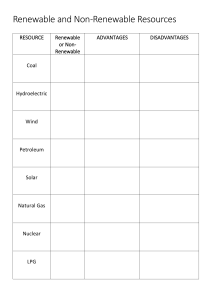
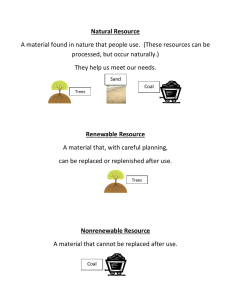
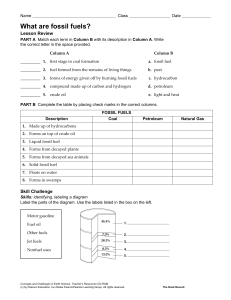
4 COAL & PETROLEUM CHAPTER CONTENTS Fuels Classification of Fuels Coal Destructive Distillation of Coal Petroleum Refining FUELS (a) Coal (b) Coke (c) Wood (d) Charcoal (e) Animal-dung cakes (f) Bagasse, Agricultural wastes Liquid fuels : Volatile liquids which produce combustible vapour are called liquid fuels. Kerosene is the most commonly used liquid fuel. Examples : Some common liquid fuels are : (a) Petrol (b) Diesel (c) Kerosene (d) Alcohol Petrol, diesel and kerosene are mixtures of hydrocarbons. Gaseous fuels : Combustible gases or mixtures of combustible gases are called gaseous fuels. Examples : Some commonly used gaseous fuels are : (a) Natural gas (b) Liquefield petroleum gas (LPG) (c) Biogas (or Gobar gas) (d) Coal gas (e) Water gas (f) Producer gas (g) Hydrogen gas (h) Compressed Natural (CNG) Petroleum gas is obtained as a by-product during the fractional distillation of petroleum. A combustible substance which on burning produces a large amount of heat and light is called a fuel. Coal, LPG , Petrol , Kerosene , wood etc. CLASSIFICATION OF FUELS Fuels are classified on the basis of physical sttes in which they occur. So fuels are classified as solid, liquid and gaseous fuels. Classification of Fuels Solid fuels Liquid fuels Gaseous fuels Solid fuels : Combustible substances which are solid at room temperature are called solid fuels. Solid fuels contain mainly carbon both as free and combined carbon. In rural areas, Firewood, Agricultural wastes, Animal-dung cakes are the major source of energy. Examples : Some solid fuels are : Characteristics of an ideal fuel An ideal fuel should have the following characteristics : It should be fairly cheap and easily available. It should burn at moderate rate. It should not produce any poisonous and irritating fumes during burning. It should leave no residue (ash) after burning. It should produce large amount of heat per unit mass i.e., it should have high calorific value. It should be safe and convenient from the storage and tranportation point of views. Its ignition temperature should be above room temperature. So that it is safe to use such a fuel. Uses of Fuels Cooking and Heating : The most common use of fuels is for cooking and heating. The commonly used domestic fuels are wood, dry cattle dung, coal, charcoal, kerosene (in rural areas) and coal, kerosene, LPG (in urban areas). For Transportation : Fuels such as petrol, diesel and CNG are used for running cars, scooters, buses, trucks and trains. These automobiles are used for transportation from one place to another. The fuel used in aeroplanes is called aviation fuel. For Generating Electricity : Fuels such as coal and natural gas are used for generating electricity on a commercial scale, in Thermal power stations. Petrol, diesel and kerosene are also used for generating electricity in smaller generators commonly used at homes and shops, etc. In Industry : Fuels such as coal, natural gas, diesel and furnace oil are used in the industry for generating steam in boilers. Steam is required in industry for heating purposes and also for generating electricity for their own use in factory. Industry in the rural areas also uses biomass such as bagasse—the cellulose material left after extracting juice from the sugarcane for running boilers. For Launching Space Vehicles : Space vehicles are launched with the help of rockets. Rockets use special fuels called propellants. A propellant is a combination of a fuel and an oxidizer. COAL Introduction : Coal is a mineral of dark brown or black colour formed from the remains of plants buried in the earth’s crust millions of years ago. Composition : Coal is a very impure form of carbon. It mainly consists of atoms of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. A small amount of sulphur is also present in it. Mining Coal is mined using two methods–opencast mining and underground mining. Opencast mining is used when the deposits of coal are near the surface of the earth. Underground mining is used when coal deposits lie deep inside the earth’s crust. Formation Coal is formed from vegatable matter burried under the earth. About 300 million years ago, the earth was covered with dense forests, marshlands and rivers. The forests grew and died and fell into the waters of the surrounding swamps. These plants were covered with tons of earth over a period of millions of years. Due to the huge pressure and temperature inside the earth, this vegetable matter got converted into coal. For this reason, coal is known