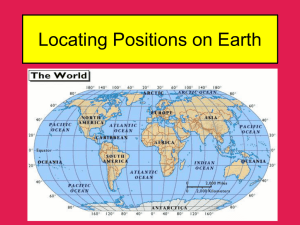
The Cultural Landscape:
An Introduction to Human
Geography
10th Edition
Classroom Response System Questions
Chapters 1-4
01-01 The movement of money from one country to
another and one currency to another has primarily been
facilitated by
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
the leadership of the United States.
advances in electronic communications.
the World Trade Organization.
transnational corporations.
global agreements brokered by the
United Nations.
01-01 The movement of money from one country to
another and one currency to another has primarily been
facilitated by
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
the leadership of the United States.
advances in electronic communications.
the World Trade Organization.
transnational corporations.
global agreements brokered by the
United Nations.
Explanation: While all of these factors have played a role,
electronic communications have made it possible to move
money around the world.
01-02 A place’s location relative to other objects or places is
called its
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
situation.
site.
absolute location.
topography.
functional region.
01-02 A place’s location relative to other objects or places is
called its
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
situation.
site.
absolute location.
topography.
functional region.
Explanation: Situation is the location of a place relative to
other objects and places.
01-03 Which of the following maps would have the largest scale?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
World
Continent
Country
State
City
01-03 Which of the following maps would have the largest scale?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
World
Continent
Country
State
City
Explanation: Large scale maps are used to show smaller areas in
greater detail, e.g., city streets and neighborhoods.
01-04 An object at 90 degrees north latitude is located
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
at the North Pole.
on the Equator.
at the Tropic of Cancer.
at the Tropic of Capricorn.
closer to Australia than to Europe.
01-04 An object at 90 degrees north latitude is located
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
at the North Pole.
on the Equator.
at the Tropic of Cancer.
at the Tropic of Capricorn.
closer to Australia than to Europe.
Explanation: Latitude measures distance north and south from
the Equator as an angle. It ranges from 0 to 90 degrees.
01-04
01-05 The frequency an object appears in a given area is its
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
density.
diffusion.
dispersion.
distribution.
region.
01-05 The frequency an object appears in a given area is its
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
density.
diffusion.
dispersion.
distribution.
region.
Explanation: Density and concentration are not synonymous.
Density is specified by the number of objects in a given area.
Concentration describes the dispersal of those objects.
01-06 Looking at a world map, choose the most correct
location for this pair of latitude and longitude coordinates
(expressed in degrees): 0,0.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Central Australia
Northwest Brazil
Southwest of Africa in the Atlantic Ocean
Near the South Pole in Antarctica
London, England
01-06 Looking at a world map, choose the most correct
location for this pair of latitude and longitude coordinates
(expressed in degrees): 0,0.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Central Australia
Northwest Brazil
Southwest of Africa in the Atlantic Ocean
Near the South Pole in Antarctica
London, England
Explanation: The coordinates 0,0 mark the point at which the
Equator intersects the Prime Meridian in the Atlantic Ocean.
01-06
01-07 Lines of ________ are drawn as east and west circles on
the globe and yet they measure distances north and south of the
________.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
longitude, Prime Meridian
longitude, Equator
latitude, Prime Meridian
latitude, Equator
latitude, Date Line
01-07 Lines of ________ are drawn as east and west circles on
the globe and yet they measure distances north and south of
the ________.
A. longitude, Prime Meridian
B. longitude, Equator
C. latitude, Prime Meridian
D. latitude, Equator
E. latitude, Date Line
Explanation: Latitude measures distance north and south from
the Equator as an angle. It ranges from 0 to 90 degrees.
01-07
01-08 Meridians of longitude on the globe
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
are the same length north to south.
converge at the poles.
terminate at the poles.
intersect the Equator.
All of the above are correct.
01-08 Meridians of longitude on the globe
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
are the same length north to south.
converge at the poles.
terminate at the poles.
intersect the Equator.
All of the above are correct.
Explanation: Lines of longitude measure distance east and
west of the Prime Meridian in angles ranging from 0 to 180.
