Biology CP
advertisement
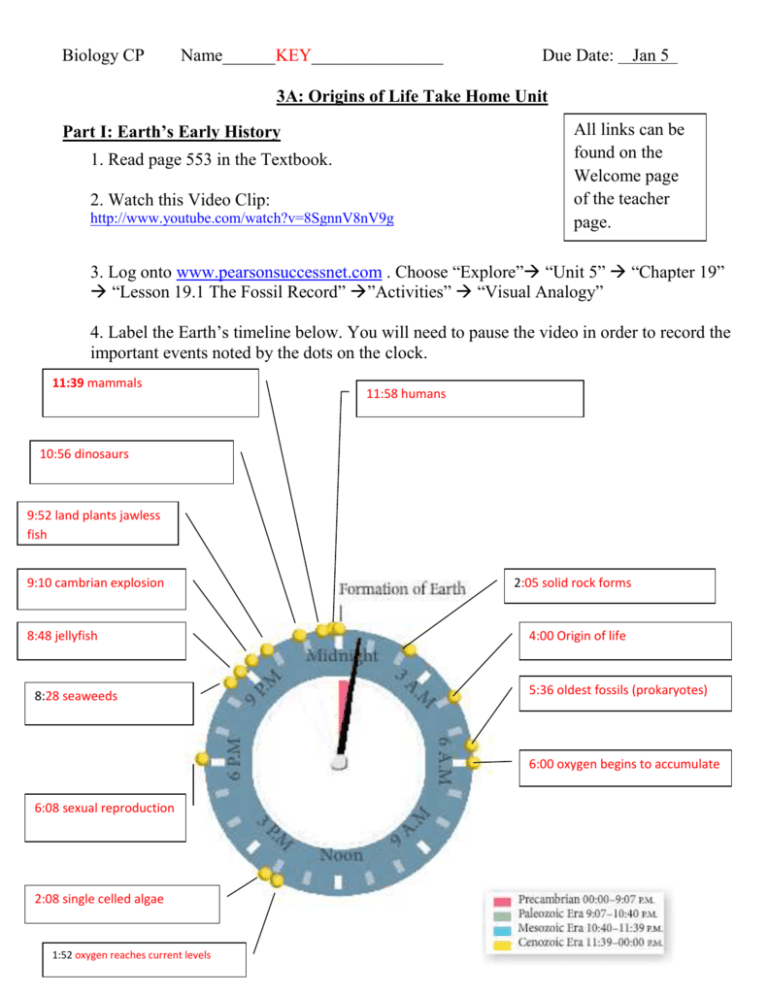
Biology CP Name______KEY_______________ Due Date: Jan 5 3A: Origins of Life Take Home Unit Part I: Earth’s Early History 1. Read page 553 in the Textbook. 2. Watch this Video Clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8SgnnV8nV9g All links can be found on the Welcome page of the teacher page. 3. Log onto www.pearsonsuccessnet.com . Choose “Explore” “Unit 5” “Chapter 19” “Lesson 19.1 The Fossil Record” ”Activities” “Visual Analogy” 4. Label the Earth’s timeline below. You will need to pause the video in order to record the important events noted by the dots on the clock. 11:39 mammals 11:58 humans 10:56 dinosaurs 9:52 land plants jawless fish 9:10 cambrian explosion 8:48 jellyfish 8:28 seaweeds 2:05 solid rock forms 4:00 Origin of life 5:36 oldest fossils (prokaryotes) 6:00 oxygen begins to accumulate 6:08 sexual reproduction 2:08 single celled algae 1:52 oxygen reaches current levels 5. Return to your home screen on www.pearsonsuccessnet.com . Choose “Explore” “Unit 5” “Chapter 19” “Lesson 19.3 Earth’s Early History” ”Activities” “Art Review Earth’s Early History” 6. Label the diagrams by dragging terms onto the image. Click “Submit” to check your answers. Record the correct answers below. 1. 5% nitrogen 5. 78% nitrogen 2. 12% CO2 6. 21% O2 3. little or no O2 7. < 1% CO2 4. 74% water vapor 8. < 3% water vapor The Big Question was… how did the first life arise on a lifeless planet?!?! Continue on to find out! Part II: Abiotic Formation of Organic Molecules-The Miller-Urey Experiment In the 1950s, Stanley Miller and Harold Urey set out to determine if organic molecules (the molecules needed for life) could be formed using only the molecules present on early Earth. They filled a container with water and gases that they thought represented the composition of Earth’s early atmosphere. They passed electric sparks through the mixture to simulate lightning. Soon, organic compounds formed. The experiment showed that molecules needed for life could have arisen from the simpler compounds found on early Earth! 1. Watch this Video Clip (from Carl Sagan’s Cosmos): http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_2xly_5Ei3U 2. Read pg. 554 in the textbook. 3. Pre-read the Miller-Urey Questions below. 4. Go to this website: http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/9834092339/student_view0/chapter26/animation_-_millerurey_experiment.html 5. Watch the animation and answer the Miller-Urey Questions below. It will be helpful to periodically pause and restart the animation so you can fully answer each question. Miller-Urey Questions 1. What was Oparin and Haldane’s hypothesis? They hypothesized that the atmosphere of the primitive earth contained gases such as nitrogen, ammonia, methane, water vapor, carbon dioxide and hydrogen. They believed that the conditions on the primitive earth gave rise to simple organic compounds, the precursors to life. 2. What gases made up primitive earth’s atmosphere? Little or no oxygen Primarily: nitrogen, ammonia, methane, water vapor, carbon dioxide and hydrogen 3. When did oxygen become part of earth’s atmosphere? Millions of years after formation of Earth. Around 2.2 billion years ago, photosynthetic organisms first arose, which began to put out oxygen. First oxygen combined with iron in the oceans, then it began to accumulate in the atmosphere. 