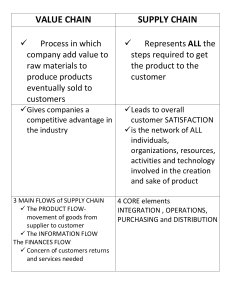
SOURCING AND SUPPLY MANAGEMENT Session 16 – August 08, 2023 Learning Objectives • Define supply management and understand its impact on a firm’s performance • Analyze how to make insourcing/outsourcing • Understand ways of manage ongoing supplier relationships • Describe how to access and select suppliers • Describe the steps in supply category management 2 • Purchasing Supply Management Purchasing is a set of function associated with acquiring the goods and services that an organization requires, including ordering, expediting, receiving, and fulfilling payment. • Procurement Procurement is the process of identifying, shortlisting, selecting and acquiring suitable goods or services from a third-party vendor through direct purchase, competitive bidding, or tendering process while ensuring timely delivery of right quality and quantity • Supply Management Supply Management is a strategic approach of planning and acquire current and future needs of an organization, aligned with the organization development orientation and competitive advantage 3 Supply Management the identification, acquisition, positioning and management of resources, capabilities and supplier relationships. 4 Supply Management Supply chain What firms do to create and deliver value? Supplier Manufacturer Distributor Retailer Customer Demand chain How demand moves from buyer to supplier Supply Management is a strategic approach of planning and acquire current and future needs of an organization, aligned with the organization development orientation and competitive advantage 5 Supply Management organization development orientation competitive advantage 6 Types of Purchases Production Materials • Raw Materials • Parts and Components Capital Equipment • Machinery • Vehicles MRO Supplies • Operating Supplies Services • Repair Services • Professional Services 7 Goals in Supply Management • Timely availability of resources • Supply chain risk • Reduce total cost 8 Goals in Supply Management Reduce total cost 9 Goals in Supply Management • Total cost in supply management When the costs occur Types of costs Before the transaction Time spent and costs of searching for, visiting, evaluating, and certifying suppliers. During the transaction Purchase price and costs of ordering, transporting, expediting, receiving, inspecting, and following up. After the transaction Cost of inventory, supply risk, production downtime, defects in FGs, warranties, safety recalls, replacements, repairs, lost sales, liability and damaged reputation. 10 Goals in Supply Management • Timely availability of resources • • Supply chain risk • Reduce total cost Enhance quality and standardization 11 • In 2015, Takata airbag inflators caused the largest automotive recall ever in the US. • 19 companies, including Honda, Toyota, BMW purchased airbags from Takata. ⇒ Must find alternative suppliers. ⇒ Customers have to wait for a long time to get their vehicles repaired. https://www.nytimes.com/2015/05/20/business/takata-airbag-recall.html 12 Goals in Supply Management • Timely availability of resources • • Supply chain risk • Reduce total cost Enhance quality and standardization 13 Goals in Supply Management • Timely availability of resources • • Supply chain risk Enhance quality and standardization • • Reduce total cost Access technology 14 Making Insourcing/Outsourcing decision Insourcing Outsourcing • Acquiring inputs from operational processes provided within the • Acquiring inputs from operational processes provided by suppliers. firm. ⇒ Make/buy decision: the choice between making a product internally or purchasing it from the suppliers. 15 10 mins game Why a company should apply insourcing or outsourcing? Insourcing Outsourcing 16 Making Insourcing/Outsourcing decision 17 Making Insourcing/Outsourcing decision Insourcing • Activities that are needed for current or future core Outsourcing • Activities that are non-core. competencies. 18 What are the core activities? In a university, which activity is the core? 19 Supplier Relationships Transaction-Oriented Adversarial Relationship • • • • • • Arm’s-length relationship Collaborative Cooperative relationship Maintain independence Self-interest Which materials/ components Focus on price require which types of suppliers and Short-term which types of supplier relationships? Hoard information Buyer-seller relations Full Partnership • • • • • • Mutual dependence Share risk/reward Focus on total cost Long-term Shared information Cross-functional relations 21 CHECK ATTENDANCE 22 BREAK-TIME 23 Sourcing the process used to acquire goods and services Identify Need and Develop Specifications Identify potential Suppliers Assess & Select supplier Manage Suppliers Relationship 24 Sourcing Identify Need and Develop Specifications Identify potential Suppliers Assess & Select supplier Manage Suppliers Relationship 25 Sourcing Identify Need and Develop Specifications Identify potential Suppliers Assess & Select supplier Manage Suppliers Relationship 26 Sourcing Identify Need and Develop Specifications Identify potential Suppliers Assess & Select supplier Manage Suppliers Relationship Weighted-point model 27 Supplier selection using a Weighted-point model Category Weight Supplier A Supplier B Supplier C Rating Score Rating Score Rating Score Quality systems 40% 3 1.2 5 2.0 3 1.2 Delivery capability 40% 2 0.8 3 1.2 4 1.6 Price 20% 5 1.0 3 0.6 2 0.4 Weighted score 100% 3.0 3.8 3.2 All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 28 Supplier selection using a Weighted-point model Category Weight Supplier A Rating Score Supplier B Rating Score Supplier C Rating Score Quality systems Delivery capability Price Weighted score All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 29 Supplier selection using a