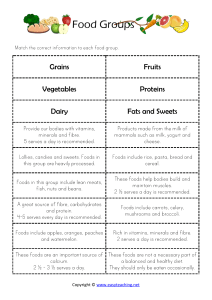
Basic Nutrition (Chapters 1 & 2) Six Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates – Main source of energy (found in grains, fruits, vegetables). Proteins – Build and repair tissues (found in meat, dairy, legumes). Fats – Provide long-term energy and cell functions (found in oils, nuts, fatty fish). Vitamins – Regulate body processes, support immunity (fat-soluble: A, D, E, K; watersoluble: B, C). 5. Minerals – Support body structures and chemical reactions (e.g., calcium, iron, potassium). 6. Water – Essential for hydration, transport of nutrients, temperature regulation. 1. 2. 3. 4. Caloric Content of Energy Nutrients Carbohydrates = 4 kcal/g Proteins = 4 kcal/g Fats = 9 kcal/g Alcohol = 7 kcal/g Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges (AMDRs) Carbohydrates: 45-65% of daily calories Fats: 20-35% of daily calories Proteins: 10-35% of daily calories Nutrient Density Nutrient-dense foods provide high levels of vitamins and minerals per calorie (e.g., vegetables, whole grains). Low-nutrient-density foods are high in calories but low in nutrients (e.g., candy, soda). Scientific Method in Nutrition Research 1. 2. 3. 4. Observation – Identifying a phenomenon. Hypothesis – Making an educated guess. Experimentation – Testing with controlled studies. Analysis & Conclusion – Evaluating results. Credible Sources of Nutrition Information Peer-reviewed scientific journals (e.g., Journal of Nutrition) Registered dietitians (RDs) Government agencies (e.g., USDA, FDA, CDC) Medical associations (e.g., American Heart Association) Factors Affecting Food Choices Personal preferences (taste, texture) Cultural influences (traditional diets) Economic factors (food cost and accessibility) Health considerations (dietary restrictions, allergies) Phytochemicals (Plant-based compounds promoting health) Act as antioxidants, anti-inflammatory agents, and immune boosters. Found in colorful fruits & vegetables (e.g., flavonoids in berries, lycopene in tomatoes). Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs) RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) – Daily intake for health. AI (Adequate Intake) – Used when RDA isn’t available. UL (Tolerable Upper Limit) – Highest safe nutrient intake. EAR (Estimated Average Requirement) – Average intake for 50% of people. Dietary Guidelines for Americans (2020-2025) Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods. Limit added sugars, saturated fats, sodium. Balance protein, grains, fruits, vegetables, dairy. MyPlate Recommendations ½ plate fruits & vegetables ¼ plate grains (half should be whole grains) ¼ plate protein sources Dairy for calcium needs Food Labels Ingredients listed in descending order by weight. % Daily Value (%DV) – Based on 2,000-calorie diet. Sugar listing – Includes added sugars separately. Digestion & Absorption (Chapter 3) Organs & Functions in the GI Tract Mouth – Chewing & salivary enzymes (amylase for starch digestion). Esophagus – Transports food via peristalsis. Stomach – Secretes hydrochloric acid (HCl) & pepsin to begin protein digestion. Small intestine – Main absorption site. Villi and microvilli increase surface area. Large intestine – Absorbs water, houses gut microbiota, forms waste. Accessory Organs & Their Roles Liver – Produces bile to aid in fat digestion. Pancreas – Produces digestive enzymes (amylase, protease, lipase) & bicarbonate. Gallbladder – Stores and releases bile. Digestive Secretions & Their Roles Enzymes – Breakdown food (e.g., amylase for starch, lipase for fats). Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) – Activates pepsin for protein digestion. Bile – Emulsifies fats for absorption. Methods of Nutrient Absorption Passive Diffusion – No energy needed (water, small lipids). Facilitated Diffusion – Uses transport proteins (fructose). Active Transport – Requires energy (amino acids, glucose). Gut Microbiota, Prebiotics & Probiotics Microbiota – Beneficial bacteria in the gut, aid in digestion & immunity. Prebiotics – Fiber that nourishes gut bacteria (found in onions, bananas). Probiotics – Live beneficial bacteria (found in yogurt, kefir). Common Gastrointestinal Disorders GERD – Acid reflux due to weakened esophageal sphincter. Celiac Disease – Autoimmune reaction to gluten. Gallstones – Bile accumulation forming stones. Constipation – Lack of fiber, water, or exercise. Lactose Intolerance – Lack of lactase enzyme, causing difficulty digesting dairy. Metabolism (Chapters 3-9) Steps of Energy Metabolism 1. Glycolysis – Breakdown of glucose for ATP. 2. Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle) – Further breakdown producing ATP. 3. Electron Transport Chain – Final ATP production step. Metabolism During Fasting vs. Feasting Feasting – Excess energy stored as fat. Fasting – Body breaks down stored glycogen, then fat, then protein. Fat Metabolism Fatty acids broken down for ATP via beta-oxidation. Protein Metabolism Only used for energy when carbs & fats are insufficient. Deamination – Removes nitrogen from amino acids; excreted as urea. How Body Uses Macronutrients for Energy Carbs = Primary fuel source. Fats = Long-term energy storage. Protein = Last resort for energy (used for tissue repair first). B-Vitamins in Metabolism Act as coenzymes for energy-producing reactions.