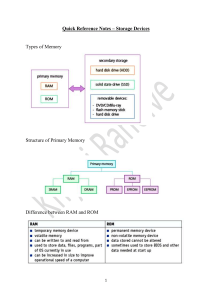
Computer System Component Computer: A programmable electronic device that can store, retrieve, and process data. The word “Computer” emerged during WWII, people who operated desk calculators were called: Computers. History of the Modern Computer Human: Could add a two 10 digit number in 10 seconds, with Calculator, in 4 Seconds. Mark 1: Also called “Harvard Mark 1” Could add two 10digit numbers in about 0.3 seconds. 30 times faster than Pencil and paper. ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer. The world's first electronic digital computer was developed by Army Ordnance to compute World War II ballistic firing Tables. Could add the same in 0.0002 seconds, 50,000 times faster than a human, and 1,500 times faster than the Mark 1. General Vocabulary and Units Bit: "Binary digIT" Computers happen to operate using the base-2 number system, also known as the binary number system ( 0, 1) Byte: 8- bit collections (single, double precision ) Digital: Send – Receive 0’s and 1’s Analog: AM - FM Hertz: Unit of Frequency Kilo-Hertz: 1000 Cycles Mega-Hertz: 1 million Cycles Giga-Hertz: 1 Billion Cycles Components of a Computer System Hardware Computer Software Motherboard Floppy Hard Drive Operating System Office 2003 Internet Explorer Components of a Computer System Storage Input Information Processing Cycle Output Process Components of a Computer System Input Process Storage Output Types of Computer A supercomputer is a computer at the frontline of current processing capacity, particularly speed of calculation. Introduced in 1960 These computers were used for complex calculations such as forecasting weather and quantum physics. Today, supercomputers are one of a kind; they are fast and very advanced. The term supercomputer is always evolving as tomorrow's normal computers are today's supercomputer. The word "minicomputer" (colloquially, "mini") is a term for a class of smaller computers that evolved in the mid-1960s and sold for much less than mainframe and midsize computers from IBM and its direct competitor. the term "minic omput er" came to mean a machine that lies in Types of Computer the middle range of the computing spectrum, in between the smallest mainframe computers and the microcomputers. A microcomputer is a complete computer on a smaller scale and is generally a synonym for the more common term, personal computer or PC A data processing system employed mainly in large organizations for various applications, including bulk data processing, process control, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and financial transaction processing. Mainframes use proprietary operating systems, most of which are based on Unix, and a growing number on Linux. Over the years they have evolved from being roomsized to networked configurations of workstations and servers that are an extremely competitive and cost effective platforms for e-commerce development and hosting. Mainframes are so called because the earliest ones were housed in large metal frames. DRAM Hardware Devices Memory Memory RAM ROM SRAM PROM Memory EPROM Random Access Memory Read Only Memory SRAM: Static RAM EPROM: Erasable Programmable ROM DRAM: Dynamic RAM PROM: Programmable ROM Memory Size in MB 1 MB 256 MB 2 MB 512 MB 4 MB 1024 MB 8 MB 16 MB 32 MB Extra Points: What mathematical equation 64 MB describes the pattern? 128 MB Monitors Output device, Soft-Copy Output Resolution is given by the amount of “Pixels” Two categories: CRT (Cathode Ray Tubes) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Printers Output Devices Hard Copy Output Resolution is given in “dsi”. Dots per Inch. Two Categories: Laser (B&W, Color) uses Toner. Inkjet (Color) uses ink cartridges. Types of Software and Their Uses Operating System Software (OS): Tell the computer how to work and what to do. Windows, Linux and Macintosh. Driver: Software that tells a hardware component how to work. Application Software: Accomplish a task Using a computer. Word, Excel, PowerPoint