as fossil fuel. It is also a non-renewable source of energy. Types of Coal Coal comes in four main varieties. The percentage of carbon in air-dried samples are as follows. Peat : This is a material in the first stage of coal formation. It contains only 27% carbon and is considered to be the lowest grade of coal. Lignite : This variety of coal contains 2830% carbon. It has poor heating power. It is brown in colour but lustrous when dry. Bituminous : It is a soft coal containing 78-86% carbon. It gives a large proportion of gas when heated and burns with a yellow, luminous flame. Anthracite : It is a hard coal and contains 94-98% carbon. It is lustrous. It burns without smoke and gives much heat and little ash. Bituminous coal is by far the most useful as a fuel, but anthracite is considered to be the most superior in quality. Uses : Coal is used as a fuel to convert water into steam to run thermal power plants for the generation of electricity. It is also used as a fuel in homes and factories, and to run steam engines. Coal is used in the preparation of fuel gases, such as coal gas. Coal is used in the preparation of synthetic oil and synthetic natural gas. Coal is also used to obtain natural gas. For this, finely ground coal is heated with hydrogen under pressure in the presence of a suitable catalyst. The complex molecules present in coal combine with The destructive distillation of coal gives coke, coal tar, coal gas, etc. Coal is the source from which a number of organic compounds such as benzene, toluene, phenol, aniline, naphthalene and anthracene are obtained. DESTRUCTIVE DISTILLATION OF COAL The process of destructive distillation is carried out be heating coal at a high temperature (1270 K) in the absence of air. This process is also called as pyrolysis and yields lot of valuable products. Products of destructive distillation of coal (A) Coke (B) Coal Tar (C) Amoniacal liquor (D) Coal gas Coke : Solid residue left after destructive distillation (high percentage carbon-nearly 98%) Uses : (i) As domestic fuel. (ii) Acts as a good reducing agent in the manufacture of steel (iii)Useful fuel gases like water gas and producer gases can be made using coke. Water gas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. It is obtained by passing steam over red-hot coke. C + H2O CO + H2 Coal Tar : Coal tar is a midture of different carbon compounds. It is a thick, black liquid. The fractional distillation of coal tar gives many chemical substances which are used in the preparation of dyes, explosives, paints, synthetic fibres, drugs and pesticides. Some of these chemical substances are benzene, toluene, phenol and aniline. Ammoniacal Liquor : The ammonia produced as a result of destrutive distillation of coal is absorbed in water. The aqueous solution of ammonia, i.e., ammonium hydroxide solution, is called ammoniacal liquor. It is used in the preparation of fertilizers such as ammonium sulphate and ammonium superphosphate. NH3 + H2O NH4OH 2 NH4OH + H2SO4 (NH4)2SO4 + H2O Coal Gas : Coal gas is a mixture of hydrogen, methane and carbon monoxide. The gases present in coal gas are combustible, and hence it is an excellent fuel. It has a high calorific value. It was used for lighting houses, factories and streets in Mumbai until 1950. It was also used for cooking until recently. PETROLEUM Petroleum is a naturally occurring oil that consists chiefly of hydrocarbons with some other elements, such as sulphur, oxygen and nitrogen. It is now known that petroleum contains hydrocarbons of the paraffin series, with upto 100 or more carbon atom s in the chain. The unrefined form of petroleum is called crude oil or rock oil (petra = rock; oleum = oil). Origin of Petroleum : Petroleum was formed from organisms living in the sea. The remains of these organisms were deposited in shallow depressions in the Producer gas is a mixture of carbon monoxide and nitrogen. It is obtained when air is passed over red-hot coke. 2C + O2 + 4N2 2CO + 4N2 sea bed long, long ago. These were covered by (iv)Used in metallurgical operations as a reducer for oxide ores. years, the organic matter present in the dead layers of sand and clay which compressed these remains. Over a period of millions of organisms underwent a series of processes before being into There are some government agencies engaged petroleum. The petroleum migrated from the in exploring and producing crude oil-Oil and source large Natural Gas Commission (ONGC) and Oil underground reservoirs beneath impermeable India Limited (Oil). There are many refineries rocks. It often floats over a layer of water and in India. The larger refineries are