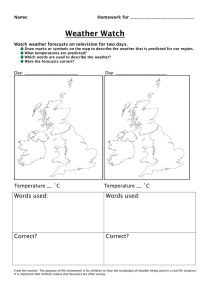
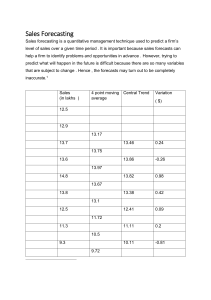
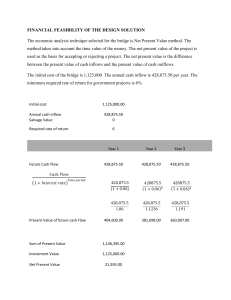
3.7 Cash Flow The Difference Between Cash and Profit • Cash: the lifeblood of a business because every organization needs cash to keep functioning • Profit: the positive difference between a firm’s total sales revenue and its total costs of production. • Are profit and cash the same thing? The Difference Between Cash and Profit • If a firm sold $50,000 of goods in a month, with 60% of its customers paying by cash, then only $30,000 cash is received. The other 40% (or $20,000) is not received until the end of the credit period. What’s the sales revenue made by the firm and what’s the cash inflow? The Difference Between Cash and Profit • Is it possible for a firm to be profitable but cash deficient? Why? – Poor credit control – The profitable business tries to expand too quickly – Seasonal variation in demand short-term liquidity problem • Is it possible to be cash rich but unprofitable? The Working Capital Cycle • Working capital: the cash or liquid assets available for the daily running of a business. – Funds available to pay for the immediate costs and expenditure – Lacking of working capital insufficient cash to fund routine operations • Liquidity: how easily an asset can be turned into cash The Working Capital Cycle • Which is the largest cause of business failure, lack of profitability or insufficient working capital? – Inadequate working capital insolvency liquidation of the firm collapse of the business • Insolvency: a situation where working capital is insufficient to meet current liabilities • Liquidation: company needs to sell off its assets to repay as much of the money owed to is creditors The Working Capital Cycle • Working capital = Current asset – Current liabilities • Current asset: the liquid resources belonging to a business that are expected to be converted to cash within the next 12 months – Cash – Debtor – Stock The Working Capital Cycle • Current liabilities: the money that a business owes that needs to be repaid within the next 12 months. – Overdrafts – Creditors – Tax The Working Capital Cycle • There is a delay between paying for costs of production and receiving the cash from selling their products production process takes time • Working capital cycle: the interval between cash payments for costs of production and cash receipts from customers The Working Capital Cycle Production costs Cash Sales Any drawbacks for holding too much cash and liquid assets? Cash Flow Forecasts • Cash flow forecast: a financial document that shows the expected movement of cash into and out of a business, per time period – Cash inflow – Cash outflow – Net cash flow Cash Flow Forecasts • Cash inflow: – Sales revenue – Payments made by debtors – Loans from a bank – Interest received from savings deposits – Sale of fixed assets – Rental income charged on property owned by the business Cash Flow Forecasts • Cash outflows: cash that leaves a business • Net cash flow: the difference between cash inflows and cash outflows, per time period Cash Flow Forecasts • Reasons for cash flow forecasts: – Banks and other lenders require a cash flow forecast to help them assess the financial health of the business seeking external finance – Cash flow forecasts can help managers to anticipate and identify periods of potential liquidity problem – Cash flow forecasts aid business planning Cash Flow Forecasts Cash Flow Forecasts • Opening balance: the amount of cash at the beginning of a trading period • Closing balance: the amount of cash at the end of trading period Closing balance Opening balance Net cash flow Cash Flow Forecasts • Causes of cash flow problems: – Overtrading: the situation occurs when a business attempts to expand too quickly (or aggressively), without the sufficient resources to do so. – Overborrowing: the larger the proportion of capital raised through external sources of finance, the higher the cash outflow on loan interest payments – Overstocking: business holds too much stock as a result of ineffective stock control system Cash Flow Forecasts • Causes of cash flow problems: – Poor credit control: a. offers customers an extended credit period, leading the business to trade for long periods without cash inflows; b. too many customers are offered credit, which increases the chances of bad debts being experienced. – Unforeseen changes: unexpected and erratic changes in demand can cause serious cash flow problems Investment, Profit and Cash Flow • Sell an investment increase in cash flow • Obtain finance for investment cash inflow improves liquidity position • How investment is financed also affects the cash flow position of a business Strategies to Deal with Cash Flow Problems • Three generic ways to deal with cash flow problems: – Reducing cash outflows – Improving cash inflows – Seeking alternative sources of finance Reducing Cash Outflows • Seek preferential credit terms – Limitation: Administrative costs and the time needed to investigate and negotiate better deals which might not results in significant differences to the cash flow position of the firm • Seek alternative suppliers – Limitation: cheaper raw materials lower quality change marketing strategies Reducing Cash Outflows • Better stock control – Works well for manufacturers of mass product – Not works well for businesses that offer a service and do not hold much stock • Reduce expenses – Scrutinizing expenses can help to identify overhead costs that can be reduced, without compromising quality • Leasing: rather than buying, reduces the burden on cash flow Improving Cash Inflows • Tighter credit control – Limit trade credit to customers or reduce credit period • Limitation: customers might switch to rivals due to the worsened trade credit terms – Debtors can be encouraged to pay earlier or on time by offering incentives – Accepting interim payments Improving Cash Inflows • Cash payments only – Limitation: customers might prefer to buy from competitors who offer trade credit • Change pricing policy – Offload excess stocks – Works best for products that have lots of substitutes or are at the end of their product life cycle • Improved product portfolio – Limitation: raises costs and risks, yet no guarantee of higher net cash inflows Seeking Alternative Sources of Finance Government assistance Overdraft Debt Factoring Selling fixed assets Limitations of Cash Flow Forecasting • Marketing • Human resources • Operations management • Competitors • Changing fashion and tastes • Economic change • External shocks Cash Flow and the CUEGIS Concepts • Contingency fund: set aside cash for unexpected changes and emergency use. – The greater the level of uncertainty faced by a business, and the more exposed it is to change, the higher its contingency fund tends to be • Working capital is essential for many aspects of business strategy: – Human resources strategy – Marketing strategy – Production strategy