01-09 Imagine that you are aboard a ship on September 21
sailing along the Equator. Glancing upward you notice that the
sun is directly overhead. Your watch is set to Greenwich time
and reads 6 P.M. What is your longitude?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
90 degrees west of Greenwich
90 degrees east of Greenwich
180 degrees west of Greenwich
180 degrees east of Greenwich
30 degrees east of Greenwich
01-09 Imagine that you are aboard a ship on September 21
sailing along the Equator. Glancing upward you notice that the
sun is directly overhead. Your watch is set to Greenwich time
and reads 6 P.M. What is your longitude?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
90 degrees west of Greenwich
90 degrees east of Greenwich
180 degrees west of Greenwich
180 degrees east of Greenwich
30 degrees east of Greenwich
Explanation: September 21 is the date of the Autumnal
Equinox. The sun appears directly overhead at noon. The
difference in hours between local time (noon) and Greenwich
(6 P.M.) is six hours. For every hour, add fifteen degrees of
longitude, placing the ship at ninety degrees west of Greenwich
01-09
01-10 Which of the following is NOT a formal culture region?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
The distribution network for USA Today newspaper
A wheat-growing county in Kansas
A Haitian neighborhood in Miami, Florida
The part of Italy called “Lombardy”
A French-language region in Canada
01-10 Which of the following is NOT a formal culture region?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
The distribution network for USA Today
A wheat-growing county in Kansas
A Haitian neighborhood in Miami, Florida
The part of Italy called “Lombardy”
A French-language region in Canada
newspaper
Explanation: Formal regions are characterized a degree of
homogeneity while functional regions are marked by a nodeand-periphery pattern.
The Cultural Landscape:
An Introduction to Human
Geography
10th Edition
Classroom Response System Questions
Chapter 2
02-01 The country with the largest population in Africa is
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Algeria.
Egypt.
India.
Nigeria.
South Africa.
02-01 The country with the largest population in Africa is
A. Algeria.
B. Egypt.
C. India.
D. Nigeria.
E. South Africa.
Explanation: Nigeria is Africa’s population leader. India is not
located in Africa. South Africa is an economic leader.
02-01
02-02 The number of people per unit of arable land is the
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
arithmetic density.
physiological density.
agricultural density.
land-use density.
population density.
02-02 The number of people per unit of arable land is the
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
arithmetic density.
physiological density.
agricultural density.
land-use density.
population density.
Explanation: This is the definition of physiological density which
is different from arithmetic and agricultural densities.
02-03 The spread of the Avian flu through Egypt and Sudan is
most closely associated with which geographic feature?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
A major interstate highway
The Nile River
The ridgeline of a mountain range
The Trans-African railway
The Orinoco River
02-03 The spread of the Avian flu through Egypt and Sudan is
most closely associated with which geographic feature?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
A major interstate highway
The Nile River
The ridgeline of a mountain range
The Trans-African railway
The Orinoco River
Explanation: The Nile is the major north-south transport route in
Egypt and Sudan.
02-04 Which of the following is the least significant factor
affecting population growth rates?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Doubling times
Sex ratio
Total fertility rate
Crude death rate
Crude birth rate
02-04 Which of the following is the least significant factor
affecting population growth rates?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Doubling times
Sex ratio
Total fertility rate
Crude death rate
Crude birth rate
Explanation: Sex ratio refers to the percentage of men and
women born in a country. The other terms are closely related to
the rise and decline of population size.
02-05 Which of the following countries has the highest infant
mortality rates?
A.
B.
C.
D.
Venezuela
Greenland
Iceland
Mali
E. Saudi Arabia
02-05 Which of the following countries has the highest infant
mortality rates?
A. Venezuela
B. Greenland
C. Iceland
D. Mali
E. Saudi Arabia
Explanation: Like its neighbors in Saharan Africa, Mali has some
of the highest infant mortality rates in the world.
02-05
02-06 In which stage of demographic transition are birth rates
stable and death rates declining?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
This situation does not occur in any of the four stages.
02-06 In which stage of demographic transition are birth rates
stable and death rates declining?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
This situation does not occur in any of the four stages.
Figure 2-14 clearly shows stable birth rates and declining death
rates in stage 2
02-06
02-07 Population growth rates are lowest in _________ of the
demographic transition.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
stage 1
stage 2
stage 3
stage 4
stage 5
02-07 Population growth rates are lowest in _________ of the
demographic transition.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
stage 1
stage 2
stage 3
stage 4
stage 5
Explanation: High birth and death rates negate one another in
stage 1 and result in very low population growth.
02-08 Dependency ratios are highest in
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Africa.
South America.
Europe.
North America.
East Asia.
02-08 Dependency ratios are highest in
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Africa.
South America.
Europe.
North America.
East Asia.
Explanation: With the highest birthrates, Africa—and other
places in stage 2 of the Demographic Transition—has a large
proportion of dependents among its population.
02-08
02-09 Which stage of the Epidemiologic Transition is
characterized by a decreasing number of deaths from infectious
diseases and a rising toll from degenerative diseases?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
Stage 5
02-09 Which stage of the Epidemiologic Transition is
characterized by a decreasing number of deaths from infectious
diseases and a rising toll from degenerative diseases?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Stage 1
Stage 2
Stage 3
Stage 4
Stage 5
Explanation: Infectious diseases characterize stages 1 and 2.
