Rate of Reactions Page 361 # 1, 2
advertisement

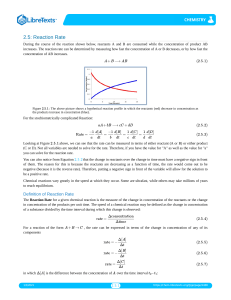
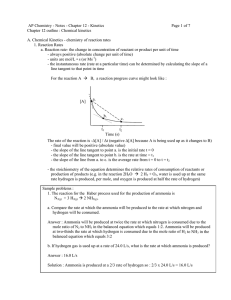
Rate of Reactions Description, Instantaneous, Measuring Page 361 # 1, 2 364 # 3 - 6 365 # 7 - 11 CHEMICAL KINETICS Chemical kinetics is concerned with the dynamics of chemical rea ctions such as the way reactions take place and the rate (speed) of the process. Chemical kinetics plays an important part in industrial chemistr y because the time taken for a reaction to take place and the energy required are o f great economic importance. The kinetic aspect of chemistry is often at odds wit h the thermodynamic side when considering the best conditions for industrial production. The basis of the study is COLLISION THEORY... COLLISION THEORY Collision theory states that... • particles must COLLIDE before a reaction can take place • not all collisions lead to a reaction • reactants must possess at least a minimum amount of energy - ACTIVATION ENERGY plus • particles must approach each other in a certain relative way - the STERIC EFFECT RATE CHANGE DURING A REACTION Reactions are fastest at the start and get slower as the react ants concentration drops. In a reaction such as A + 2B ——> C the concentrations might change as shown Reactants (A and B) Concentration decreases with time Product (C) C Concentration increases with time • the steeper the curve the faster the rate of the reaction • reactions start off quickly because of the greater likelihood of collisions • reactions slow down with time as there are fewer reactants to collide [B] decreases twice as fast as [A] (stoichiometric ratio) [C] increase at the same rate as [A] decreases A B TIME MEASURING THE RATE Experimental Investigation • the variation in concentration of a reactant or product is fol lowed with time • the method depends on the reaction type and the properties of reactants/products e.g. Extracting a sample from the reaction mixture and analysing it by titration. - this is often used if an acid is one of the reactants or products A reactant or product has to be an acid or base to use this method Using a colorimeter or UV / visible spectrophotometer. A reactant or product has to be coloured to use this method Measuring the volume of gas evolved. A product has to be a gas to use this method Measuring the change in conductivity. . A reactant or product has to have ions Chemical Kinetics Thermodynamics – does a reaction take place? Kinetics – how fast does a reaction proceed? Reaction rate is the change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). A B D[A] rate = Dt D[A] = change in concentration of A over time period Dt D[B] rate = Dt D[B] = change in concentration of B over time period Dt Because [A] decreases with time, D[A] is negative. A B time D[A] rate = Dt D[B] rate = Dt Br2 (aq) + HCOOH (aq) 2Br- (aq) + 2H+ (aq) + CO2 (g) slope of tangent slope of tangent slope of tangent [Br2]final – [Br2]initial D[Br2] average rate = =Dt tfinal - tinitial instantaneous rate = rate for specific instance in time