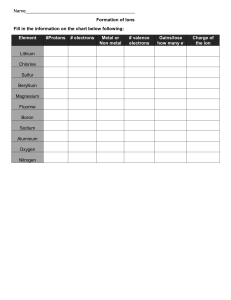
Chemistry Homework Ionic and Covalent Bonding IONIC BONDING DEFINITION Ionic bonding occurs when a metal transfers one or more electrons or more electrons to a nonmental in an effort to attain a stable octet of electrons. For example, the transfer of an electron from sodium to chlorine can be depicted by a Lewis dot diagram. Classify each of the following elements as an alkali metal, an alkaline-earth metal, transition metal, metalloid, halogen, or noble gas based on its position in the periodic table: boron _______________________________________ gold _______________________________________ krypton _______________________________________ calcium _______________________________________ Show the transfer of electrons in the following combinations.: K+F Mg + I Be + S Al + Br Na + O COVALENT BONDING DEFINITION Covalent bonding occurs when two or more nonmetals share electrons, attempting to attain a stable octet of electrons at least part of the time. Fill in the missing information in the chart below: Element # of Protons # of Electrons # of Valence Electrons Carbon Hydrogen Chlorine Helium Phosphorus Oxygen Sulfur Nitrogen Show how covalent bonding occurs in each of the following pairs of atoms: H+H F+F O+O H+O+O C+O+O # of electrons to fill outer shell. TYPES OF CHEMICAL BONDS Classify the following compounds as ionic (metal + nonmetal), covalent (nonmental +metal) or both (compound containing a polyatomic ion). SO3 CaCl2 CO2 LiBr H2O KI K2O NaOH BaSO4 HCl CH4 MgO Cl2 KCl 1. Explain why oxygen is considered reactive while neon is not. 2. Why do some atoms lose electrons, and some atoms gain electrons during ionic bonding? 3. Why do atoms like fluorine and chlorine have similar reactivity? 4. Please explain the octet rule.