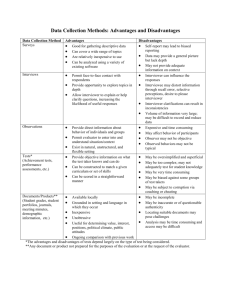
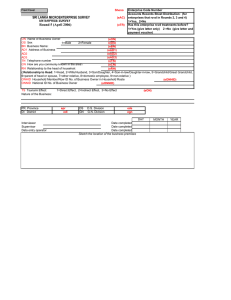
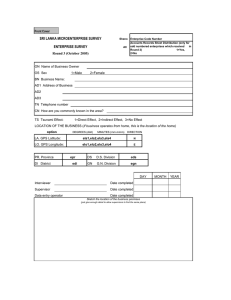
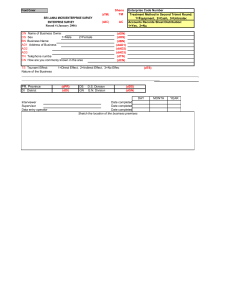
Market Information & Planning
advertisement

Market Information & Planning Andrew Ouellette Tomas Miller Jon Janney Focus Groups a group of people are asked about their perceptions, opinions, beliefs, and attitudes towards a product, service, concept, advertisement, idea, or packaging. Pros It is comparatively easy to conduct It is economically efficient It generates opportunity to collect data from the group interaction It gives speed in the supply of the results It allows a relatively large sample size for a qualitative study Cons The research is not carried out in a natural setting; and the researcher has less control over the data generated The data may be difficult to analyze The interviewer must have good interview skills Assembling a group may require additional resources Qualitative vs. Quantitative Qualitative- gathers in depth information about potential customers. Quantitative- gathers mathematical information such as how many times a customer visits a store. Techniques Brainstorming- Respondents think of words that are associated with the product of brand. Sentence Completion- an incomplete sentence that a group has to finish. Word Sorting- presents groups with a number of words or sentences and asks to sort them into groups according to the attributes of a product, brand, or need that they have. Techniques Developing a campaign- challenges a group to work together to come up with a marketing campaign. Creating Fantasy- gives the group the power to change anything in regard to the discussion topic. Creating Analogies Questions- ask questions comparing items to one another. Techniques Futuristic Imagination- having responders think about items that are not already being sold. Personification- respondents convert a product or brand into a person with a full range of personality, psychographic, demographic, and behavioral dimensions Role Play- having the interviewer play as the role of a customer and have responders sell a new product to the interviewer.