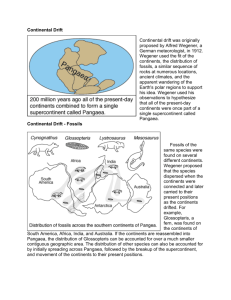
Continental Drift Key terms continental drift: The theory that the continents were once one landmass but that they have drifted apart over time • Changes in the position of continents over time. • It is believed that all the continents used to be joined and forming one big continent. • It was called Pangaea. • Pangaea then split into two forming Laurasia and Gondwana. • Surrounded by one worldwide super-ocean called Panthalassa • Gondwana eventually also broke up into South America, Africa, Australia, Madagascar, Antarctica and India • Plate tectonics: theory about the movement of crustal plates Changes in the position of continents • In 1912, a German scientist called Alfred Wegener said that the continents were once all joined in a single landmass. • He called the single landmass Pangaea, which is Greek for ‘all land’. • Alfred Wegener, a German meteorologist, who is given total credit for his detailed theory of the breakup of a single super-continent and the drifting apart of the individual continents. • He is known as ‘the father of continental drift theory’. Notice that Pangaea split into two separate land masses called Laurasia and Gondwanaland. The continents continued to move until they looked like today’s map of the world Changes in the position of continents • All the continents appear to fit neatly together, like a jigsaw puzzle. • This was what made Wegener think that maybe they really were joined together at one time and then something caused the continents to drift apart over time. • He called his ideas the theory of continental drift. • In his theory, Wegener suggested that about 200 million years ago, the map of the world would have looked something as in. Evidence for movement of the continents • Rocks of similar type, age and formation are found in south-east Brasilia and South Africa, suggesting Africa and South America used to be joined. • The continents fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. • Coal, which forms in hot and wet conditions are found beneath the Antarctic ice cap. • Fossils of similar small reptiles were found in south-east Brasilia and South Africa. Evidence continues….. • Glaciers that covered large parts of the continents in the southern hemisphere in the Palaeozoic Era moved in the same direction. • Glaciers are masses of ice with limited width that move outward from an area of accumulation. They are slow moving large rivers of ice. • Fold mountain systems are said to be linked with floating continents. • The Rift Valley of Africa shows that Africa is slowly splitting into two. fossils The discovery of Mesosaurus fossils in both Africa and South America proved that these two continents had once been joined. Scientists also found fossils of the Lystrosaurus in Antarctica, southern Africa and India. Like the Mesosaurus, Lystrosaurus was a land animal, so this was further proof that the continents were once joined at the time these animals lived. Mountain ranges When geologists plotted the positions of old mountain ranges on the map of Pangaea, they found that these mountain ranges all lined up. They also found that the mountains were formed of rocks of the same type, age and structure. Sea-floor spreading The Atlantic Ocean did not exist when the continents were joined together. Once the continents started to move apart, the Atlantic Ocean appeared and has been getting wider ever since. We call this ocean floor spreading, New land is constantly forming along the midAtlantic sea floor. Geologists have found rocks of the same age and type on either side of the midAtlantic.