at Jamnagar, is held in this position under pressure beneath Mathura, Bharuch, Digboi, Haldia and Barauni. rock finally to be transformed entrapped in a layer of natural gas. REFINING Oil Wells in India : In India, oil was first struck at Makum in The process of separating the various Assam in 1867. The oil fields of Assam were components of petroleum from one another is the only source of petroleum in our country known as the refining of petroleum. This is until about 40 years ago. Some other places in done by a process called fractional distillation our country where oil wells have been dug are whih is based on the fact that the different components of petroleum have distinctly Ankleshwar and Kalol in Gujarat, different boiling points. Offshore areas west of Mumbai, and Offshore deltas of the Godavari and Kaveri rivers. Petroleum Gas Below 40ºC–170ºC (C1 – C4) Petrol (Gasoline) 40ºC–170ºC (C5 – C10) Kerosene oil 170ºC – 250ºC (C10 – C12) Diesel oil 250ºC – 350ºC (C13 – C15) Fuel oil 300ºC – 400ºC (C15 – C18) 400ºC Crude oil Lubricating oil > 400ºC (C17 – C20) Residual oil (Boilling point greater than 400ºC) Paraffim wax > 400ºC (C20 – C30) Asphalt > 400ºC (C30 – C50) Asphalt : Asphalt is a black and sticky substance. It is used for making the surface of roads. It does not burn readily. Paraffin Wax : It boils at above 673 K. It is obtained by the fractionation of residual Products of Petroleum Refining oil. It is used for making candles, vaseline, grease, polishes, etc. Lubricating Oil : It boils at well above 673 K. It is obtained by the fractionation of residual oil. It is used for lubricating machinery. Fuel Oil : The boiling range of fuel oil is 623 K to 673 K. It is used in industries to heat boilers and furnaces. It is a better fuel than coal because it burns completely leaving behind no ash, whereas coal burns producing a large amount of ash which has to be removed regularly. Diesel Oil : Its boiling range is 573 K to 623 K. It contains straight-chain alkanes with the number of carbon atoms varying from 20 to 25. It is used in cars, trucks, buses, and locomotives. Kerosene : Its boiling ranges is 443 K to 523 K. It contains straight-chain alkanes with 10-16 carbon atoms. It is used for domestic purposes, for lighting petromax, lanterns, lamps, stoves, etc. Petrol : Its boiling range is 313 K to 443 K. It is also called gasoline. it contains paraffins from pentane to dodecane. It is used as a fuel in two-wheelers, threewheelers and cars. Residual Oil : The residual oil obtained from the primary distillation of petroleum is known as reduced crude. Reduced crude is distilled in vacuum to yield bitumen as residue. Bitumen is largely used in making road surfaces, and also for coating cables to provide electrical insulation. Uses Petroleum gas is used as a fuel. It is also used in the form of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) for domestic purposes. Gasoline or petrol is used as a fuel in cars, scooters, etc. Kerosene is used as a household fuel. Diesel oil is used as a furnace fuel and fuel for diesel engines. Lubricating oil is used for lubrication of machinery, etc. Vaseline is used for softening skin. Paraffin wax is used for making candles Most industrial chemicals are produced from petroleum and natural gas. These chemicals are called petrochemicals. Petroleum is the major source of medicines, insecticides, rubbers, plastics, perfumes, explosives, motor fuels, etc. Petroleum Gas : It is a mixture of ethane, propane and butane. Its main constituent is butane which burns giving off a lot of heat. Butane is easily liquefied under high pressure. In the liquid form it is supplied in cylinders and is commonly known as Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG). Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) : Liquefied petroleum gas is petroleum gas in liquid state. It is a mixture of ethane, propane and butane, but the major component is butane. LPG is a colourless, odourless (when pure) gas. The commercially supplied LPG contains a strong smelling compound called ethyl mercaptane (C2H5SH) to permit its detection in the case of any leakage. EXERCISE # 1 Q.9 What is meant by refining of petroleum ? Q.10 Where is petroleum found in India ? Q.11 Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads. Name the fraction of petroleum used for making ointments and candles. Q.12 Expand CNG. Q.3 How is coke obtained Q.13 Q.4 Name the purest form of carbon. Name two fuels which are used for running automobiles. Q.5 How is coal tar formed ? Q.14 Why is food regarded as a fuel for our body? Q.6 Give the main use of coal gas. Q.15 Name a