Difference between speed and velocity - mirnay
advertisement

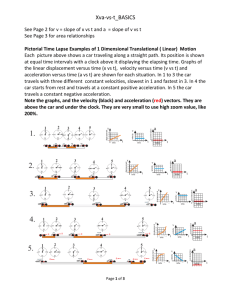
Difference between speed and velocity Objectives • 1. Define velocity • 2. Differentiate between speed and velocity • 3. Explain the difference between instantaneous and average speed and velocity • 4. Determine average velocity • 5 Use position-time graphs to determine instantaneous and average velocities • 6. Write the equation of motion for average velocity VELOCITY Difference between speed and velocity - Velocity is different than speed. While speed describes only how fast an object is moving, velocity gives both magnitude and direction. - For example, "5 meters per second" is the speed of a moving object ,whereas "5 meters per second east" is a vector. - Does this sound familiar? • Explain. ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Things to agree on: 1. 2. 3. 4. 4. 5. 6. Displacement = ∆d= df – di Time interval= ∆t= tf – ti For a uniform motion: The position time graph is a straight line Slope= displacement/time = ∆d/ ∆t . _ Average Speed= s =absolute value of the slope. Average speed= distance /time _ Average Velocity= v=slope. y- intercept= initial vector position . A steeper line represents a greater speed and velocity ( as shows fig 2-20 p:43 on your textbook) Application: 1. Find the average speed, average velocity and initial vector position of the moving object whose motion is represented by the figure at the right. Write an equation representing the motion. APPLICATION • Find the average speed, velocity and initial vector position of the motion represented by the following position-time graph. • Write the equation of the motion • Solve question p 45 no.27 Look at the following motion diagrams representing the motion of two cars 1. Plot the position-time graph for each car. 2. Find the slope for each line. ------------------------------------3. What is the speed for each motion -------------------------------------4. What is the velocity for each motion. --------------------------------------5. Find the initial vector position for the two cars. Write the equation of motion for each car. --------------------------------------6. Where and when the two cars meet? -----------------------------------------------Application: 1. Find the average speed, average velocity in figure 2-21 page 44 in your textbook. 2. Draw a corresponding motiondiagram for the moving object. Difference between velocity and speed Conclusion: To have a constant velocity, an object must have : 1. constant speed 2. motion in a constant direction. Constant direction means a straight line and constant orientation. Application The figure at the right shows the motion of a car in a roundabout. Conclude. ------------------------------------------------- Conclusion • Speed is how fast an object moves. It only has a magnitude. It is a scalar In a position-time graph of a linear uniform motion, the average speed is the absolute value of the slope. • Velocity is the speed of an object in a given direction. It has a magnitude and direction. It is a vector. In a position- time graph, the average velocity is equal to the slope. • Application: Solve Questions p:45 no.35,26 & 27 + p53 no.49-51 The following Diagram represents the motions of two moving objects. Answer the below questions. 1. What type of motion is represented by each object? --------------------------------------2. Calculate the average speed of each object ---------------------------------------3. Do the two objects have the same velocities? Explain. ----------------------------------------4. Calculate the instantaneous speeds for each object between 0.1 s and 0.2 s. ------------------------------------------------5. Conclude. ------------------------------------------------- Difference between average velocity and instantaneous velocity Average velocity _ • Average speed= s = distance time __ V= displacement/time= ∆d/∆t • Is the average velocity during the whole path • It has the direction of the motion Instantaneous velocity • Represents the velocity at a particular moment. • It has the speed and direction of the moving object at a certain moment. Assessment: Solve questions II and III Uniformly accelerated motion •Velocity is not kept constant •Velocity –time graph is a straight line •Slope= velocity change= time interval =∆v=aceleration (m/s2) ∆t • equation: _ V= at+ vi Application: Find the equation of velocity of the motion represented in the figure, Find velocity at t= 1 s. Find the time when velocity is 12 m/s. Application • Find the equation of velocity of the motion represented in the figure. • Find velocity at t= 1 s. • Find the time when velocity is 12 m/s. Look at the following diagram and answer the below questions 1. Find the average speed of object A and B ----------------------------------2. Represent the average velocity for A and B by corresponding vectors. 3. Find the instantaneous velocities at instant 0.1 and 0.5 s for every object. Conclude. -----------------------------------------4. What type motion is represented by each object? -------------------------------------------5. Calculate the value of the velocities at instant 0.1-0.5 s for each object ----------------------------------------------6. Draw for each object the position-time graph 7. Draw for each object the velocity-time graph. 8. Find the acceleration for each object 9. Write the equation of motion for object A ----------------------------------------------------------------10. Write the equation of each object. ----------------------------------------------------------------11. Write the equation of motion of object B ------------------------------------------------------------------ Uniformly accelerated motion • Velocity is not kept constant • Velocity –time graph is a straight line • Slope= acceleration Equation of a Linear uniform motion • Position time graph line of best fit: ------------• Position-time relationship: ---------------------• Equation: ---------------------------------where: the average velocity represents -------and the initial vector position represents ------So the equation would be: Application: Find the equation of the the motion represnted by the previous graph. Solve page 53 no 54 For next time: • Continue solving the worksheet • Download PowerPoint presentation on your macbook from wikispaces. • Quiz next lesson sections 1.3 and 2.2 • Homework page 53 no.56 & 57