Stage 5 marks the resurgence of infectious and parasitic
diseases.
02-10 The most lethal global epidemic disease in recent years
has been
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
tuberculosis.
malaria.
AIDS.
SARS.
Ebola.
02-10 The most lethal global epidemic disease in recent years
has been
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
tuberculosis.
malaria.
AIDS.
SARS.
Ebola.
Explanation: While tuberculosis and malaria are deadly killers,
none of the choices exceeds the global destruction caused by
AIDS.
02-10
The Cultural Landscape:
An Introduction to Human
Geography
10th Edition
Classroom Response System
Questions
Chapter 3
03-01 The largest number of internal refugees are found in
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Sub-Saharan Africa.
Eastern Europe.
Central America.
Iberia
Southeast Asia
03-01 The largest number of internal refugees are found in
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Sub-Saharan Africa.
Eastern Europe.
Central America.
Iberia
Southeast Asia
Figure 3-2 graphically portrays the magnitude of internal
displacement in Africa.
03-02
03-02 Which region has the greatest number of international
refugees?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Southeast Asia
West Africa
Siberia
South America
Middle East and Southwest Asia
03-02 Which region has the greatest number of international
refugees?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Southeast Asia
West Africa
Siberia
South America
Middle East and Southwest Asia
Figure 3-1 graphically portrays the magnitude of international
displacement in Palestine and Afghanistan.
03-02
03-03 Moving from San Francisco to Iowa would be considered
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
international migration.
intraregional migration.
interregional migration.
forced migration.
net migration.
03-03 Moving from San Francisco to Iowa would be considered
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
international migration.
intraregional migration.
interregional migration.
forced migration.
net migration.
Explanation: Moving from one region to another—the American
Midwest to the West Coast—is an interregional migration.
03-04 Globally, the largest source of international
migrants is
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
North America.
South America.
Africa.
Asia.
Europe.
03-04 Globally, the largest source of international
migrants is
A. North America.
B. South America.
C. Africa.
D. Asia.
E. Europe.
Explanation: Asia sends the largest number of migrants globally.
The flow of migrants is predominantly from less-developed
countries to Europe and North America.
03-04
03-05 Globally, the most likely destination of international
migrants is
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Australia.
China.
Germany.
Japan.
the United States.
03-05 Globally, the most likely destination of international
migrants is
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Australia.
China.
Germany.
Japan.
the United States.
Explanation: The United States attracts the majority of
immigrants. Other destinations include: Australia, Canada,
France and Germany.
03-05
03-06 In which decade was immigration into the United States
the lowest?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1880s
1930s
1950s
1970s
1990s
03-06 In which decade was immigration into the United States
the lowest?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1880s
1930s
1950s
1970s
1990s
Explanation: Immigration to the United States declined due to
restrictive legislation and the global economic depression.
03-06
03-07 Which country has been the largest source of immigrants
from Asia to the United States over the last two decades?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
China
India
Japan
Philippines
South Korea
03-07 Which country has been the largest source of immigrants
from Asia to the United States over the last two decades?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
China
India
Japan
Philippines
South Korea
Explanation: India has sent 65,000 immigrants to the United
States.
03-08 The greatest number of undocumented immigrants in the
United States come from
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Canada.
Caribbean.
China.
Germany.
Mexico.
03-08 The greatest number of undocumented immigrants in the
United States come from
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Canada.
Caribbean.
China.
Germany.
Mexico.
Explanation: It is estimated that 9.3 million undocumented
individuals entered the U.S. in 2007. 5.3 million were from
Mexico.
03-09 Cuban emigrants to the United States
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
are considered political refugees.
typically support Fidel Castro.
settle primarily in and around New York City.
are usually turned back at sea.
usually try to return to Cuba.
03-09 Cuban emigrants to the United States
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
are considered political refugees.
typically support Fidel Castro.
settle primarily in and around New York City.
are usually turned back at sea.
usually try to return to Cuba.
Explanation: Unlike migrants fleeing repression and severe
economic hardship in Haiti, Cubans are considered political
refugees.
03-10 Which decade witnessed the least movement of the
United States’ center of population?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1810s
1830s
1850s
1920s
1950s
03-10 Which decade witnessed the least movement of the
United States’ center of population?
A. 1810s
B. 1830s
C. 1850s
D. 1920s
E. 1950s
Explanation: Restrictive immigration legislation and the onset of
the Great Depression resulted in fewer people moving west than
in previous decades.
