WH Chapter 7 Section 3 - Woodridge High School
advertisement

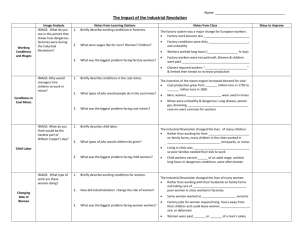
Chapter 7 Section 3 Hardships of Early Industrial Life Lesson Objectives • Compare and contrast the industrial working class and the new middle class • Understand how the factory system and mines changed the way people worked. • Analyze the benefits and challenges of industrialization. Life in the new industrial city • Industrial Rev. brought rapid urbanization (movement of people to cities) – Movement of farmers to the city – Soaring population growth – Increasing demands for workers in factories – Small towns grew around iron & coal mines Manchester, England • Manchester, England – 17,000 people in 1750 – 40,000 people in 1780 – 70,000 people in 1801 Tenements • Tenements (multistory buildings divided into crowded apartments) – No running water – No sewage or sanitation systems – Waste & garbage – Diseases like cholera spread like crazy • Wealthy & middle class lived in pleasant neighborhoods Factory System • Factory system changed the way people lived – The factory was the heart of the industrial city – Rigid discipline, unvaried, monotonous work – Strict schedule of long hours, 12-16 hours a day – Exhausted workers suffered accidents - loss of limbs, even lives • Coal miners - lungs destroyed • Textile workers – breathed in lint • Workers got sick or injured, often lost jobs Women Workers • Women workers – Preferred by employers – Adapted more easily to machines – More easily managed – Able to pay less for same work – Away from home 12+ hours • Return to tenements – feed, clean for & clothe families Child Labor • Parents let their children work because families needed the money – Textile mills – Small fingers changed spools – Crawl under machines to fix parts • Children worked in coal mines – Pushed carts – Climbed into narrow spaces to chip minerals off mine walls • Parliament slowly passed laws to regulate child labor Working Class • Developed sense of community • Forbidden to: – Organize groups – Bargain for better pay or working conditions – Strike – Protestors were repressed or crushed Luddites • Protests led by the mythical Ned Ludd – Resisted “labor-saving” machines, were costing their jobs – Smashed machines, burnt factories Methodism • Spread of Methodism – religious movement founded by John Wesley – Promised forgiveness of sin, better life to come & gave workers some comfort – Studied the Bible, learned to read & write – Turned workers away from revolution & toward reform New Middle Class • Benefited the most from Industrial Revolution – Were entrepreneurs (business owners) who began Industrial Revolution – Felt poor factory workers were responsible for their own poverty & misery • Came from several sources – Rose from rags to riches – Merchants – invested growing profits in factories – Inventors – created new technologies Middle Class Women • “Ladylike” activities – drawing, embroidery, playing piano • Did not work outside the home or do their own housework Reformers • Reformers pressed for laws to improve working conditions – Labor unions (worker’s organizations) won right to bargain with employers for better wages, hours, & working conditions – Working class men gained right to vote & political power • Material benefits – Demand for mass-produced goods > new factories > more jobs – Wages rose > extra $$ for reading material & entertainment – Cost of rail travel fell > people able to travel