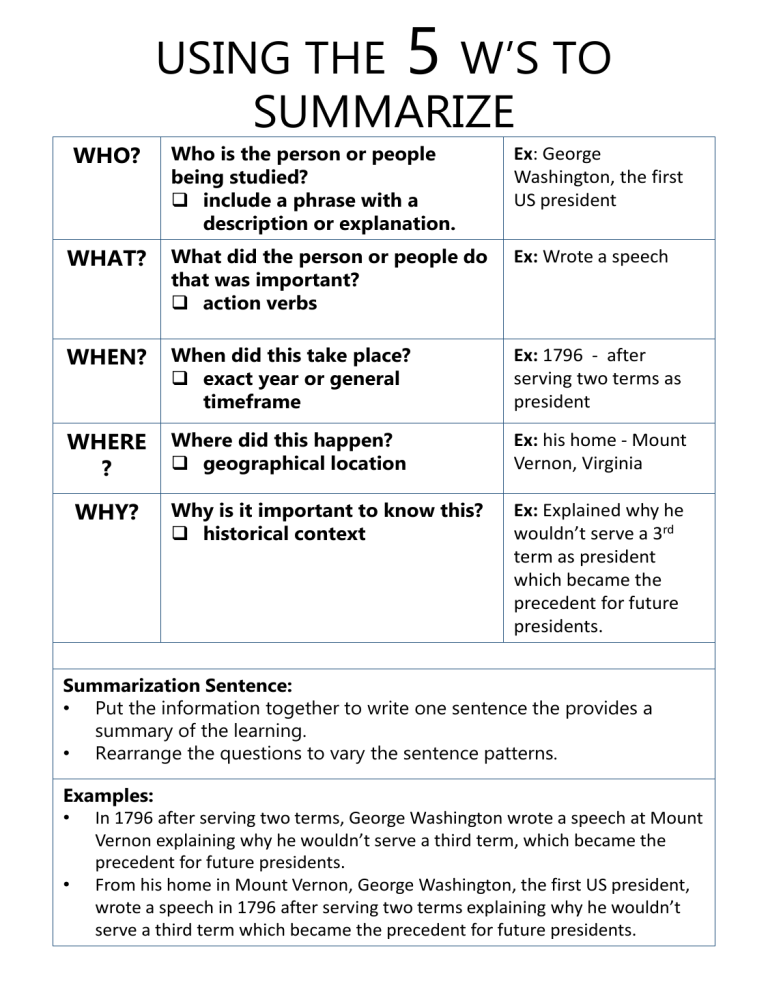
USING THE 5 W’S TO SUMMARIZE WHO? Who is the person or people being studied? include a phrase with a description or explanation. Ex: George Washington, the first US president WHAT? What did the person or people do that was important? action verbs Ex: Wrote a speech WHEN? When did this take place? exact year or general timeframe Ex: 1796 - after serving two terms as president WHERE ? Where did this happen? geographical location Ex: his home - Mount Vernon, Virginia Why is it important to know this? historical context Ex: Explained why he wouldn’t serve a 3rd term as president which became the precedent for future presidents. WHY? Summarization Sentence: • Put the information together to write one sentence the provides a summary of the learning. • Rearrange the questions to vary the sentence patterns. Examples: • In 1796 after serving two terms, George Washington wrote a speech at Mount Vernon explaining why he wouldn’t serve a third term, which became the precedent for future presidents. • From his home in Mount Vernon, George Washington, the first US president, wrote a speech in 1796 after serving two terms explaining why he wouldn’t serve a third term which became the precedent for future presidents. WHO? USING THE 5 W’S TO SUMMARIZE Who is the person or people being studied? include a phrase with a description or explanation. WHAT? What did the person or people do that was important? action verbs WHEN? When did this take place? exact year or general timeframe WHERE? Where did this happen? geographical location WHY? Why is it important to know this? historical context Summarization Sentence: • Put the information together to write one sentence the provides a summary of the learning. • Rearrange the questions to vary the sentence patterns. Answering Questions with C. E. R. Claim – Evidence – Reasoning 1. What is the claim? • Restate the question in order to make a claim. 2. What evidence can be provided to support the claim? • Cite primary and secondary source documents used to make the claim or answer to the question. 3. How does the evidence given support the claim that was made? • Explain how this justifies the answer. QUESTION What is the historical significance of the Magna Carta? CLAIM The historical significance of the Magna Carta is that it was a guide for future documents such as the US Constitution. EVIDENCE The Magna Carta and the Constitution both include the right of people to be governed by representatives. REASONIN G The “founding fathers” used historical documents such as the Magna Carta as a basis for the US government. The historical significance of the Magna Carta is that it was a guide for future documents such as the US Constitution. The Magna Carta and the Constitution both include the right of people to be governed by representatives which shows that the “founding fathers” used historical documents such as the Magna Carta as a basis for the US government. The Magna Carta was historically significant because it was used as a guide for documents such as the US Constitution. Both included the right of people to be governed by representatives and protected individual freedoms. 1. Answering Questions with C. E. R. Claim – Evidence – Reasoning What is the claim? • Restate the question in order to make a claim. 2. What evidence can be provided to support the claim? • Cite primary and secondary source documents used to make the claim or answer to the question. 3. How does the evidence given support the claim that was made? • Explain how this justifies the answer. QUESTIO N: CLAIM EVIDENCE REASONI NG Identifying Cause and Effect Cause and Effect is a relationship in history between an event, a condition, or a decision (the cause) and the events or results that follow it (the effect). Understanding cause and consequence is a key aspect of historical analysis and helps historians to understand how and why things happened in the past. As we study historical events, we discover that things do not simply ‘happen’ without reason. • Historical events are caused by things that occurred before them. • Historical events also have effects or consequences both immediately and long after the event is over. Cause 1 Effect 1 Short term (right before) Cause 2 Intermediate (leading up) Short