibits, you may have to search for them, the words in bold may give you clues about where to search. ) Evidence - Related Exhibits 5. The scientific method begins with an observation, information drawn from these observations rests on the principles of scientific thinking. What are the 3 principles of scientific thinking? Observation—testing---predictions---hypothesis 6. Finding fossils can be difficult, name 4 locations on the earth where significant hominid fossil finds occur. Answers will vary 7. When a fossil is found, profiling can be done to answer questions about the organism. How do scientists determine: The species – Every species has a unique diagnostic feature. We must study the anotomical features such as teeth, skull and skeleton The age – study teeth and bones The sex – males are larger, females are smaller, female pelvis are generally smaller The health – study skeletons which show diseases, fractures, dislocations Anatomy 8 What is the closest living relative to the human? African Chimpanzee 9. What is a common ancestor? Bipedal hominids 10. How does the human foot compare to the foot of a chimpanzee? – humans have a straight toe in line with the other toes…..chimp toe is more separated. 11. How does the skull of Homo erectus compare to the skull of Homo sapiens – homo sapiens have bigger brains Anatomy - Related Exhibits 12. Humans are like other primates in many ways. Name two similarities between humans and other primates. Humans have bigger brains…the rest is very similar 13. Bipedalism requires anatomical changes in bone structure to allow walking upright. Name one difference between the skeleton of a chimpanzee and a human that aids humans in walking upright. Iliac blades are different in both these species….they are not twisted in apes like humans. Lineages 14. Where are most Neanderthal fossils found? - Neander Valley, Germany, Europe 15. How did the face of Neanderthals differ from modern humans? – Neanderthal has a long and low face 16. Suggest one reason why Neanderthals became extinct. -blended with early human beings (interbreeding) -Direct conflict with early humans (economical conflict) Lineages - Related Links 17 What is the Missing Link and why is it not an accurate term for hominid evolution? -a half man and half ape creature slowly turned into us!! 18. How humans populated the globe is a question among paleoanthroplogists. Compare the "Out of Africa Theory" to the "Multiregional Theory" -Out of Africa – one local group of humans spread out of Africa and replaced all other human populations as it spread out. Multiregional Theory – Human populations in regional areas slowly evolved into modern humans. Modern traits arose in some populations and spread to other through genetics. 19. How does evolution explain the diversity of people throughout the world, like types of skin color? People who live in areas that have high ultraviolet radiation have more melanin which blocks some radiation preventing skin cancer but allowing enough to produce vitamins D Culture 20. What do the various indentations in the cave represent? - profound change able to understand abstract concepts 21. Why are the Majority of the Australian cave drawings of the female body? - Represent fertile area and plant life Culture - Related Exhibits 22. What cultural beliefs exist in regards to the human body after death? - simply an object sacred and should be specially prepared out of respect or fear body must remain intact so the soul can use it in the afterlife