PSAA Curriculum
advertisement

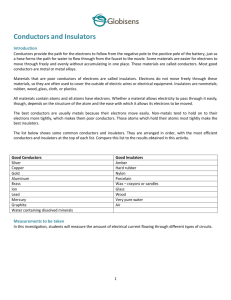
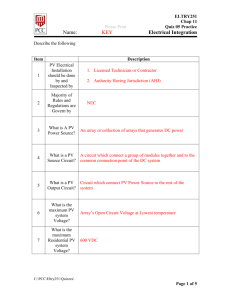
PSAA Curriculum Unit Physical Science Systems Problem Area Energy and Power Systems Controlling Electrical Current: Circuits, Conductors, and Insulators Lesson Identify the various materials used in these cords/cables. What are these materials? What are they mainly used for? Are they good insulators or conductors? Why? Learning Objectives Explain electricity and how electricity flows along a complete circuit. Describe the components of a complete electrical circuit. Explain the functions of conductors and insulators and identify common conductors and insulators used in agricultural facilities. Terms Alternating current Circuit Complete circuit Conductor Current Direct current Electricity Insulators Semiconductors How is electrical energy controlled? Electricity is a flow of electrons along a conductor. The conductor is the path along which the electrons flow. For such a flow to exist, it is necessary that there be a complete circuit. The complete circuit must allow for the electricity to flow from the source to the load and back to the source. Conductors A conductor is a piece of metal in the form of a wire. Metals are excellent conductors of electricity. Circuit The circuit is a path for electrons to move through components and wires. Electrons moving in a negative to a positive direction along a conductor is current. Currents Direct current flows in one direction only, from source to load. Alternating current involves a change in direction by the electrons, occurring at a rate of 60 times per second or 60 hertz. All residences in the United States use alternating current in their circuits. What is necessary for a complete electrical circuit? To have an electrical circuit, there must be a source of applied power, a load to which the power is applied, a path for the electrons to pass from the source to the load, and a return path for the electrons to pass from the load to the source. What is necessary for a complete electrical circuit? A switch is used as a means to control the electron flow. Overcurrent protection in the form of a fuse or circuit breaker is added for safety. What is an insulator and a conductor and what determines if a substance is an insulator or a conductor? What is a semiconductor? All materials may be classified as either conductors of electricity, non-conductors of electricity (insulators), or partial (semi) conductors of electricity. Insulators & Conductors… Atoms of conductors give up electrons resulting in electron flow. By surrounding a conductor with an insulator electron flow can be controlled and used. Insulators are non-conducting material lacking a sufficient supply of free electrons to allow for movement of current through the material. Semiconductors Semiconductors have resistivity values between those of insulators and conductors. Silicon is an example of a semiconductor. The electrons in semiconductors are bound more strongly than in conductors, but less strongly than in insulators. Semiconductors (cont.) The electrical properties of semiconductors can be controlled by adding other elements to alter their structure and change their electrical properties. These altered semiconductors are the basis of all modern electronic circuits. Semiconductors are used to make transistors, integrated circuits, and chips for microelectronics. Common insulation materials, cables, and flexible cords used in electrical wiring Common insulation materials, cables, and flexible cords used in electrical wiring Review/Summary How is electrical energy controlled? What is necessary for a complete electrical circuit? What is an insulator and a conductor and what determines if a substance is an insulator or a conductor? What is a semiconductor?