Chapter 8
advertisement

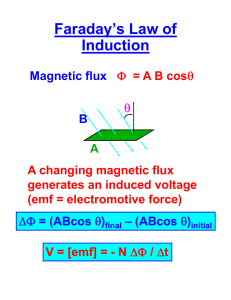
Chapter 8 Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic Induction is very important in our life. Transformers, Electric Generator, Magnetic Media Player all use the same effect. Faraday’s Law The emf induced in a loop of wire is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the coil The emf induced by a changing magnetic flux is called an induced emf and the current it produces is called an induced current or an induction current Magnetic Flux The magnetic flux m is defined as the number of magnetic filed lines that passes thorough and area A. m = B A cos (the magnetic flux) The SI unit for the magnetic flux is weber (wb) The relationship between the weber and the unit of magnetic field Testa (T) is 1 Wb = 1 T m2 Lenz’s Law The direction of an induced current is such that its own magnetic field opposes the original change in magnetic flux that induced the current. We can combine the Faraday’s Law and Lenz’s Law into these equations: m =t Change of magnetic flux per time The minus sign indicate the direction of the emf and in agreement with Lenz’s law If there are N number of loops (turns) m =-N t Motional Emf The emf generated due to moving object in a magnetic field. The emf develop around the loop is obtained from the Faraday’s Law L V x Consider a rod with length of L, and moving with a speed v, for a distance x m BA B( Lx) =t = - = - t = - t = - B L v (motional emf) AC Generators AC generator is widely use in Hydro electric generator plant and Nuclear Reactor Plant Emf Time (s) m = B A cos Angular velocity = m =t =- B A d dt t (cos ) = - B A d dt (cos t) = B A sin t If there are N number of loops = N B A sin t Back EMF Electric motor normally convert electrical energy to mechanical energy. However, like a generator, a motor has a rotating armature in a magnetic field. This induced emf is called back emf or counter emf due to its polarity is opposite of the voltage that is driving the motor The net voltage V net = V - b I= Vnet V b R R B = V- IR Transformers Transformer is use to transform or change the value of the AC voltage use. There are two types of transformer a. Step up transformer (exp: 250V to 10kV) b. Step down transformer (exp: 250V to 5V) The transformer consists of a primary coil and a secondary coil with a laminated iron core. The power for any electrical equipment should be conserved Power in Pin = Power Out Pout Iron Core Primary Coil Secondary Coil A basic construction for a transformer Pin = Pout I1V1 = I2V2 Vs= -Ns Vp = - Np t t The ratio of Vs over Vp gives ) Vs t V p N ( ) p t Vs N s Vp N p Ns ( Inductor Inductor is basically a coil with many turns, N N number of turns Total magnetic flux passing through the coil = N m The summation of magnetic flux I N m= L I L = self inductance N m= L I ( Nm ) I =t = = - L t I = - L t L = volt-second / ampere A changing of current in a coil induces an emf opposing that change, and this induces emf is proportional to the inductance of the coil.