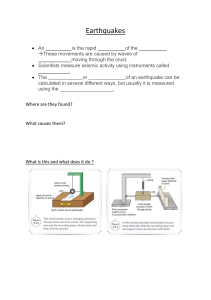
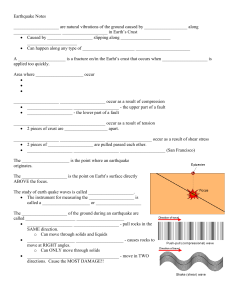
EARTHQUAKES & FAULTS PREPARED BY: CHERYL L. RECIPROCO Using models or illustrations, explain how movements along faults generate earthquakes S8ES -IIa - 14 Differentiate the epicenter of an earthquake from its focus; 2 intensity of an earthquake from its magnitude; 3 active and inactive faults S8ES -IIa - 15 How do earthquakes occur and how are they detected? How can people be prepared for earthquakes? ACTIVE and INACTIVE FAULTS EARTH CRUST The surface/outermost layer of the Earth Earth’s Crust Two Sections Continental Crust Makes up Earth’s landmasses Oceanic Crust Found in the ocean floor and usually thinner than continental crust Why are some parts of the crust thicker than other? How does the crust change its shape over time? Some force is at work pushing and pulling on the crust causing changes on the surface and often well beneath the surface • This push-pull is called stress • As rocks undergo stress, they slowly change shape and volume. What can stress do to rocks? A rock to become more compressed or squeezed • Becomes smaller in volume • A rock to stretch out over a large area. • The volume increases • The rock to twist or tear apart. • Causes the formation of fault What can stress do to rocks? A rock to become more compressed or squeezed • Becomes smaller in volume • A rock to stretch out over a large area. • The volume increases • The rock to twist or tear apart. • Causes the formation of fault What is a fault? Fracture in rocks along which movement occured. Some faults may cause the ground to crack, rise or lower. Two blocks of a faulted rock Hanging Wall • The block of rock above the fault Foot Wall • The block of rock below the fault Kinds of fault Normal Fault/Normal Dipslip Fault • If a stress pulls the rocks apart due to tension, the hanging wall will move down relative to the foot wall. Kinds of fault Reverse Dip-slip Fault/ Thrust Fault • If stress squeezed the rocks due to compression, the hanging wall will move up relative to the foot wall. Kinds of Fault Strike – slip Fault/Wrench Fault The blocks move by sliding and slipping along each other horizontally but in opposite directions. Active faults are structure where there is displacement Usually produce a shallow earthquake One that has moved in the past and expected to move again. Inactive Faults are structures that can be identified but which do not cause earthquakes. • If a fault has been inactive for million years, it is safe to call it inactive. PHIVOLCS Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology • Philippines has several fault lines • Faults and trenches are found in the entire country • Trenches are the deepest part of the oceans and are usually VShaped. Faults & Trenches Are found close to the continents Near strings of islands. Near these TRENCHES: – The crust is active causing stress and creating faults. About trenches… Scientist believe that the ocean floor is being pushed down deep into Earth along the trenches When these rocks are pushed deep enough, they are melted by the heat of Earth. Some of the molten rocks will rise up through the crust and produce volcanoes but most of it will become part of the Earth’s Mantle. EARTHQUAKE Focus and Epicenter Earthquake… • Shaking and trembling of earth that results from the sudden movement of Earth’s crust Faulting… • The most common cause of earthquake During Faulting… • Energy is released as the rocks break and move. • As they move, they cause the nearby rocks to move also. • The rocks continue to move this way until the energy is used up. Tsunami… Giant ocean wave cause by Earthquake that occur on the ocean floor. • These waves can travel at speed of 700 – 800km/h. • Can be as high as 10 – 20 meters (as they approach the coast). • The effects are devastating • One of the world’s worst natural disaster Focus • The point/region where an earthquake ruptures and the rocks break • hypocenter • Underground point of origin of an Earthquake. Epicenter • The point on Earth’s surface directly above the focus • This where the most violent shaking of the ground occurs. Focal Depth • The distance between the focus and the epicenter Earthquake Waves… • Seismic Waves • Are the waves of energy caused by the sudden breaking of rock within the Earth or an explosion. • They are the energy that travels through Earth and is recorded on seismographs. Three main types of Seismic Waves Primary Waves (P Waves) • The fastest of the seismic wave • The first to arrive at a seismic station before any other type of seismic wave • Can move through the solid rocks and fluids (like water and liquid layers of Earth) Three main types of Seismic Waves • Can move through the solid rocks and fluids (like water and liquid layers of Earth) Three main types of Seismic Waves Secondary Wave (S Wave) • The second wave you feel in an earthquake • S wave is slower than a P wave and can only move through solid not through liquid or gases What happens to S WAVES when they reach the liquid part of the earth? • S waves move rock particles up and down, or side – to – side perpendicular to the direction the wave is traveling in. Three main types of Seismic Waves Surface Wave (L Wave) Travel from focus directly upward to the epicentre. Earth’s surface moves up and down with each L wave that passes Cause most of the damage during the earthquake because they bend and twist Earth’s surface. Seismograph… An instrument that detects and measures waves. Seismograms… • Seismograph’s record of the waves. Richter Scale… Measures how much energy an earthquake releases by assigning the earthquake number from 1 to 10. • The more energy the earthquake releases, the stronger the earthquake is. Earthquake Magnitude and its Effects Richter Magnitude Effects Near Epicenter 2.0 and below Generally not felt, but recorded 2.0 – 2.9 Potentially perceptible 3.0 – 3.9 Felt by some 4.0 – 4.9 Felt by most 5.0 – 5.9 Damaging Shocks 6.0 – 6.9 Destructive in populous regions 7.0 – 7.9 Major earthquake; inflict serious damage 8.0 and above Great earthquake; Destroys communities near epicenterr