Pulp and Paper Making in South Africa
advertisement

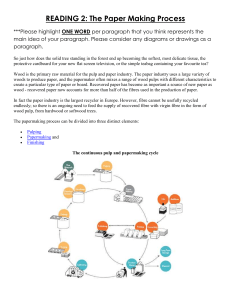
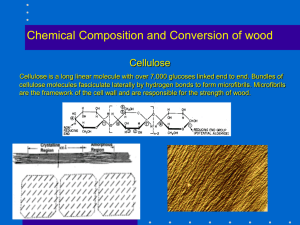
Pulp and Paper Making in South Africa Raw Materials Derived from Renewable Resources Pulping Processes • • • • Chemical Pulping Mechanical Pulping Chemo-Mechanical or Semi Chemical Waste Repulping Mechanical Pulping Mechanical action breaks the ML which is more brittle than the fibre wall. • The fibre wall is left intact, but substantial fibre cutting occurs • Chemical composition is not altered very much. Mechanical Pulping Wood physically taken apart – recovery high • Dense species not usually used due to short thick walled fibres and high % of vessels •Resinous species can also present problems •Yield - high but pulp unsuitable for many uses due to lignin content which stiffens fibres • Lignin also results in yellowing of pulp with time Mechanical Pulping -SWG Mechanical Pulping – SWG Pulp produced by pressing logs against rotating grindstone Fibres are compressed, and loosened Friction creates heat to soften the lignin Mechanical Pulping -Refiner Mechanical Pulp (RMP) Wood chips are broken down into fibres by bars on two rotating or one rotating and one stationary discs Chemi-thermomechanical Pulps (CTMP) To decrease energy cost or to improve pulp quality, chemical treatments (alkaline sulphite, sodium sulphite) are often added to mechanical pulping Pretreatment of chips (to lower energy) Inter-stage treatment (lower energy, increase fibre flexiblity) Post-treatment (fibre flexiblity) Chemical Pulping Chemicals degrade & dissolve the lignin. Hemicellulose also removed. Mainly secondary wall material remains Chemical Pulping • Soda • Soda Anthra Quinone • Kraft = Caustic Soda + Sodium Sulphide (High strength; efficient recovery of chemicals; handles a variety of species; tolerates bark) • Neutral Sulphite Semi Chemical = Sodium Carbonate + Sodium Sulphite • Sulphite – H2SO3 + bisulfite; bright pulp & easy to bleach; higher yield; easier to refine Kraft Recovery Cycle • Black Liquor is Concentrated in Multiple Effect Evaporators to about 65 – 70% Solids • This Heavy Black Liquor is fired in a Soda Recovery Furnace • The Smelt is dissolved in water to form Green Liquor – Sodium Carbonate and Sodium Suphide • Green Liquor is causticised with un-slaked lime, filtered and polished to form white liquor • The Calcium Carbonate sludge is burnt in Kilns Soda Recovery • Soda or Soda/AQ Liquor is concentrated to 55-60% Solids in Multiple Effect Evaporators • Strong Liquor is sprayed to form droplets in a Fluidized Bed Reactor • Further evaporation takes place as droplets fall • Organics burn in the fluidized bed • Inorganics recovered in the form of Sodium Carbonate Washing Aim is to: • minimize black liquor carryover • recover dissolved solids Solution contains • Lignin (30-45 %) • Hemicellulose (28-36 %) • Extractives (2-5 %) • Na2O (25-40 %) Beating and Refining Purpose To flatten fibres to ensure maximum surface area for hydrogen bonding in paper Beating also unravels fibres Beating is done in refiners Fluted plug rotates inside similar shaped housing with ribs Beating and Refining Freeness Freeness is term used to describe pulp potential Measured by rate of water passing through set amount of fibre formed on wire mesh Well beaten fibre does not allow water to pass, so Freeness is low Burst and tensile strength increased by beating time – increases inter-fibre bonding Chemical vs. Mechanical Pulping Chemical vs. Mechanical Pulping Bleaching Processes Conventional • Chlorination – Elemental Chlorine (aromatic substitution of H and addition reactions over the C=C) • Alkali Extraction – Sodium Hydroxide • Chlorine Dioxide or Sodium Hypochlorite • Alkali Extraction Bleaching Processes Modern Trends • Sulpher Dioxide • Oxygen (radical mechanism) or Ozone (addition over the C=C) • Chlorine Dioxide • Alkali Extraction • Chlorine Dioxide • Hydrogen Peroxide • Exotics Paper Making Chemicals • • • • • • • Cellulose Fibers – the bulk Fillers – Clay, Calcium Carbonate – 0 to 25% Strength Additives – Starch, CMC – 0 to 10% Sizing Agents – Rosin + Alum, AKD, ASA Wet Strength Additives – 0 to 2% Dyes Retention Agents Major Grades of Paper South African Pulp and paper Industry • Number of Paper & Board Mills – 17 • Number of Pulp Mills – 9 • Paper & Board Capacity = 2.421 Mt – Local Consumption = 75% • Pulp Capacity = 2.472 Mt – Local consumption = 60% • The Industry is a very important foreign exchange earner Per Capita Paper Consumption kg 350 300 250 1993 1999 2002 2004 200 150 100 50 0 USA Europe RSA WORLD AFRICA Pulp and Paper Making in South Africa