Newton’s Second Law Pre-Lab Acceleration vs. Mass with constant Force
advertisement

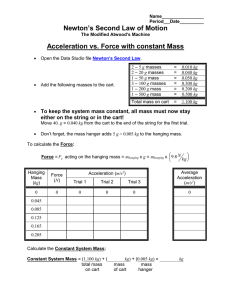
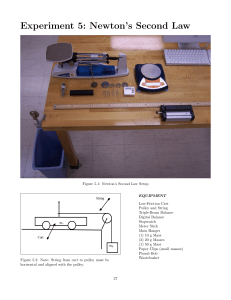
Newton’s Second Law Pre-Lab Acceleration vs. Mass with constant Force Open the Data Studio file Newton’s Second Law. Keep the force constant by placing 95 g = 0.095 kg onto the mass hanger which with the 5 g = 0.005 kg mass hanger is a total hanging mass of 100. g = 0.100 kg and leave it there for this half of the lab. Start your first trial without any masses in the cart. Then change the System Mass in 200. g = 0.200 kg increments by placing masses on the cart. Newton’s Second Law Pre-Lab Acceleration vs. Mass with constant Force To calculate the System Mass: System Mass = ( kg) + ( kg) + (0.100 kg) Mass of cart Added Mass Total Hanging on Cart Mass Your graph of Acceleration vs. Mass will not be linear. You must linearize it by modifying the mass by either squaring, square rooting, or inverting (1/mass). If you are thinking, try to determine which relationship is represented before you make your attempt to linearize … or you can guess and check !