03-10
The Cultural Landscape:
An Introduction to Human
Geography
10th Edition
Classroom Response System
Questions
Chapter 4
04-01 “Everyday, without fail, I make time call my father on the
phone.” This statement from an individual indicates a(n)
A.
B.
C.
D.
cultural characteristic.
habit.
custom.
trait.
E. annoyance.
04-01 “Everyday, without fail, I make time call my father on the
phone.” This statement from an individual indicates a(n)
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
cultural characteristic.
habit.
custom.
trait.
annoyance.
Explanation: Recurring individual behaviors are classified as
habits while recurring group actions are called “customs.”
04-02 Popular culture is practiced
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
only where folk culture is absent.
by large heterogeneous groups.
by individuals only.
only in the more developed countries.
at specific places.
04-02 Popular culture is practiced
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
only where folk culture is absent.
by large heterogeneous groups.
by individuals only.
only in the more developed countries.
at specific places.
Explanation: Popular culture is closely associated with urban,
industrial society.
04-03 Folk culture is most likely to spread by
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
hierarchical diffusion.
contagious diffusion.
stimulus diffusion.
copycat diffusion.
relocation diffusion.
04-03 Folk culture is most likely to spread by
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
hierarchical diffusion.
contagious diffusion.
stimulus diffusion.
copycat diffusion.
relocation diffusion.
Explanation: While popular culture spreads quickly via
hierarchical diffusion, folk culture spreads slowly via migration.
04-04 Complete the following analogy: Habit is to custom as
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
diffusion is to region.
individual is to group.
folk is to popular.
place is to space.
form is to function.
04-04 Complete the following analogy: Habit is to custom as
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
diffusion is to region.
individual is to group.
folk is to popular.
place is to space.
form is to function.
Explanation: Individuals possess habits; groups are characterized
by customs.
04-05 Complete the following analogy: Split-level is to Neocolonial as
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
“great room” is to living room.
mansard is to family room.
folk is to popular.
half-timbered is to low-pitch roof.
modern is to neo-eclectic.
04-05 Complete the following analogy: Split-level is to Neocolonial as
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
“great room” is to living room.
mansard is to family room.
folk is to popular.
half-timbered is to low-pitch roof.
modern is to neo-eclectic.
Explanation: The split level is an example of a modern style and
the Neo-colonial is neo-eclectic.
04-06 Globally, the lack of hog production in North Africa and
Southwest Asia corresponds most closely to the spatial
distribution of
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
animism.
capitalism.
Christianity.
Hinduism.
Islam.
04-06 Globally, the lack of hog production in North Africa and
Southwest Asia corresponds most closely to the spatial
distribution of
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
animism.
capitalism.
Christianity.
Hinduism.
Islam.
Explanation: The prohibition on the consumption of pork makes
hog production very small among Muslims.
04-06
04-07 Wine production typically requires all of the following,
except
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
well-drained soils.
supportive customs.
proximity to water.
cool summers.
cool winters.
04-07 Wine production typically requires all of the following,
except
A. well-drained soils.
B. supportive customs.
C. proximity to water.
D. cool summers.
E. cool winters.
Explanation: The production and consumption of wine relies on
both a supportive culture and environment.
04-07
04-08 Complete the following analogy: Bourbon whiskey is to
the Upper South as
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
tea is to the Northwest.
rum is to Midwest.
tequila is to the Southwest.
vodka is to the Southeast.
gin is to the Northeast.
04-08 Complete the following analogy: Bourbon whiskey is to
the Upper South as
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
tea is to the Northwest.
rum is to Midwest.
tequila is to the Southwest.
vodka is to the Southeast.
gin is to the Northeast.
Explanation: While high income and advertising account for the
consumption of alcohol in MDCs, some regional differences exist.
04-08
04-09 In Europe, Internet usage was first concentrated in
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Albania.
Belgium.
Finland.
France.
Germany.
04-09 In Europe, Internet usage was first concentrated in
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Albania.
Belgium.
Finland.
France.
Germany.
Explanation: In 1995, the highest concentration of Internet users
in Europe were found in Finland.
04-09
04-10 The presence of similar restaurants, gas stations, and
stores throughout the United States
A. illustrate how popular culture can create a uniform
landscape.
B. show how folk culture can diffuse.
C. are a prime example of regionalization.
D. increase cultural awareness.
E. None of the above is correct.
04-10 The presence of similar restaurants, gas stations, and
stores throughout the United States
A. illustrate how popular culture can create a uniform
landscape.
B. show how folk culture can diffuse.
C. are a prime example of regionalization.
D. increase cultural awareness.
E. None of the above is correct.
Explanation: While some regional differences persist, the spread
of popular culture in MDCs is far reaching.