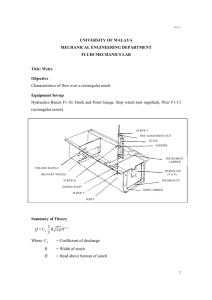
University of Duhok College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics Laboratory (Fluid Dynamic) Presented by Jahfar Supervised by Naeem aref Group(B) Experiment No. 1 Experiment Data.13/2/2022 Contents 1 Introduction .................................................................................................... 2 1.1 What is a V notch weir? ............................................................................ 2 1.2 Objective .................................................................................................. 2 2 Pros of Vee notch weirs ................................................................................. 3 3 Cons of Vee notch weirs ................................................................................ 3 4 Experimental Procedure ................................................................................. 4 5 Calculations & Results ................................................................................... 5 6 Discussion & Conclusion ................................................................................ 7 7 References ..................................................................................................... 8 1 1 Introduction Weir is defined as a barrier over which the water flows in an open channel. A weir is a notch on a larger scale – usually found in rivers. It is used as both a flow measuring device and a device to raise water levels. A notch is a device used for measuring the rate of flow of a liquid through a small channel or tank . It is an opening in the side of a measuring tank or reservoir extending above the free surface. A weir is a concrete or masonary structure , placed in an open channel over which the flow occurs . It is generally in the form of vertical wall ,With sharp edge at the top. 1.1 What is a V notch weir? V notch weirs really are just that – a thin plate weir with a ‘V’ notch cut into it. The weir is placed to obstruct open channel flow and allow water to flow over the notch. This enables us to accurately measure the flow, by measuring the head upstream of the V notch. These types of weirs are particularly effective at measuring low flow rates, as the V notch weir design allows small changes in head to be accurately measured and thus the flow rate calculated. 1.2 Objective The objectives of the Experiment are: 1) To show the measurement of flow rate. 2) To determine the relationship between upstream head and flow rate for water flowing over a V-Notch weir. 3) To calculate the discharge coefficient Cd (0.58 to 0.61). The purpose of experiment 2 i.To calibrate a Bourdon type pressure gauge and to establish the calibration curve of Bourdon Gauge. ii.Also determine the gauge errors. 2 Pros of Vee notch weirs Simple design that is easy to install Ideal for cleaner effluent, such as industrial discharge and final effluent outfall Can be supplied as part of a compliant gauging structure Relatively low cost to design and install Good option for low flow rates Can be fitted into an existing chamber, if size allows 3 Cons of Vee notch weirs There needs to be an adequately sized weir pool and approach to sufficiently condition the flow before it reaches the weir plate to ensure accuracy in measurement Periodic maintenance is required – it’s important that the weir crest itself is regularly checked to ensure there is no sediment or fouling. Over the longer term, no rounding or surface abrasions which can impact flow (SIRIS weir plates are manufactured using marinegrade steel to avoid this problem) V notch weirs are not designed to work in submergence conditions and need the weir crest to be high enough to allow for free-flowing discharge Not considered accurate for flow heads above two feet 3 4 Experimental Procedure 1) Make sure that the Hydraulic Bench is leveled. 2) The weir plate was placed and fixed carefully perpendicular to the sides and bottom of the Hydraulic Bench and leveled on all axes by a carpenter’s level. 3) A series of different flow rates were overtopped over the weir and the corresponding heads above the weir crest were recorded. The flow head over the weir crest, using a point gauge, was measured at a distance (3-4) H upstream of the weir after the zero on the weir crest or the apex of the weir. Take enough care not damage the weir plate and the point gauge. 