May 13, 2016
advertisement

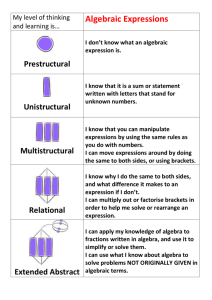
May 13, 2016 3rd grade: Students are working on Hands-On-Equations. Hands-On-Equations is a visual and kinesthetic approach to algebra. In Level 1 students solve algebraic equations through the use of physical “legal moves.” This level consists of 7 lessons, by the time they are done with the lessons they will be able to physically set up and solve equations such as: 2X + X + X + 2 = 2X + 10 and 2(X +4) + X = X + 16 4th grade: Students have just completed Level 2 of Hands-On-Equations. This week we will begin our last unit of study for this year Unit 10 Using Data; Algebra Concepts and Skills. This unit will be an introduction to pre-algebra concepts and skills. Students will concentrate on solving problems using a pan-balance mode, which means making sure that a change to one side must be compensated with a change to the other side. Students will also represent relationships as algebraic expressions that will help them generate input-output tables. Linking the data in the tables to corresponding points on a coordinated grid will help students better understand and interpret the data. Unit 10 has 4 main areas of focus: To solve equations using a pan-balance model, To represent relationships as algebraic expressions, To generate input-output tables, and To link data in tables to corresponding points on coordinate grids. To help reinforce the concepts and skills covered in this unit you may want to draw several circles and ask you child to find the radius, diameter, and circumference of each. Cut them out and make a design. You can also practice evaluating simple algebraic expressions by asking your child, “if y is equal to 4 what is …. y + y, 3 + y, y X 2? “ and so on. 5th grade: Students are staring to work on Unit 9 More about Variables, Formulas, and Graphs. Unit 9 significantly extends students’ experience with algebra and, at the same time, deals with important geometry and measurement ideas using the language and notation of algebra. Concepts in this unit include evaluating and applying formulas for circumference, perimeter, area, volume, and the Pythagorean Theorem. Unit 9 has 4 main areas of focus: To explore the distributive property, To apply the order of operations and distributive strategies to simplify algebraic expressions, evaluate formulas, and solve equations, To apply the Pythagorean theorem, and To find missing lengths in similar figures using a size-change factor. To help reinforce the concepts and skills covered in this unit you may want to use a ruler to draw a rectangle, a triangle, and a parallelogram. With your child, recall the formula for finding the area of each shape: rectangle (A = l X w), triangle (A = ½ X b X h), and parallelogram ( A= b X h). Find the area of each shape in square inches. Use graph paper to draw polygons with given areas. For example, see if your child can draw a trapezoid with an area of 10.5 square inches, or a rectangle with an area of 30 square inches and a perimeter of 15 square inches. The last Scholastic Math magazine is due on FRIDAY MAY 27.