Chemical Bonds - Camden Central School
advertisement

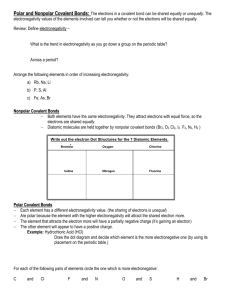
Test 7: Chemical Bonding Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Basic Info (Put these notes on page 1 of your Bonding Packet) 1. Chemical bonds are attractive forces that hold atoms together. 2. Compounds – 2 or more different atoms chemically bonded together ex: NaCl or H2O 3. Diatomic Elements – 2 of the same atoms bonded together ex: H2 O2 F2 Br2 I2 N2 Cl2 (Put on page 1 of packet) 4. Electronegativity – an atom’s attraction for electrons (Table S) Metals – Low #’s Nonmetals – Big #’s Think Metals lose e- & form + ions Nonmetals gain e- & form - ions Electronegativity (attraction for another atom’s electrons) Get lost, loser! Hey! I find your electrons attractive! Chart to Memorize! Type of Bond Ionic Electronegativity Difference… >1.7 1.7>x>0 (equal to or more than 1.7) (less than 1.7 but more than zero) Transferred Shared unequally 2 Different Nonmetals H2O Valence Electrons are… How to Recognize… Chemical Formula for one example… Metal & Nonmetal NaCl (page 1) Polar Nonpolar Covalent Covalent = zero Shared Equally 2 of the same Nonmetals H2 Electronegativity Chart To Determine Electronegativity Difference for CaBr2: Br = 3.0 Ca = 1.3 Difference is 1.7 So CaBr2 Bond is Ionic Formation of Ionic Bond Note: Electrons are transferred NaCl Crystal Lattice The melting points of some Ionic Compounds are as follows: NaF KCl LiCl 993 oC 770 oC 605 oC These high melting points are experimental evidence that Ionic Bonds are VERY STRONG. (Hard to break just by heating). Formation of Polar Covalent Bond Note: Electrons are shared Animation for Bonds Chemical Bonding (page 2) 1. Octet Rule – Atoms want to have 8 valence electrons (except H & He – need 2). 2. Forming Bonds – releases energy. Mg + S MgS + energy (energy after means its given off) 3. Breaking Bonds – requires energy. MgS + energy Mg + S (energy before means its needs or absorbed) 4. Ionic Bond – ED 1.7 or more 5. Polar Covalent Bond – ED greater than 0, but less than 1.7 6. Nonpolar Covalent Bond – ED = zero 7. Table S – to calculate ED 8. Metallic Bonds – sea of mobile e(this is a special type of bond that holds atoms of metals together & accounts for a metal’s luster and ability to conduct electricity) Bond Wheel Ionic 1.7 or more (page 3) Polar Covalent less E.D. than 1.7 Nonpolar Covalent = zero HW • Do page 5 & 6 Nonpolar Molecules • May have PC or NPC chemical bonds, but are Nonpolar Molecules due to their symmetry. • Examples: H2 O2 F2 etc. CH4 CCl4 CF4 etc. CO2 Polar Molecules • Polar Molecules have PC bonds and are Asymmetrical. • They have uneven e- distribution. • They have a positive and negative end. • Examples: H2O NH3 HF HBr HCl CO Intermolecular Forces • Attraction between polar molecules • Example Hydrogen Bonding • Extra strong IMF • Found for H with NOF • H2O NH3 HF