Weighted-point model Category Weight Supplier A Rating Quality systems 40% Delivery capability 40% Price 20% Score Supplier B Rating Score Supplier C Rating Score Weighted score All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 30 Supplier selection using a Weighted-point model Category Weight Supplier A Rating Quality systems 40% Delivery capability 40% Price 20% Weighted score 100% Score Supplier B Rating Score Supplier C Rating Score All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 31 Supplier selection using a Weighted-point model Category Weight Supplier A Rating Score Supplier B Rating Score Supplier C Rating Quality systems 40% 3 5 3 Delivery capability 40% 2 3 4 Price 20% 5 3 2 Weighted score 100% Score All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 32 Supplier selection using a Weighted-point model Category Weight Supplier A Supplier B Supplier C Rating Score Rating Score Rating Score Quality systems 40% 3 1.2 5 2.0 3 1.2 Delivery capability 40% 2 0.8 3 1.2 4 1.6 Price 20% 5 1.0 3 0.6 2 0.4 Weighted score 100% All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 33 Supplier selection using a Weighted-point model Category Weight Supplier A Supplier B Supplier C Rating Score Rating Score Rating Score Quality systems 40% 3 1.2 5 2.0 3 1.2 Delivery capability 40% 2 0.8 3 1.2 4 1.6 Price 20% 5 1.0 3 0.6 2 0.4 Weighted score 100% 3.0 3.8 3.2 All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 34 Supplier selection using a Weighted-point model Category Weight Supplier A Supplier B Supplier C Rating Score Rating Score Rating Score Quality systems 40% 3 1.2 5 2.0 3 1.2 Delivery capability 40% 2 0.8 3 1.2 4 1.6 Price 20% 5 1.0 3 0.6 2 0.4 Weighted score 100% 3.0 3.8 3.2 All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 35 A Weighted-point model Exercise 36 A Weighted-point model Exercise Supplier Name • • • Dazzling Lighting Inc. in Ohio, the USA is evaluating suppliers for its new line of products to be sole to home builders. Three potential suppliers have been identified and evaluated by a crossfunctional team. Using the data, please apply a weighted-point model for the supplier selection decision. EZ Lite North-South Trading Zhenjiang Lighting Annual Sales $200 million $350 million $100 million Location Ohio, the USA Mexico China Defective parts per million (ppm) 75 130 120 Transportation Time 1 day 5 days 45 days On-time Delivery 99% 92% 86% Purchase Price $4.50/unit $3.00/unit $2.15/unit 37 A Weighted-point model Exercise Supplier Name Category Quality performance EZ Lite North-South Trading Zhenjiang Lighting Annual Sales $200 million $350 million $100 million Location Ohio, the USA Mexico China Management capabilities Defective parts per million (ppm) 75 130 120 Delivery performance Transportation Time 1 day 5 days 45 days On-time Delivery 99% 92% 86% Purchase Price $4.50/unit $3.00/unit $2.15/unit Purchase Price 38 A Weighted-point model Exercise Category Weight North-South Trading EZ Lite Zhenjiang Lighting Rating Score Rating Score Rating Score Quality performance 40% 4 1.6 3 1.2 3 1.2 Management capabilities 30% 4 1.2 3 0.9 3 0.9 Delivery performance 20% 5 1 4 0.8 2 0.4 Purchase Price 10% 1 0.1 4 0.4 5 0.5 Weighted score 100% 3.9 3.3 3 All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 40 A Weighted-point model Exercise Category Weight North-South Trading EZ Lite Zhenjiang Lighting Rating Score Rating Score Rating Score Quality performance 40% 4 1.6 3 1.2 3 1.2 Management capabilities 30% 4 1.2 3 0.9 3 0.9 Delivery performance 20% 5 1 4 0.8 2 0.4 Purchase Price 10% 1 0.1 4 0.4 5 0.5 Weighted score 100% 3.9 3.3 3 All scores on a 5-point scale with 1 = poor, 5 = excellent 41 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) 42 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) a comprehensive system 43 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) a comprehensive system managing the firm’s interactions with its supply base. 44 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) 45 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) • Streamlines processes and interactions 46 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) • Streamlines processes and interactions • Identifies critical suppliers 47 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) • Streamlines processes and interactions • • Supplier performance Identifies critical suppliers 48 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) • Streamlines processes and interactions • • Supplier performance Identifies critical suppliers • Access supply risks 49 Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) • Streamlines processes and interactions • • Supplier performance Identifies critical suppliers • • Manages administration Access supply risks 50 Supplier scorecards • Quality, delivery, cost reduction, service, innovation and sustainability. • Using colour coding. For example: 51 Supplier scorecards • Quality, delivery, cost reduction, service, innovation and sustainability. • Using colour coding. For example: Excellent suppliers 52 Supplier scorecards • Quality, delivery, cost reduction, service, innovation and sustainability. • Using colour coding. For example: Excellent suppliers Accepted suppliers 53 Supplier scorecards • Quality, delivery, cost reduction, service, innovation and sustainability. • Using colour coding. For example: Excellent suppliers Accepted suppliers Need-to-improve suppliers 54 Supplier scorecards 55 How to Create Supplier Scorecards with Sheets • https://www.youtube.com /watch?v=16QNrt659Gk 56 Question for NEXT WEEK? 57 Question for NEXT WEEK? • In term of Supply Chain Management, what makes Japan become the Asia Dragon from the 1960s to the 1980s despite the country’s lack of natural resources and unfavored geographical location? 58 THANK YOU!