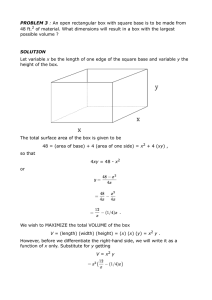
ARASU ENGINEERING COLLEGE, KUMBAKONAM - 612501 DEPARTMENT OF BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject Code: BM3251 Subject Name: Biosciences For Medical Engineering UNIT – I FUNDAMENTALS TO BIOCHEMISTRY PART –A 1. Define biochemistry. 2. Why living things need energy? 3. How organisms get energy? 4. Differentiate autotrophs and heterotrophs. 5. What is an example of a biological membrane? 6. What are examples of membrane transport? 7. What is weak acid and weak base? 8. What is pH and mention the blood pH value? 9. Write short notes on buffer and mention some examples. 10. State Handerson-hasselbalch equation. 11. List few examples of radio isotopes. 12. Write the importance of electrolytes. 13. List any four properties of water. 14. Why water is called as a biological solvent? 15. Write briefly the polarity of water. 16. State the importance of biomolecules. 17. Define PH. 18. List any four biomolecules. 19. Define ions and its function in living organisms. 20. What is food chain? Year/sem: I/II PART- B & C 1. Describe in detail about biochemistry and its importance. 2. Explain in detail about weak acid and weak base with example. 3. Illustrate about pH and buffers with clear example. 4. Explain in detail about physiological buffers in living organism. 5. Describe in detail about Handerson-hasselbalch equation with neat derivation. 6. Describe in detail about properties of water and its application. 7. Explain in detail about biomolecules with example. 8. Explain in detail about biological membranes. 9. Explain in detail about electrolytes and radioisotopes with examples. 10. Describe in detail about energy in living organism with neat diagram. UNIT –II CARBOHYDRATES, PROTEIN, LIPIDS PART-A 1) Define carbohydrates. 2) Differentiate mono and disaccharides. 3) List out the functions of carbohydrates and it types and it Benefits. 4) Draw the structure of monosaccharides. 5) List the physical properties of carbohydrates. 6) List out the chemical properties of carbohydrates, 7) What is oxidation and reduction? 8) Define lipids. 9) What are the main types of lipids? 10) Define fatty acid and types of fatty acid. 11) Differentiate saturated and unsaturated fatty acid. 12) Define proteins and Write down the functions of proteins. 13) Define primary and secondary structure of protein. 14) Define tertiary structure of protein. 15) List out the properties of protein. 16) Define amino acids and its classification. 17) Define nucleic acid. 18) Differentiate DNA & RNA. 19) Draw the structure of amino acid. 20) List out the various form of DNA and structure of DNA. PART – B & C 1) Explain in detail about carbohydrates and its classification. 2) Describe in detail about structure, physical and chemical properties of carbohydrates. 3) Illustrate about classification of lipids. 4) Explain in detail about structure and properties of proteins, 5) Describe in detail about classification and properties of amino acids. 6) Explain in detail about nucleic acids with example. 7) Describe in detail about double helical structure of DNA(Watson and crick model) 8) Explain in detail about the functions of lipids. 9) Give brief notes on nucleoside & nucleotide. 10) Explain indetail about nucleic acid with example. UNIT- III CELL DEGENERATION, REPAIR AND NEOPLASIA PART – A 1. 1. Define cell injury. 2. List out the 4 response of cellular injury. 3. What is reversible cell injury? 4. Differentiate reversible and irreversible cell injury. 5. Define intracellular accumulation. 6. What is pathological classification? 7. Differentiate dystrophic and metastatic state. 8. List out the types of cellular adaptation. 9. What is cellular adaptation? 10. Differentiate hypertrophy and hyperplasia. 11. List out the four stage in the repair of a broken bone. 12. Define neoplasia. 13. What is benign? 14. What is malignant? 15. Differentiate autopsy and biopsy. 16. Define carcinogenesis. 17. What is biopsy? 18. What is the procedure for autopsy? 19. Differentiate necrosis and apoptosis. 20. What is the impact of neoplasia? PART –B & C 1. Explain in detail about cell injury and its types with neat diagrammatic representation. 2. Describe about intracellular accumulation and pathological classification. 3. Explain in detail about cellular adaptation of’ growth and differentiation. 4. Illustrate about neoplasia and its classification with neat diagram. 5. Describe about carcinogenesis, autopsy and biopsy. 6. Discuss the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 7. Describe apoptosis and necrosis with neat diagram. 8. Describe in detail about cell degeneration. 9. Illustrate about pathological calcification. 10. Describe in detail about inflammation and repair including fracture healing. UNIT IV FLUID AND HEMODYNAMIC DERANGEMENTS PART – A 1. Define edema. 2. List out the causes of edema. 3. List out the types of edema. 4. What is hyperemia? 5. What are ischemia and its types? 6. Define homeostasis. 7. Write short notes on thrombosis. 8. Differentiate thrombosis and embolism. 9. Define intravascular coagulation. 10. List out the risk factors of intravascular coagulation. 11. What is embolism? 12. Mention the types of embolism. 13. Explain infraction. 14. Define shock. 15. Define chronic venous congestion. 16. What are hematological disorder and its example? 17. Define bleeding disorder. 18. What is leukemia? 19. Define lymphomas. 20. What is hemorrahage? PART- B & C 1. Explain in detail about edema, hyperemia and ischemia. 2. Describe about homeostasis, thrombosis and embolism. 3. Explain in detail about disseminated intravascular coagulation. 4. Illustrate about chronic venous congestion and hematological disorder. 5. Describe about lymphomas & hemorrhage. 6. Describe in detail about leukemia and its effects. 7. Define hematological disorders. 8. Discuss the phenomenon of hemostasis. Explain briefly the steps involved. 9. What are the effects of bleeding disorders? 10. What are the treatment options available for blood disorders? UNIT – V FUNDAMENTALS OF MICROBIOLOGY AND IMMUNOPATHOLOGY PART –A 1. List the types of microorganisms. 2. Differentiate gram positive and gram negative bacteria. 3. What are the different shapes of bacteria? 4. Write few diseases caused by bacteria. 5. List common diseases caused by fungi. 6. What are the parts of microscope? 7. Draw a neat light microscope. 8. Differentiate TEM & SEM 9. What is immunity? 10. What is the principle of TEM? 11. What is the principle of SEM? 12. State the difference RIA & ELISA. 13. What are antibodies? 14. What is antigen? 15. What are the types of antibodies available? 16. What is monoclonal antibody? 17. Define ELISA. 18. What is RJA? 19. Define cell mediated cell injury. 20. What is electrophoresis? PART-B & C 1. Explain the working principle of TEM with neat diagram. 2. Explain the working principle of SEM with neat diagram. 3. Explain in detail about the symptoms, causes and effects of diseases caused by virus. 4. Explain in detail about the symptoms, causes and effects of diseases caused by bacteria. 5. Explain in detail about the symptoms, causes and effects of diseases caused by fungi. 6. Illustrate about the morphological features and structural organization of bacteria. 7. Illustrate immuno electrophoresis in detail. 8. Evaluate the principle and application of RIA. 9. Write detailed notes on ELISA. 10. Discuss in detail about immune diffusion.