Laser beam welding (LBW)
advertisement

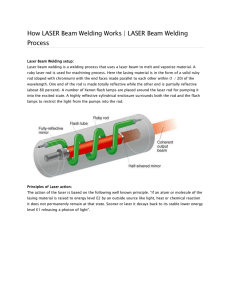
GHARIA PRADIP SINH.G 096470319100 GUIDED: M.M.K Laser beam welding (LBW) - the heat from laser can be used to heat the surface of material or penetrate the entire depth of the joint (good for thin gauge metals). The major problems with the current lasers lie in the cost and bulk of the power source. High Energy Density Processes shielding gas nozzle (optional) Laser beam Plasma plume Plasma keyhole Keyhole welding workpiece motion Molten material WORKING PRINCIPLE In laser beam ruby laser are most likely in case of ruby . Its chromium atom is formed from its ground level to higher level by a using an external force which excites the atoms when this energy is absorbed the electrons increase their spin & expand their orbit . this exited state is short lived and atoms drops back to at immediate level in which atoms losses is heat energy . Laser Beam Welding Uses a laser beam to melt the metals; can be used for deep, narrow welds Laser Weld Advantages •Deep narrow welds •Low heat input •Minimal distortion •High joint completion rates •Joint design flexibility •Minimal use of consumable •Ease of automation LASER WELDIND DISADVANTAGES • Welding speed is very slow . • It is limited up to the depth of 1.5 mm. • Mat like mg tend to vaporize . APPLICATIONS • To join hard & high melting point metal alloy. • For joining the metals like copper, nickel, al, etc • It is also used for micro welding purposes. • To joint & prepare joint ele part integrate circuit. • For welding like gauge mat in space & aircraft ind. THANK YOU