term (immediate) Even t Cause 3 Long term (documented in history) Treaty of Paris created 13 independent states Boston Massacre Boston Tea Party Colonist wanted freedom from British rule Intermediate (as time went on) Effect 3 Long term (years before) England imposed taxes against colonist Effect 2 American Revolution US Constitution written to unite states Westward expansion Identifying Cause and Effect Cause and Effect is a relationship in history between an event, a condition, or a decision (the cause) and the events or results that follow it (the effect). Understanding cause and consequence is a key aspect of historical analysis and helps historians to understand how and why things happened in the past. As we study historical events, we discover that things do not simply ‘happen’ without reason. • Historical events are caused by things that occurred before them. • Historical events also have effects or consequences both immediately and long after the event is over. Event in Cause 1 Effect 1 history Short term Short term Cause 2 Effect 2 Intermediate Intermediate Cause 3 Effect 3 Long term Long term Comparing and Contrasting Comparing and contrasting is used to analyze the similarities or likenesses and differences in two or more people, places, events, or ideas, Comparing and contrasting with a Venn Diagram: 1. Identify the two concepts. 2. Create a chart listing all of the qualities of each. 3. Highlight those qualities that appear on both lists. These are the similarities and will go into the center circles that overlap. 4. List the remaining items (the differences) for each concept in the out portion of each circle. Concept 1 Concept 2 Qualities Qualities facts facts notes notes Sparta Athens Assemblies of free men debated laws Assemblies of discussed and voted on laws Greek city state Greek city state Focus on military and strength Focus on education and citizenship Mandatory military training at age 7 Military training at age 18 Dependent on farming Dependent on trade Women had some right to own land and have jobs Women had no rights to property Had slave trade Had slave trade Concept 1 only Similarities Concept 2 only SPARTA BOTH ATHENS Greek city states focus on military focus on education Slavery Farmers women could own property Military training Assemblies discussed laws tradesmen women had little rights Comparing and Contrasting Comparing and contrasting is used to analyze the similarities or likenesses and differences in two or more people, places, events, or ideas, Comparing and contrasting with a Venn Diagram: 1. Identify the two concepts. 2. Create a chart listing all of the qualities of each. 3. Highlight those qualities that appear on both lists. These are the similarities and will go into the center circles that overlap. 4. List the remaining items (the differences) for each concept in the out portion of each circle. Concept 1 Concept 2 Where in the World??? Geographers can describe a place in different ways: Location – a place on a map • Absolute location – a location based on a fixed point • Coordinates (longitude and latitude), Southern Hemisphere • Name (Statue of Liberty) • Address (1600 Pennsylvania Avenue, Washington DC) • Relative location – location based on relation to other places • Relative location can change based on the reference (Lafayette, LA is west of the Mississippi river, but East of the Sabine River) • North of the Equator Region - a specific area that has common features such as language, government, religion, or climate • Midwest, New England, Cajun Country Place – a description of the physical and human characteristics of a given location • Cold, urban, Southern, wilderness New Orleans, LA LOCATION REGION PLACE 30 N, 90 W Southeastern US North of the Gulf of Mexico Hot, humid summer months Mild winters French and Spanish influence Known for Mardi Gras celebrations Where in the World??? Location – a place on a map • Absolute location – a location based on a fixed point • Coordinates (longitude and latitude), Name, Address • Relative location – location based on relation to other places Region - a specific area that has common features such as language, government, religion, or climate Place – a description of the physical and human characteristics of a given location LOCATION REGION PLACE