Organizing Middle East Unit Notebook
advertisement

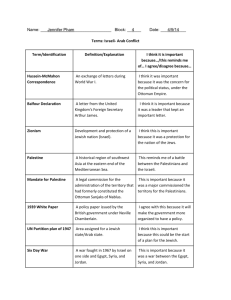
Filling in Gaps in Arab-Israeli Graphic Organizer Not Covered By My Introduction Powerpoint, The Supplemental Reading, Or The Pair Posters Where Information Came From For Graphic Organizer • Who Are Palestinians: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • Israeli Claims: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • Palestinian Claims: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • Pogroms: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint • Zionism: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • Role of World War One: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • Violence in 1920s: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint Where Information Came From For Graphic Organizer • Mandate System: Talking to the Text • 1928-1929 Arab Riots: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • 1936-1939 Arab Revolt: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • 1937 Peel Commission: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint • 1939 White Paper: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint • Nazis and Holocaust: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint Where Information Came From For Graphic Organizer • Exodus and Detention Camps: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint • United Nations Plan: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • Arab League 1947: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint • May 14, 1948 Independence: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint • 1948-1949 War of Independence: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • Nakba: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • Right of Return and Refugees: Introduction to A-I Conflict Powerpoint and Talking to the Text • 1956 Suez Crisis: Posters Where Information Came From For Graphic Organizer • 1967 Six Day War: Posters and Talking to the Text • Terrorism and PLO: Posters • 1973 Yom Kippur War: Posters • OPEC Oil Crisis: Posters • Camp David Peace Accords: Posters • 1st Intifada: Posters and Talking to the Text • 1993 Oslo: Posters and Talking to the Text • 2nd Intifada: Posters and Talking to the Text • West Bank Barrier: Posters and Talking to the Text • Operation Cast Lead: Posters Any Other Categories Covered In The Following Slides Es Samu • 1966 some Israeli soldiers were killed by a road-side bomb. • Israel blamed the newly formed PLO for this terrorist outrage and mobilised a large force of men and tanks. • The target was a Palestinian refugee camp at Es Samu thought to harbour terrorists.This camp was on Jordanian land. • The IDF attacked the camp, and also Jordanian soldiers who were nearby, before withdrawing. Israeli tank of 1967 Samu raid. The Second Intifada from 2000 to 2008--Retaliation and Demolition • What is less well known about the Intifada is that Palestinian casualties were much higher than Israeli ones. • From the 29 September 2000 until 30 April 2008 – 1053 Israelis and 4,789 Palestinians were killed. Whilst between 2000 until 2010 127 Israeli children and 1,435 Palestinian children were killed. • In addition tens of thousands of Palestinians were imprisoned and thousands of homes demolished. Demolition of houses • On 17 February 2005, the Minister of Defense announced a cessation of punitive house demolitions. • From October 2001 (when house demolitions as punishment began again after a break of almost four years) to January 2005, Israel demolished 675 homes in the Occupied Territories as punishment. Betselem 3000 houses destroyed by Israeli Army during current intifada – (Haaretz, 11 Aug, 2003) Disengagement in 2005 • In 2005 Israel withdrew its 8,000 illegal settlers from Gaza. • To the world this was presented as a peace move and a painful sacrifice. • However, Israeli government adviser Dov Weisglass justified it differently as ensuring the 2002 Roadmap would not be implemented: • “The disengagement is actually formaldehyde. It supplies the amount of formaldehyde that's necessary so that there will not be a political process with the Palestinians." The Gaza Strip • In 2005, Israel removed its settlements from the Gaza Strip and gave much control of the area to the Palestinian government (with exceptions such as the border, airspace, coastline) • Gaza later comes under the control of Hamas, a group considered by Israel and other countries to be a terrorist organization. • As of June 2008, Hamas and Israel have entered into a cease fire agreement. Gaza Controversy • • • • • Even before the disengagement Gaza was under a partial siege, since the capture of Israeli soldier, Gilad Shalit and Hamas’ winning of elections this siege