Life Cycles of Stars
advertisement

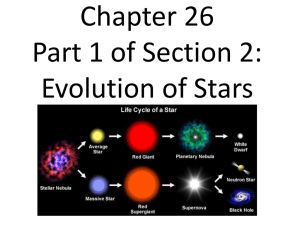
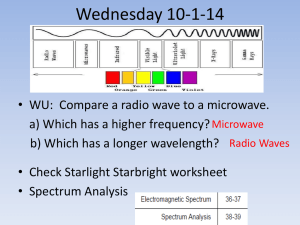
A Stars Lifespan depends on its Mass Massive Stars live shorter lives. Low mass stars live longest. 1.Gravity contracts the Hydrogen gas 2. Gas Spins 3. Gas Heats 4. Protostar Stage 5. Fusion begins in the clouds core 6. Cloud glows brightly 7. Main Sequence Star Gravity pulls the densest pockets of hydrogen gas inward The Gas spins faster, and heats up. Hydrogen collects in the center of the swirling disk . The cloud begins to shine brightly, a young star is born in the cloud Sun Like Star – Long Lifetime The protostar is now a stable main sequence star . Gravity pulls in – Pressure pushes out Star is in balance Neither shrinks or expands Yellow shining mass The Sun is a Main Sequence Star It fuses hydrogen gas into helium Lifetime: 10 billion years. Near the end hydrogen fuel is depleted and the star begins to die. Our Sun is considered to be an ordinary star with a spectral classification of G2 V, a yellow dwarf main sequence star. Sun Like Stars how do they do it? • In the star’s core protons collide and stick together with a strong nuclear bond. • A chain reaction occurs, 4 protons weld together to make 2 protons & 2 neutrons. • Hydrogen converts to Helium through nuclear fusion. • Every second the Sun through thermonuclear reaction converts 600 million tons of hydrogen into Helium within its core and emits a tiny fraction of energy E=MC2, • the radiation escapes into space bathing the star’s surroundings in heat and light. • This is what warms our solar system As the Sun ages, Eventually, the Supply of hydrogen in the core ends, and a shell of hydrogen surrounds the helium core. The Sun’s core becomes unstable The helium core contracts and gets hotter. Red Giant star seen from a planet The Sun’s hydrogen shell expands The Sun is now a Red Giant Hydrogen in the shell around the core continues to burn Its core temp continues to increase Red Giant Phase • Now the Helium core contracts • When the Hydrogen shell ignites: • The shell continues to push outward • Sun becomes enormous • It goes from • 1 million to 100 million miles in size • Helium ignites, it starts to fuse into Carbon and Oxygen. The core collapses. • The outer layers are expelled. • It becomes a brilliant cool variable star for thousands of years like Betelgeuse in Orion. Actual photograph of Betelgeuse Eventually all of the hydrogen gas in the outer shell of the Red Giant is blown away by stellar winds to form a ring around the core. This ring is called a planetary nebula. The core is now a hot white dwarf star. A white dwarf star is left in the center of the dying red giant star, surrounded by the red giant’s expanded atmosphere • A White dwarf star is a dense stable star about the size of the Earth weighing three tons per cubic centimeter. • It radiates its left-over heat for billions of years. • When its heat is all dispersed, it will be a cold, dark black dwarf essentially a dead star When massive stars ( At least 5 times larger than the Sun) reach the red giant phase, their core temperature increases because carbon is formed from the fusion of helium. Gravity pulls carbon atoms together. The core temp goes higher forming oxygen, then nitrogen, and eventually iron. • The core becomes iron, fusion stops. No energy. • Iron is the most stable element and requires the most energy of any element to fuse. • So, the core heats to 100 billion degrees, the sudden lose of energy causes the core to collapse • • The iron atoms in the core are crushed. • The core becomes rigid. • In falling layers of the star strike the core, • then recoil in a Shockwave. • The shockwave hits the surface and the star explodes. If the core of a massive star collapses when it is 1.5 to 3 times as massive as our Sun’s core. It ends up as a neutron star. The protons and electrons are squeezed together by gravity, leaving a residue of neutrons, creating a neutron star. Neutron stars (right) are about ten miles in diameter. Spin very rapidly (one revolution takes mere seconds!). Neutron stars are fascinating because they are the densest objects known except for black holes. A teaspoon of neutron star material weighs 100 million tons. Massive Stars (8 times or more larger than the Sun. Core remains massive after the supernova. Fusion is stopped. Nothing supports the core. The core is swallowed by its gravity. It becomes a black hole Black holes are detected by Xrays given off matter that falls into the black hole. If Black Holes are Black, How do We See Them ? Optical • Material swirls around central black hole. • Gas near black hole heats up to UV and X-ray temperatures. • This heats surrounding gas, which glows in the optical. Ultraviolet Seeing Matter Disappear • Hubble observed pulses of UV light emitted by material as it fell into a black hole. • Pulses arise from material orbiting around intense gravity of the black hole. • Light pulses, lasting 0.2 s, are red-shifted from X-ray to UV, as they fall into gravity of the black hole. Radio Jets from Black Holes Many black holes emit jets. Material in jet moving at 0.9c. Jet likely composed of electrons and positrons. Magnetic fields surrounding black hole expel material and form the jet. Interaction of jet material with magnetic field gives rise to Radio emission. M87 - An Elliptical Galaxy With a curious feature Radio shows the origin of the Jet X-ray: Jets Cen A is known to be a peculiar galaxy with strong radio emission. Optical image of Cen A But it is also a strong X-ray emitter, and has an X-ray jet. Chandra image of Cen A Black Holes