4. What two sources of energy could have allowed the formation of organic molecules? Lightning and UV radiation from the sun 5. Why did Miller and Urey add water, hydrogen gas, methane, carbon dioxide, ammonia and nitrogen to their closed system? To simulate conditions of the early Earth 6. What was the purpose of the electricity provided by the electrodes? To mimic lightning 7. Show how Miller and Urey’s closed system mimicked primitive earth. Label the sketch with the phrases from the word bank: A. Gases of early Earth -2 B. Condensation like rain-4 C. Heated water like evaporation-1 D. Electricity to mimic lightning -3 E. Primordial soup containing organic compounds -5 Textbook pg. 554 8. Why is it significant that over time the following compounds were made from Miller and Urey’s experiment: formaldehyde, hydrogen cyanide, urea, formic acid, etc. These simple organic compounds are the building blocks for proteins and other organic macromolecules. This experiment showed that these building blocks could be formed from the gases present in the primitive atmosphere with the input of electrical energy. 9. In summary, what was the purpose of the experiment? The purpose of the experiment was to show that the mixtures of the organic compounds necessary for life could have arisen from the simpler compounds formed from the conditions on primitive Earth. Part III: Reading and Review Read Section 19.3 in your textbook (starting on p. 553) and answer the questions 1-3 from page 558 below. 1a. It was made up mainly of carbon dioxide water vapor and nitrogen; little or no oxygen 1b.In the environmental conditions of early Earth, simple compounds could have given rise to mixtures of organic compounds 1c. Probably not, because the same conditions no longer exist on Earth, and oxygen in t atmosphere would destroy organic molecules. 2a. A symbiotic relationship evolved between ancient eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells within them 2b.Mitochondria evolved from endosymbiotic prokaryotes that were able to use oxygen to generate ATP. 2c. Mitochondria and chloroplasts share many features of free-living bacteria. They contain similar DNA and ribosomes. They also reproduce by binary fission. 3a. Sexual reproduction increases genetic variation, which gives natural selection more raw material to work on 3b. development of photosynthesis, free oxygen in the atmosphere, development of eukaryotic cells, sexual reproduction Part IV: Which came first? Over the course of evolution of life on our planet, organisms have increased in complexity. They have gone from very simple, to infinitely complex. THINK!! Each pair of words below shows different categories for how living things function. From each pair of words, circle the organism that is SIMPLER. (*You may have to refresh your memory of the definitions of these words) 1. Unicellular or multicellular 2. Prokaryotic or eukaryotic 3. Heterotroph or autotroph (this one can be tough, think about what is simpler, to eat food or to go through the process of making one’s own food). 4. Therefore, the earliest organisms (the ancestors of all organisms alive today) were: (circle a. or b.) a. Unicellular, prokaryotic, heterotrophs b. Multicellular, eukaryotic, autotrophs 5. The Heterotroph Hypothesis states that the first living things were (circle one) consumers or producers? What do you think they fed on? organic compounds present on Earth or other organisms Watch the following video clip: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kz2DrZxUH3U The early Earth had no oxygen because there was no photosynthesis yet to produce it! 6. Therefore, photosynthetic organisms evolved before or after (circle one) heterotrophic organisms? 7. The first photosynthetic organisms (autotrophs) were (circle a. or b.): a. prokaryotic b. eukaryotic 8. Place the following sequence of events in order from the first (1) to occur in the evolution of life to the last (4) to occur in time: __4__ multicellular eukaryotes form ___3_ unicellular eukaryotes evolved __1__ the first prokaryotes form __2__ the first evidence of photosynthesis