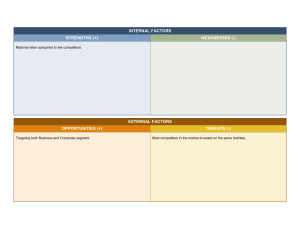
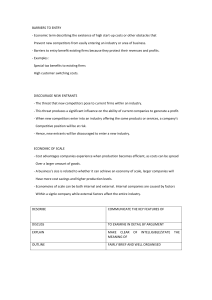
Competition Industry Concept of Competition Monopoly - Only one firm provides the product/service - Very few (if any) partial substitutes Oligopoly - Small number of firms: o produce identical products and sell at comparable price o differentiated products and sell at premium Monopolistic Competition - Many competitors produce differentiated products - Go after different segments - Charge a premium Pure Competition - Many competitors offer the same/identical product - No basis of differentiation - Charge same price Michael Porter and Competition 1) Internet Rivalry 2) Threat of New Entrants 3) Threat of Substitutes 4) Bargaining Power of Buyers 5) Bargaining Power of Suppliers Red Oceans Strategy Analysing Existing and Potential Competitors: Step 1: Identifying Competitors Step 2: Targeting Competitors Step 3: Assessing Competitors (Competitors Behaviour/Own Behaviour) Identifying Competitors Through Factors Like: Form/Category/Generic/Budget Substitutability Similarity/Consideration sets/Substitution by use/Opportunity cost Switching/Cross-elasticity Targeting Competitors: Factors to Consider: Own and Competitor Strategies + Resources Customer Segment Time Horizon Rate of Technology Change Assessing Competitors: Know your competitor’s: - Strategies - Objectives - Strengths - Weaknesses - Current position and strategy o Market share and sales o Target market and positioning o Marketing mix o Manufacturing and R&D o Financial strength (profitability, liquidity, financial position, etc.) - Future goals o Product portfolio o Share/profit goals o Product differentiation/Cost Leadership - Abilities o Designing new products o Manufacturing o Market research/marketing o Financing products o Managing resources - Share of Market (value and volume) - Share of Mind* (awareness) - Share of Heart* (preference) ** Gains in mind and heart share will lead to gains in market share: awareness and then preference (brand loyalty) How to find this information? - Annual reports, SEC filings - Press quotes, announcements, speeches - Talk to external stakeholders (customers, distributors, suppliers) - Observations Reaction Patterns Laid Back Competitor: slow to respond – do not notice, lack funds, own loyal customers (bureaucratic) Selective Competitor: responds to specific attacks only (price cuts, but not to advertisements) Tiger Competitor: react swiftly and strongly to all competition Stochastic Competitor: unpredictable trends/patterns (small businesses based on affordability) Classification of Firms Market Leader - Expanding market Protect current market share Increase market share Expanding the Market Find new users (market penetration, geographical representation) Find new uses (for same product) More usage (per occasion) Protecting Market Share Plug any holes Build on strengths Pre-emptive attacks against competitors Continuously innovating Expanding Market Share New products Improved product/service quality Increasing marketing/promotional expenditure Market Challenger - Aim to increase market share They attack: o Market leader: risk-reward play, usually if leader isn’t serving the market well o Firms their own size: not doing job well, under financed, poor products o Small players: gobble up local competition (eat up) Strategies: Market Follower Follow rather than challenge market leader Product imitation (no product innovation) Offers advantages in financing, services, location, no retaliation Low differentiation High stability (shown by market shares) Capital intensive, homogenous product industries Strategies: Market Nicher Target small markets/niches, no interest in competing with larger firms Large share of small markets, meets customer needs the best way High value products, charge premium prices, high profitability SPECIALISATION: - Customer - Product - Other Blue Oceans Strategy Don’t just compete for a share in the market, increase the size of the market Examples: Tesla, Uber, Cirque du Soleil Cirque du Soleil Problem: Market for circus declining Costs increasing (animals/star performances) Animal cruelty (public opinion/views changing public tastes and preferences) Limited demand (kids forget easily, prices of tickets high) Solution: Transform it into a show Target a greater audience (family, not just kids) Increase prices Reduce costs (get rid of animals/stars) Blue Oceans Strategy: focus on needs rather than technology, new ways of satisfying existing needs, blending multiple needs