liquid fuel which is used in homes? Q.7 How is petroleum formed ? Q.16 Write the full forms of (a) CNG (b) LPG Q.8 Why is petroleum called a fossil fuel ? VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 Q.2 Name any two products of petroleum refining. EXERCISE # 2 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Q.8 Q.1 Why are coal and petroleum known as fossil fuels ? Q.9 Q.2 Give two characteristics of coal. Q.3 Give two use of coke. Q.4 Why should the fossil fuels be used with care ? Q.5 (a) Name two places in India where oil wells are found ? (b) From which natural substance are liquid fuels formed ? (b) When and where in India where oil wells first found ? (c) Which gas is the main constituent of LPG ? (a) Name the products obtained when coal is heated in the absence of air. (d) How was petroleum formed in nature ? (b) Write any two uses of its products. (e) Why do green leaves not catch fire easily? Q.6 Q.7 How is 'petrol' related to 'petroleum' ? Name four most important products obtained from petroleium. Name three products of distillation of petroleum of petroleum and give their uses. Give reasons – (i) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood. (ii) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment. LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS Q.10 Q.11 (a) What is CNG ? Give its one use. How is coal formed ? ANSWER KEY EXERCISE # 1 Sol.1 Kerosene and Petrol Sol.2 Bintumen Sol.3 Coke is obtained by heating coal in the absence of air. Sol.4 Coke. Sol.5 When destructive distillation of coal is done, the vapours which condense in the water form coal tar. Sol.6 Coal gas is mainly used as a fuel in the coal processing plants. Sol.7 Petroleum is formed by the decomposition of dead aquatic plants and animals. Sol.8 Petroleum is called a fossil fuel as it is obtained from the bodies of dead organisms. Sol.9 The separation of different fractions of petroleum on the basis of their different boiling points is known as refining of petroleum. Sol.10 In india, petroleum is found in Assam, Gujrat, Bombay High and in the river basins of Godavari and Caurverui. Sol.11 Paraffin wax. Sol.12 CNG is Compressed Natural Gas. Sol.13 Petrol and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) Sol.14 Food reacts with oxygen in our body and is broken down into simpler food with the production of heat. Hence it is regarded as a fuel for our body. Sol.15 Kerosene Sol.16 (a) CNG – Compressed Natural Gas (b) LPG – Liquefied Petroleum Gas EXERCISE # 2 Sol.1 Coal and petroleum are formed from the dead remains of living organisms that is why they are called fossils fuels. Sol.2 Coal is hard and is of black in colour. Sol.3 Coke is used in the extraction of metals and in the manufacture of steel. Sol.4 If we use fossil fuels carefully, it will result in better environment, less risk of global warming and thdy will be available for longer period. (i) 1. LPG (55000 kJ/kg) has higher calorific value than wood (17000-22000 kJ/kg). 2. LPG does not gives smoke and any harmful gases but wood gives smoke and harmful gases like CO on burning. So LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood. (ii) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment because water may conduct electricity and harm those trying to extinguish the fire. Sol.5 (a) Oil wells are found in Assam and Bombay high. Sol.10 (a) CNG – Compressed Natrual Gas. It is used as a fuel. (b) The first oil wills were found at Makum in Assam in 1867. (b) All liquid fuels are formed from petroleum. (a) Coke is formed when coal is heated in absence of air. (c) Butane is the main constituent of LPG. Sol.6 (b) Coke is used : – as a fuel. – as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals. Sol. 7 Petrol is one of the fractions obtained during fractional distillation of petroleium. Petrol, diesel, kerosene and lubricating oil are four most important products obtained from petroleum. Sol.8 A (i) Petrol (ii) Liquefied Petroleum Gas (iii) Coal B Scooter Cooking Thermal Power Station Sol.9 (d) Petroleum is formed by the sedimentation of dead remains of microscopic marine plants and animals, which were buried under the surface of the earth, millions of years ago. (e) Green leaves do not catch fire easily because they contain moisture. Sol.11 Coal is formed by the slow decay of dead trees buried under the earth. As the trees died, they were covered by mud and sand. This process continued for millions of years. Sometimes earthquakes and volcanoes buried entire forests deep inside the eath. The high temperature and pressure inside the earth slowly converted the buried vegetation into coal.