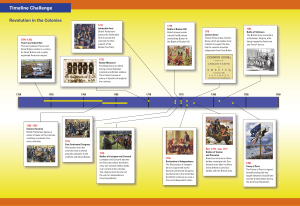
The Treaty of Tordesillas contained a provision to
advertisement

APUSH Bell Work: As preparation for our test. Here is a series of sample multiple choice questions. Pick the ones that best answer the prompt. We will then discuss a possible thesis for the following Free Response Question. The Treaty of Tordesillas contained a provision to a) b) c) d) e) Give Spain all right to settle in the Americas. End Aztec domination in Mexico End rebellion of the Pueblos in New Mexico Divide the Americas between Spain and Portugal to colonize. Allow England to colonize North America and Spain to colonize Central and South America. D: The Treaty of Tordesillas was drafted by the Pope in 1494 to prevent conflict and give these two Catholic nations rights to settlement in Africa and America. A principle of the economic theory of mercantilism was that a) b) c) d) e) Centralized control of the economy was essential to increasing a nation’s wealth. Free trade and the market system would increase a country’s productivity. The world’s wealth increased as the population grew. Importing goods from other countries would conserve a nation’s resources and make it wealthier. Government should not be involved in a nation’s economy. A: Mercantilism held that wealth was fixed and that a nation must export more than it imported to funnel wealth in the country. Central control was necessary to make sure this happened. The Calvert family adopted the Toleration Act in 1649 because a) Catholics found Protestants friendly and helpful. b) Warfare between Indians and settlers was destabilizing the colony. c) Indentured servants refused to join the Catholic Church. d) The Calverts decided to abandon the original goal of providing a refuge for Catholics. e) Protestants quickly outnumbered Catholics in the colony. E: With a Protestant majority, the Toleration Act would ensure Maryland Catholics the freedom to worship. Puritan theologian Jonathan Edwards strayed from Puritan orthodoxy in his belief that a) b) c) d) e) Few would be saved and individuals could do nothing to affect their salvation. Salvation was available to all and easy to gain. God and ministers shared power to save sinners. God’s power was absolute, but one could work toward salvation although it was difficult to gain. Bishops could determine who in the congregation would be saved. D: Edwards reacted to many Awakeners by adopting a stricter Calvinist theology than other Awakeners that emphasized the sovereignty of God but also the ability of one to work toward his or her salvation. A major reason for the French merchant construction of fortresses in Ohio valley in the mid-eighteenth century was a) b) c) d) e) Its desire to protect French farmers settles in the area from English. Ongoing wars with the Iroquois and other Indian nations because of French encroachment on Indian lands. Tension between the French merchant aristocracy on the coast and French settlers inland. To counter rising English influence when the Iroquois granted them trading concessions. To protect overzealous Jesuit priests undertaking a new campaign to convert the natives to Catholicism. D: There was not a significant population of Europeans in New France and their relations with Indians were generally good. The France forts were to establish a French presence in an area where English settlers were moving. As a result of the French and Indian War a) b) c) d) e) The colonies were more dependent on Britain because they relied on English soldiers for protection. The French agreed to stay within the boundaries of Louisiana and Canada and not incite Indians to attack western British settlements. The French and the Indians agreed to a peace that lasted until the Revolutionary War. The British regarded Americans as loyal subjects, good soldiers in the cause, and strong financial supporters of the war. The colonists resented British interference in local affairs, and America militia noted marked differences between themselves and their English brethren. E: As this war was the first time that many colonists had any personal contact with the English, a significant result was that the Americans saw themselves as quite different from the English. After the battles at Lexington and Concord, the Continental Congress sent the Olive Branch Petition to the king to a) b) c) d) e) Acknowledge the colonies’ independence and lay the groundwork for the Declaration of Independence to follow. Seek a reconciliation with the Crown by stating colonial grievances. Declare complete submission to the king and the intent to rebel no longer. Declare the colonial intent to resist English rule by force until the king withdrew his force from America. Inform him of the colonial association’s boycott of British goods until the British troops left Boston. B: It took the colonies more than a year after Lexington and Concord to declare Independence. Most colonists still acknowledged the king but wanted him to accept colonial republican ideals concerning representation and taxation. The sentiment expressed in this phrase from Declaration of Independence, “[T]hat whenever any form of government becomes destructive of these ends [securing life, liberty and property], it is the right of the people to alter or abolish it,” best expresses the political philosophy of a) b) c) d) e) Baron de Montesquieu. Thomas Hobbs. John Locke. Voltaire William Pitt. C: In his treaties concerning England’s Glorious Revolution, John Locke stated that a people have the right to overthrow a government that does not protect natural rights of life, liberty, and property. The Battle of Yorktown most clearly demonstrated which of the following? a) The overwhelming superiority of American troops toward the end of the Revolutionary War. b) The inability of Britain to support its armies across the Atlantic Ocean. c) The waning support of the British public to continue support of a war to retain its colonies in British North America. d) The misplaced emphasis British generals put on support from Loyalists in its southern strategy. e) The significance of French aid to the Patriot cause. E: The temporary superiority of the French fleet in the Chesapeake cut off any means retreat for Cornwallis. The Treaty of Paris at the end of the Revolutionary War contained provisions for a) b) c) d) e) An end to the fighting and provisions for America and France to divide Britain’s North American possessions. Recognition of the United States’ independence and Britain’s withdrawal from the North American continent. Treaties of trade and alliance between France and the United States. The United States western boundary to be the Mississippi River and British recognition of its independence. An end to fighting and a return to the status quo antebellum. D: Other provisions included consideration of both Loyalist claims and paying debts incurred by Americans before the war. Britain would continue its presence in Canada.