4) For each flow rate, wait until steady condition is attained then measure and record the head (H) above the weir. 5) The theoretical flow rates passing over the weir were calculated from the flow equation of VNotch plate weir. 𝟖 𝜽 𝟓 𝑄𝑡ℎ = 𝟏𝟓 √𝟐𝒈 𝐭𝐚𝐧(𝟐) 𝐇 𝟐 Where: 𝑄𝑡ℎ = Theoretical flow rate, g = acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/sec 2 ), H = head of water over the notch, θ = 300angle of the notch (deg.). 6) While for each flow rate (actual discharge), measure and record the volumes in the 𝑄𝑎𝑐𝑡 = collecting tank and the time required to collect that volume by stopwatch. 𝐕 𝐭 Where: 𝑄𝑎𝑐𝑡 = actual flow rate, V = volume of the collecting tank, t = time taken to rise volume (liter). Fluid Mechanics Second Stage The coefficient of discharge Cd is defined as the ratio of actual discharge obtained experimentally to the theoretical discharge. Cd = 𝐐𝐚𝐜𝐭 𝐐𝐭𝐡 Where: Cd = Coefficient of discharge is a dimensionless discharge coefficient which takes account the effects of neglecting losses and the contraction of the jet as it passes over the notch in Qth. 7) Repeat the above procedure for different flow rates by adjusting the inlet valve opening and tabulate the readings. 8) Complete the tabulation and find the mean value of Cd (0.58 to 0.61). 9) Draw the necessary graphs and calibrate the notch. 4 5 Calculations & Results No.1/ H = crest level –Water level H = 140 – 94 = 46 mm = 0.046 m 𝑄𝑡ℎ = 𝑄𝑡ℎ = 𝜽 8 30 √𝟐𝒈 𝐭𝐚𝐧(𝟐) 𝐇 𝟐 𝟏𝟓 𝑄𝑎𝑐𝑡 = Cd = 5 √2𝑔 tan( 2 ) ( 0.046 )2 = 1.2188 × 10−3 m/sec 3 15 𝑄𝑎𝑐𝑡 = Cd = 𝟓 𝟖 𝐕 𝐭 𝟓𝟏 𝟖.𝟑 = 1.2048 × 10−3 m/sec 3 𝐐𝐚𝐜𝐭 𝐐𝐭𝐡 1.20 × 10−3 1.22 × 10−3 = 0.99 Note: No.2, 3, 4, 5 is solved like this No. 1 2 3 4 5 Crest level (mm) Watar Level 140 140 140 140 140 94 87 78 72 61 Results with V-Notch Weir Volume Time Qact Qth 𝟑 H (m) (Liter) (Sec) (𝒎 /sec) (𝒎𝟑 /sec) 5 5 5 5 5 20.1 17.1 10.34 8.21 7.36 0.046 0.053 0.062 0.068 0.079 0.000248 0.000292 0.000483 0.000609 0.000679 0.000278 0.000409 0.000605 0.000763 0.001110 Cd 0.866 0.714 0.798 0.7979 0.6118 Draw in log-log paper the relation between Qact and H , and find the equation Q=KH 𝑛 5 1 H (m) 0,0001 0,001 0,01 0,1 1 y = 0,8832x0,3505 0,1 H (m) Степенная (H (m)) Qact (m^3/sec) 0,01 6 6 Discussion & Conclusion From the experiments that we did, we are going to determine the characteristics of a triangular (v) notch. The flow pattern of water from the V-notch is being observed. Other than that we are going to determine the discharged coefficient of the notch. The discharged coefficients are going to be determined from the volumetric flow rate calculated from the time taken and the volume collected. The v notch weir is very good for measuring a low flow rate of open channel flow. The head over the v notch is measured and correlated with flow rate through the open channel. A v notch weir equation will give the open channel flow rate. The purpose of this lab report was to enhance us as the civil engineering students to observe and appreciate the use of v notch in determination of state of flow. This experiment is to find out the reading of actual discharge and theoretical discharge to calculate the coefficient of discharge of V-Notch with the given formula and this experiment has successfully found out the readings of actual discharge and theoretical discharge in this experiment. From the results, it clearly shows that the actual discharge always differs from the theoretical discharge due to frictional loss, turbulence loss and the upstream depth of water. Parallax error can be avoided by checking the height of water level which should be above the water surface. Last but not least, ensure to drain the water in volumetric tank to avoid overflow of the water and damage the experimental setup. 7 7 References https://siris.co.uk/v-notch-weir-design-how-does-it-work/ https://www.encardio.com/geotechnical-instruments/v-notch-weir-seepage-monitoring https://www.openchannelflow.com/support/whats-the-accuracy-of-a-weir https://www.engineeringexcelspreadsheets.com/2011/04/v-notch-weir-calculator-excelspreadsheet/ https://www.industrysearch.com.au/improving-safety-procedures-for-flow-measurement-ofv-notch-weirs/f/20404 8