Heat is a type of energy and is measured in joules and kilojoules
advertisement

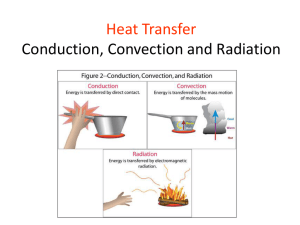
Heat Topic - Notes Temperature is a measure of the hotness or coldness of something and is measured in 0C. Conduction Heat travels through solids by conduction. Heat travels from atom to atom and this is possible because the atoms in solids are close together. The heated atoms vibrate more quickly and pass the vibrations on to neighbouring atoms so spreading the heat. Conductors are substances that let heat pass through them easily. Metals are the best conductors. Insulators do not let heat pass through them easily. Many solids are insulators such as rubber, plastic, cork, glass and wood. Air is an extremely good insulator. Our clothes keep us warm by trapping the air between the fibres – keeping the heat in Conductors we use in the home are pots – which conduct heat to the cooking food and radiators which provide heat for our homes. 1 Heat Topic - Notes Insulators used in the home are pot handles – which stop us burning our hands. Also oven gloves and insulating jackets for hot water tanks. Our clothes are insulators to stop our bodies losing heat. Convection Heat travels through liquids and gases by convection. Liquids and gases cannot conduct heat because the particles are close enough together to pass heat to one another. Instead when we heat a liquid or gas a convection current is set up. The particles that are heated rise up and colder particles move in below them. The continual movement of hot and cold particles eventually heats up the whole container of gas or liquid. We looked at a convection current by putting a purple dye crystal in water and observing the movement of the dye as the water was heated. This clearly showed that the particles of water were rising when heated and falling when cooled. The air in our homes is heated in a similar way by radiators and fires. The moving air near radiators often causes dust to move and sometimes it sticks to the wall just above the radiator. Homes with high ceilings are hard to heat as the hot air goes to the top and it takes longer for warmer air to circulate through a room. 2 Heat Topic - Notes Convection and Density When we heat air particles they move about more and spread out. They become less dense – less closely packed. The air which is less dense is ‘lighter’ than the colder air so it rises to the top. This principle is used in hot-air balloons. The hot air inside the balloons is less dense than the air outside so the balloon floats. Radiation Lots of heat comes to us through space from the sun. Space has very few particles in it. We say that space is a vacuum. Conduction or convection cannot take place in space because there are no particles that can vibrate or move. The heat is travelling to earth by another method called radiation. Radiation travels from the sun in straight lines in all directions. The suns rays contain many different types of radiation including ultra violet and infra red. The most important one for this course is infra red which is another term for heat. 3 Heat Topic - Notes Radiation and Surfaces We found out that: Black and dark surfaces are best at absorbing heat Black and dark surfaces are best at radiating heat Shiny and white substances are poor at absorbing heat. Shiny and white substances are poor at radiating heat. So in warm sunny countries light clothing is worn to reflect the heat. Car radiators are black in colour because that makes them better at taking heat away from the engine. Uses of Infra-red radiation Infra-red radiation is another word for heat. Our bodies give out infra-red radiation. This can be picked up by thermal cameras and can be used for finding people that are lost up a mountain at night or are trapped in a smoke filled building. Infra-red can also be used to operate TV remote controls and to trigger burglar alarms and security lights. 4