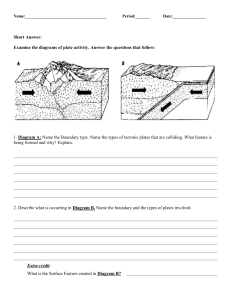
DYNAMIC EARTH Click on the following site: https://www.learner.org/series/interactive-dynamic-earth/ Earth's Structure (review only) Plate Tectonics. Left 1. Does the right or left side look more like our current depiction of what the Earth looks like? ______________ Click that side. Are you right? Yes 2. What does the other side show a picture of? Earth before the continents divided Click How Do We Know This? 3. What is the name of the scientist who noticed that the coastlines of South America and Africa looked like they fit together like a puzzle piece. Alfred Wegener 4. What did this scientist call this supercontinent? Pangaea 5. True or False: Although scientists have constantly tried to disprove the theory of the supercontinent, it is still the basis for the development of the theory of plate tectonics. True Click on Continents Over Time. Follow Directions. 6. What is the name of the theoretical future Pangaea? Pangaea Ultima Click on Plate Boundaries 7. How many major tectonic plates currently exist? 15 8. What is the name of the crust that is underneath land? Continental 9. What is the name of the crust that is underneath water? Oceanic 10. How thick is continental crust? _______ How thick is oceanic crust? _______ 30 to 70 km, 7 to 10 km 11. What is the border between two tectonic plates called? Boundary 12. Explain, and give an example of the difference between the 3 types of plate boundaries. Convergent – When two plates push toward each other. Divergent – Plates that move apart from each other. Transform – When two plates slide past each other. 13. Which type of boundary is closest to us in NC? Caribbean Complete the Plates and Boundaries Challenge to get to the next section. Click next. Slip, Slide, and Collide 14. What is happening to the Himalayan mountains? They grow taller every year 15. True or False: The different types of occurrences at plate boundaries cause specific types of natural phenomena to occur. False Click See What Happens at Plate Boundaries. 16. If oceanic and continental plates collide, which one will go under the other one? WHY? Oceanic because it is denser 17. What is this known as? Subduction 18. As the ocean crust sinks, what is formed at the edge of the continent? A valley 19. Use the diagram to define the following terms: Volcanic Arc – An arc-shaped chain of volcanoes Trench – A steep-sided depression on the ocean floor Subduction Zone – Where one plate is being pulled to the other 20. What happens when 2 oceanic plates collide? It forms Island Arcs 21. What else exists as these plates collide? (Hint: what causes tsunamis?) A shift in the ocean floor causes tsunamis 22. What happens when two continental plates converge? It creates mountain ranges 23. How much taller are the Himalayan Mountains each year? 50 to 20 mm per year Click next. Divergent Boundaries. 24. What causes seafloor spreading? Divergent boundaries in the middle of the ocean Transform Boundaries. 25. Explain what causes stress to build up at fault lines. Friction 26. What happens when this stress is released? It causes a dip in the landslide 27. What is another name for a transform boundary? A strike-slip fault 28. Where is the most frequently studied fault of this nature? San andreas in california