PlantGeneaology04

Plant Genealogy and
Taxonomy Notes
Know underlined terms
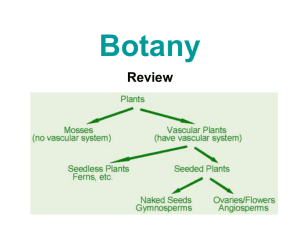
I. NON-VASCULAR PLANTS:
• Algae, mosses
• First to evolve on earth (about
470 million years ago). No special vessel-like system for transmission of fluids.
II. VASCULAR PLANTS :
A plant’s “circulatory system”
• Special vessel-like system for transmission of fluids:
• A. Non-Seed Bearing (spores):
• EX: Ferns
Evolved about
400 mya.
II. VASCULAR PLANTS :
• B. Seed-bearing:
• 1. Gymnosperms “naked-seed”
(no fruit). Evolved ˜ 360 mya:
• male/ female parts; disperse, collect pollen; form seeds
• EX: Conifers (pines, redwoods, etc.)
II. VASCULAR PLANTS :
• B. Seed-bearing:
• 2. Angiosperms “covered seeds”; flowering plants (fruit). Evolved ˜180 mya.
• male/ female parts in flower; disperse, collect pollen; form fruits and seeds
II. VASCULAR PLANTS :
• 2. Angiosperms:
Where seed stores food
--like an egg’s yolk.
• a. Monocots (1 cotyledon [1 seed lobe], parallel leaf veins):
• EX: Grasses, corn
II. VASCULAR PLANTS :
• 2. Angiosperms:
• b. Dicots (2 cotyledons [2 seed lobes], networked leaf veins):
• EX: most other spp.
II. VASCULAR PLANTS :
• 3. Other descriptions of vascular plants (may be gymnosperms or angiosperms, monocots or dicots):
• Annuals: Plants that complete their lifecycle in a year or less
(go to seed every year)
• Perennials: Plant that lives for more than 2 years.
QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.
QuickTime™ and a
TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture.
III. PLANT EVOLUTION
• Consider the power and role of evolution in plant genealogy:
• A. Background: What is evolution?
• Cumulative changes in a population as a result of:
• 1. appearance of variation in a population (often caused by mutation),
• 2. a selective force that selects for or against the survival of certain individuals in the population
• 3.
reproduction : passing on of the selected characteristic that allowed for survival.
III. PLANT EVOLUTION
• B. Where did flowers come from
(what is the source of variation in the plant population)?
• Modified/ adapted leaf structures.
• C. Why were flowers selected?
• Sexual reproduction increases variation--vital to evolutionary process. Flowers are a means of sexual reproduction.