became near total with only 40 products consisting of basic foodstuffs and detergents allowed in. The UN, the ICRC and all human rights and aid agencies have declared the siege an illegal collective punishment it continues regardless. UN Special Rapporteur for Human Rights, John Dugard said, “Gaza is a prison and Israel appears to have thrown away the key.” Save The Children UK, before the attack on Gaza of December 2008 stated, “50,000 children were malnourished, and 70% had vitamin A deficiency and almost half of children under age two were anaemic due to the border blockade.” B’Tselem reports that 12% of child deaths in Gaza are due to diarrhea. Gaza Violence • • • • It is well known that since 2000 Palestinian militants have fired approximately 10,000 mortars and rockets at Israel. Up to 17 January 2009 Palestinian rocket fire had killed 20 Israeli civilians, two soldiers, a foreign worker and five Palestinians. Less well known is that Israel has fired tens of thousands of shells into Gaza. For example, well before the latest war between 27 June 2006 and August 2006 Israel fired over 3,500 shells and launched 190 air strikes. According to B’Tselem, between 2000 and the start of Israel’s December 2008 attack on Gaza, Israeli forces had killed 3000 people in the Gaza Strip, including 635 children. Ongoing Occupation Issues • • • • • • • • • • • • The Right to Self-Determination; The Illegal Settlements; The Siege of Gaza; The Right to Water; The Right of Return; The Cleansing of East Jerusalem; The Prisoners; The Right to Freedom of Movement; The Right to Health; The Wall; House Demolition; The Confiscation of Land. Current Issue: Security and Terrorism Israeli Perspective • Terrorist organizations like Hamas (which controls the Gaza Strip) and Hezbollah (based in Lebanon and who was at war with Israel in the summer of 2006) continue to fire rockets into Israel. Individuals also continue to commit other acts of terror. Palestinian Perspective • Can’t stereotype all Palestinians as terrorists as the majority are not terrorists. • Palestinian government denounced terrorism. Current Issue: Jerusalem Israeli Perspective Palestinian Perspective • • Sees East Jerusalem as its capitol Sees united Jerusalem as its capitol Current Issue: Settlements Israeli Perspective Palestinian Perspective • For religious, political, and security reasons a large number Israeli settlements exist in the West Bank and East Jerusalem. • Israeli settlements go against the idea of a future Palestinian state. – 270,000 Israeli settlers in the West Bank Current Issue: Movement Israeli Perspective Palestinian Perspective • Palestinians need permission to leave West Bank. • Israelis see this as needed security to prevent terrorism. • The restriction on movement limits jobs, health care, education, etc. contributing to standard of living in West Bank being significantly less than that of Israel. Current Issue: Right of Return Israeli Perspective Palestinian Perspective • If Palestinians living in Arab nations or in the Occupied Territories return to Israel to reclaim land, it can mean the end of Israel as a Jewish state. • As refugees, Palestinians believe they should be able to return to their or their families land in Israel. Organizing Middle East Unit Notebook From Front of Binder to Back Open Up Binder • 1. Blue Course Overview • (Your Geography and Developing Countries Materials SHOULD BE IN A SEPARATE BINDER!) • 2. Pink Middle East Unit Study Guide • 3. Middle East Geography Lesson Plan • Writing Prompts Should Be Fully Answered • 4. Middle East Geography Graphic Organizer • Should be fully completed with notes from Powerpoint and Supplemental Reading including VISUALS • 5. Printed Up Supplemental Reading on Middle East Geography • 6. Labeled Political and Physical Maps of Middle East • • • • 7. Middle East Religions Lesson Plan Writing Prompt Should Be Fully Answered 8. Middle East Religions Graphic Organizer Should be fully completed from Ms. Barben’s Introduction Powerpoint, the Group Religious Caricatures, the Supplemental Reading, and the Specific Powerpoints on Judaism, Christianity, and Islam • 9. Returned Graded Introduction To The Abrahamic Faiths Talking To The Text • 10. Middle East Geography and Religions Returned Unit Test • 11. Arab-Israeli Conflict Lesson Plan • Writing Prompt Should Be Fully Answered • 12. Arab-Israeli Conflict Main Events Graphic Organizer • Should be completed from Ms. Barben’s Introduction Powerpoint, the Supplemental Reading, the Pairs Posters, and your Textbook Pages • 13. Returned Graded Arab-Israeli Conflict Talking To The Text---Still Being Graded • TONIGHT: GET CAUGHT UP WITH NOTEBOOK! • 14. Blue Propaganda Strategies Handout • 15. Pink Propaganda Poster Grade Sheet