Latitude, Longitude, and GIS - Spectrum Loves Social Studies
advertisement

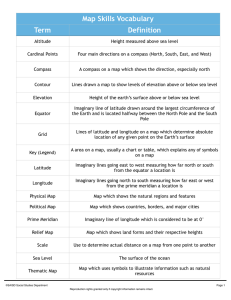
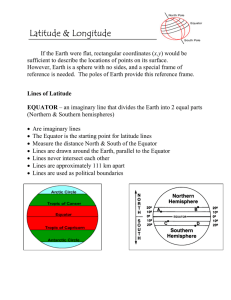
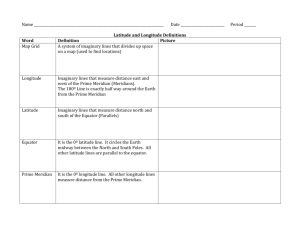
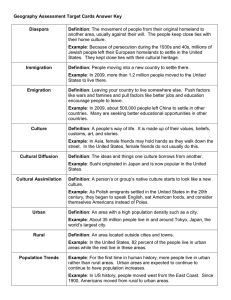
Latitude, Longitude, and GIS “Where’s Waldo” just got a lot less fun Find Waldo in the picture. Write his relative location on the top of a piece of paper 1A 2 B C D E F G 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Hemispheres • To help geographers classify and describe places on Earth, the globe is divided into 4 hemispheres: – Northern – Southern – Western – Eastern • Equator: Imaginary line that divides the Northern and Southern Hemisphere • Prime Meridian: Imaginary line that divides the Eastern and Western Hemisphere • Grid system: criss-crossing lines that help find exact places on earth’s surface Latitude • Lines on the grid system that circle the Earth parallel to the Equator • Described as North or South • Equator: 0° • Poles: 90 ° North/South Longitude • Lines on the grid system that circle the Earth parallel to the Prime Meridian • Described as East or West • Prime Meridian: 0° • The opposite side of the Earth from the Prime Meridian is the International Date Line Absolute Location • Latitude and Longitude describe an absolute location • Tokyo, Japan’s absolute location: 36 °N 140 ° E • Relative location describes a place in relation of one location to another • Tokyo, Japan’s relative location? Geographic Information Systems • Computer program that combines maps, satellite images, statistics, and other data to create a complex map with several layers of information. • Google Earth uses GIS technology to present multiple layers of information at the same time. The user chooses the information needed. • WANNA SEE?!?!?!