1385-20101105140000
advertisement

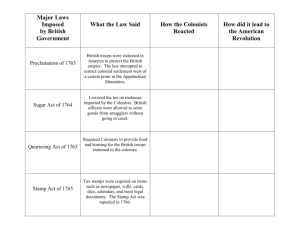
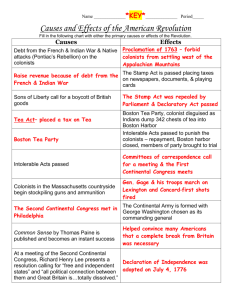
British Policies Graphic Organizer Nelson Sanchez 6th period Social Studies Navigation Acts (1650-1700s) Control of trade, Sugar Acts, Special courts, Currency Act, and stifling colonial manufacturing resentment Proclamation of 1763 Passed after the French and Indian War by King George III. It recognized the Indian rights to the Ohio River Valley. Colonists cannot go pass the Appalachian Mountains. It was issued in 1763. Currency Acts (1764) Assumed control of the colonial currency system. Resement continued to grow. Stamp Act (1765) Taxed on all paper goods, and organized a protest. Declaratory Act (1765) Parlament had full control of authority over the 13 colonies Quartering Act (1765) Standing army of soldiers with blank search warrants. Required colonists to quarter or house and feed British soldiers. Increased Tension between the colonists and the British. Townshend Acts (1767) Pay taxes on imported tea, glass, paper, and other items. Women organized Daughters of Liberty. The British wanted to show they had power to tax. Their anger grew against British government. Boston Massacre (1770) March 5, 1770, angry colonists argued with British soldiers. Shots were fired and 5 colonists were killed. Samuel Adams infuence the incident as a public opinion. Tea Act/Boston Tea Party (1773) The only company who was allowed to sell tea was British East India company. Colonists were unhappy because they were force to pay. December 16, 1773, Sons of Liberty diquised as Mohawk Indians illegally. They got on a boat and dump 243 crates of tea into the Boston Harbor. Coercive (Intolerable) Acts (1774) These Acts were an effort to make colonists to pay for the tea and to keep planning attacks. Revolutionary spirit through the country.