Electrostatics
advertisement
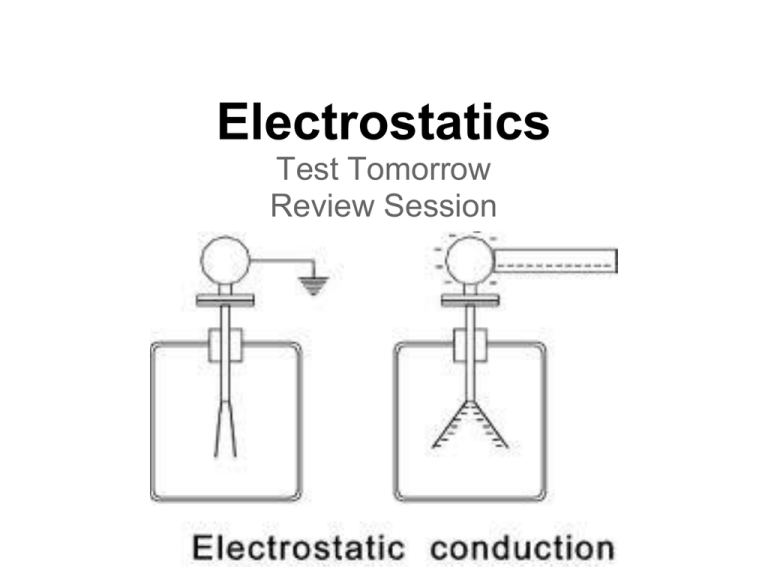
Electrostatics Test Tomorrow Review Session Electric Force ● Like charges repel ● Opposite charges attract Conservation of Charge ● Charge cannot be created or destroyed ● Charge can move from one object to another, however the total amount of charge remains the same Question When walking across the carpet you acquire a certain charge from friction. How does your charge compare to the charge of the floor? Ions ● An atom or molecule with a different number of electrons than protons ● Ions can gain electrons making them....? ● Or if they lose electrons they become....? Charging an Object ● Charge by friction ● Charge by conduction ● Charge by induction Charge by Conduction ● Contact between two charged objects For an Insulator: ● Some of the electrons will move For a conductor: ● Charge will average between the two objects Question When three metal spheres are touched what is the resulting charge on each one? -2 +5 +3 Charge by Induction ● This effect works with conductors 1. Forces caused by a nearby charged object will cause polarization of a conductor 2. The far side of the conductor is connected to ground 3. Some of the access charge leaves the conductor 4. A net opposite charge is left on the conductor Question When a conductor is charged by induction, how does the charge on the conductor compare to the charge on the charged object? Polarization Electric forces causing an object to have a more positive and negative side The object remains at zero net charge Question Why will dust be attracted to a CD or computer screen which has been wiped with a dry cloth? Conductor vs. Insulator ● Conductors allow free movement of electrons ● Insulators do not allow free movement of electrons ● Conductors can be charged by induction ● Attraction with polarization typically happens with insulators. Coulomb's Law ● Determines the force between charges ● Force depends on both charges and distance ● Follows inverse square law Question If two charged objects have a force F between them. How does the force change if the charge is doubled on both? What if the distance between the two is then doubled? Q 2Q Q d 2d 2Q Question Two charged objects have a force F between them, what if the distance between them reduced to 1/4th the original? Electric vs Gravitational Force