Chapter 12 - Mrs. Walden's Science Site

Chapter 15
Kinetics
Kinetics
Deals with the rate of chemical reactions
Reaction mechanism – steps that a reaction takes
Haber Process: uses iron oxide as a catalyst
N
2
+ 3H
2
2NH
3
Spontaneous – will occur on its own – not necessarily fast
Reaction Rate
Change in the concentration of a reactant or product over time
Rate = Δ[A]/Δt
A- Molarity (final – initial)
Units – moles/L/s or M/s
Reactants can have neg. rates – change to a +
Average rates – M changes over a given time period
Instantaneous rate – found at any given second.
Rate is affected by 2 factors:
1. Coefficients in the balanced equation.
2. Time
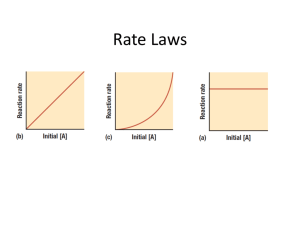
Rate Laws
Concerned only with the concentration of the reactants
Rate = k[A] n
k = rate constant; n = order – must be determined by experimental data
Rate is directly related to concentration
2 types of rate laws:
1. differential - (rate law) – shows how reaction depends on concentration.
2. Integrated – shows how concentration depends on time
Determining the order of the differential rate law:
Order is not the same as the coefficient in the balanced equation
Following method only works for differential rates (concentration and rate are given)
First you must find the order
To determine the order:
If there are 2 or more reactants:
Find where one of the reactants concentrations remains the same will the other reactant’s concentration changes.
Compare rates by the division method demonstrated.
It is easier if the larger concentration goes on top.
But whichever experiment goes on top for the concentration, the rate for the same experiment must be on top in the other side.
Order:
1 st order – concentration doubles – rate doubles
2 nd order – concentration doubles – rate quadruples
3 rd order – concentration doubles – rate increases by a factor of 8
0 order – concentration doubles
– rate stays the same
Do the same thing for each reactant in the table. Then put them together in one rate law.
Overall reaction order – sum of all the orders
General pattern for units:
L (n-1) /mol (n-1) *s
N is the overall reaction order
To calculate the rate constant – plug #’s of any row back in the equation and solve for k
Integrated rate laws:
Use this method when concentration and time are given
Must graph integrated rate laws to determine the order.
Slope is related to the rate constant.
To determine the concentration at a certain time, plug back into the appropriate equation for the rate law to solve. The initial concentration is the M at time = 0.
To determine the rate, plug back into the rate law to solve.
Pseudo- first order rate law – if more than 1 reactant
Can determine the rate law by graphing one reactant at a time.
Then put them together in one rate law.
Factors affecting reaction rates:
1. Concentration – (from rate laws)
2. Temperature – speed up when temp. is increased
3. Catalyst – speeds up a reaction without being used up itself
How does temperature affect the reaction rate?
Collision model – molecules must collide to react
Higher the temp – higher the KE
– more collisions
Two requirements for reactants to collide:
1. The molecules must be oriented correctly to allow bond formation
2. The collisions must have enough energy to produce a reaction
Activation Energy - E
a
Energy required to break a chemical bond and produce a new one in a chemical reaction
To be broken the KE must be high enough to overcome its bond and convert it to PE in the new product
If the E a is low happens fast
– reaction
If the E a is high happens slow
– reaction
Arrhenius Equation
Ln(k) = -E a
/R(1/T) +ln(A)
Ln(k) – y axis; (1/T) – x axis
When graphed a straight line should form.
R= 8.31J/mol*K
Units for E a
= J/mol
Slope = -E a
/R
Ln(k
2
/k
1
) = E a
/R(1/T
1
– 1/T
2
)
**Use this form if temperature changes**
Catalyst – lower the E a
Does not affect the overall energy difference of the reaction
2 types of catalyst:
A. Homogeneous – same phase as the reacting molecule
B. Heterogenous – different phase
(usually 2 gases being absorbed on the surface of a solid)
Reaction Mechanisms:
Series of steps for a chemical reaction
Must meet 2 requirements:
1. Sum of the elementary steps must give overall balanced equation for the reaction
2. The mechanism must agree with the experimentally determined rate law
Elementary steps – reaction whose rate law can be written by looking at the # of species colliding
3 types of molecularity (same as the order)
A. Unimolecular – 1 molecule – 1 st order
B. Bimolecular – 2 species – 2 nd order
C. Termolecular – 3 species – 3 rd order – rare since all have to hit at the same time
Intermediate – a species that is neither in the overall reactant or product but is used up during the reaction
To determine the rate law look at the rate determining step.
Rate determining step – in multistep reaction it is the slowest step